Past Continuous/Progressive Tense | English Language & Comprehension for SSC CGL PDF Download
Introduction
The Past Continuous tense holds significance in English as it allows us to express ongoing actions or activities that were happening at a specific point in the past.
How to make the Past Continuous tense?
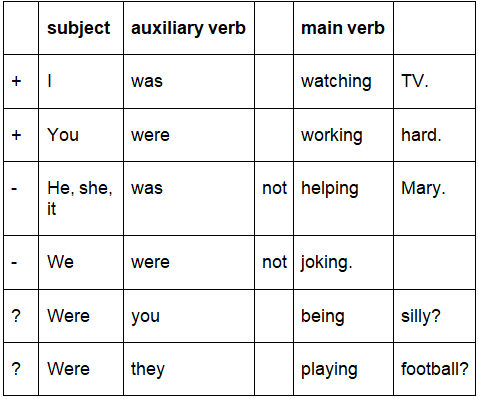
The structure of the past continuous tense is:

The auxiliary verb (be) is conjugated in the Past Simple: was, were
The main verb is invariable in present participle form: -ing
For negative sentences we insert not between the auxiliary verb and the main verb.
For question sentences, we exchange the subject and the auxiliary verb.
Look at these example sentences with the Past Continuous tense:
How to use the Past Continuous tense?
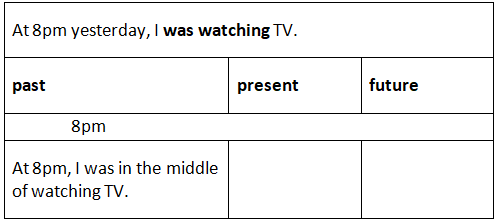
The Past Continuous tense conveys an action occurring at a specific moment in the past. The action commenced before that moment but was still ongoing at that point. For instance, yesterday, I was watching a film on TV. The film began at 7 pm and concluded at 9 pm.
When we use the Past Continuous tense, our listener usually knows or understands what time we are talking about. Look at these examples:
- I was working at 10pm last night.
- They were not playing football at 9am this morning.
- What were you doing at 10pm last night?
- What were you doing when he arrived?
- She was cooking when I telephoned her.
- We were having dinner when it started to rain.
- Ram went home early because it was snowing.
The Past Continuous tense is frequently employed to establish the context in narratives, providing a description of the background situation at the moment when the action commences. Many times, the story initiates with the Past Continuous tense and subsequently transitions into the Past Simple tense. Here is an example:
"James Bond was driving through town. It was raining. The wind was blowing hard. Nobody was walking in the streets. Suddenly, Bond saw the killer in a telephone box..."
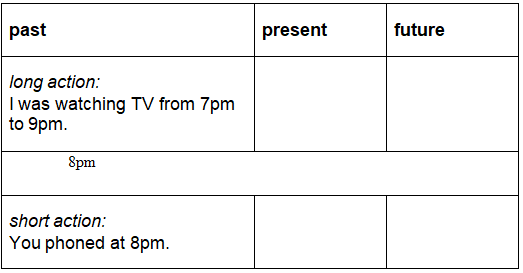
In the following example, we have two actions:
- long action (watching TV), expressed with Past Continuous
- short action (telephoned), expressed with Past Simple
We can join these two actions with when:
- I was watching TV when you telephoned.
Notice that "when you telephoned" is also a way of defining the time (8pm).
We use:
- when + short action (Past Simple)
- while + long action (Past Continuous)
There are four basic combinations:
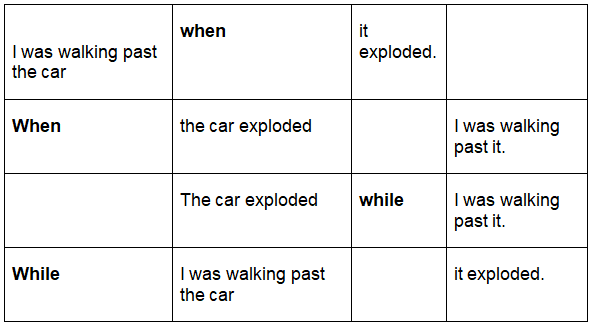
Notice that the long action and short action are relative.
- "Watching TV" took two hours. "Telephoned" took a few seconds.
- "Walking past the car" took a few seconds. "Exploded" took milliseconds.
|
136 videos|246 docs|146 tests
|
FAQs on Past Continuous/Progressive Tense - English Language & Comprehension for SSC CGL
| 1. What is the structure of the Past Continuous tense? |  |
| 2. When should I use the Past Continuous tense? |  |
| 3. Can the Past Continuous tense be used with specific time expressions? |  |
| 4. How do I form negative sentences in the Past Continuous tense? |  |
| 5. How do I form questions in the Past Continuous tense? |  |
















