UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 6th December 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Painganga River |

|
| Section 34 of the Indian Penal Code (IPC) |

|
| National Archives of India (NAI) |

|
| Chandrayaan-3 |

|
| Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary |

|
| Guillain-Barre syndrome |

|
| Parkinson's disease |

|
GS-I
Painganga River
Subject: Geography

Why in News?
Protests were staged against a proposed dam project on the Painganga river in the Vidarbha region of Maharashtra recently.
About the Painganga River:
- The Painganga River (also known as the Penganga River) is the chief river of the Yavatmal district in Maharashtra and flows along the south-east boundaries of the district in a winding, meandering course.
- Origin: It originates in the Ajantha ranges in Aurangabad district in Maharashtra.
- It is a major tributary of the Wardha River, the other major river in the district. The Wardha River flows into the Wain Ganga Riverto form the Pranhita River, which finally joins the Godavari River.
- It is acutely deep-rooted and difficult to navigate.
- The total length of the river is 676 km.
- Major Tributaries: Include the Adan, Kas, Arunavati,Kayadhu, and Pus Rivers.
- The Penganga River gets flooded in the rainy and winter seasons and partially flooded in the summer.
- It provides irrigation to the Washim and Yavatmal districts in Maharashtra.
- There are two dams being constructed on the river, namely Upper Painganga and Lower Painganga. This dam is also known as Isapur Dam.
Source: The Print
GS-II
Section 34 of the Indian Penal Code (IPC)
Subject: Polity

Why in News?
The Supreme Court recently clarified that for Section 34 of the Indian Penal Code to be applicable, there must be a common intention among all co-accused individuals, indicating a shared purpose and design.
About the Section 34 of the IPC:
- Section 34 IPC states the acts done by several persons in furtherance of common intention.
- The section explains that “When a criminal act is done by several persons in furtherance of the common intention of all, each of such persons shall be liable for that act in the same manner as if it were done by him alone.
- This provision, which creates ‘joint culpability’ for an act, deviates from a basic concept of criminal law, which states that a person is only responsible for crimes committed by himself and not for the actions of others.
- Section 34 does not state a specific offence. It only lays down the rule of evidence that if two or more persons commit a crime in order of common intention, each of them will be held jointly liable.
- The punishment for this offence will be consistent with the crime they committed. For example, if the offence of murder has been committed in furtherance of a common purpose, each one of them will be held liable under Section 302 and Section 34 of the Indian Penal Code, 1860.
- Section 34 helps in ascertaining individual accountability in cases where it is difficult to prove individual liability for activities done in support of the common objective of all persons engaged in a criminal act conducted by a group.
- It is crucial to note that Article 34 does not require each accused to actively participate in every aspect of the criminal act. As long as there is a shared intention and active participation in the overall commission of the crime, each individual will be held equally responsible.
- For Article 34 to apply, the following essential ingredients must be present:
- A criminal act committed by multiple people.
- There must be a common intention of all to commit that criminal act. In reference to this principle, In the case of Hari Om v. State of Uttar Pradesh, it was held that “it is not necessary that there must be a prior conspiracy or pre-meditation; the common intention can be formed in the course of the occurrence as well.”
- Active participation of each accused: Each accused must have actively participated in the commission of the criminal act. A mere presence at the scene of the crime is not sufficient.
Source: Live Law
National Archives of India (NAI)
Subject: Polity and Governance

Why in News?
A book fair and an exclusive exhibition-cum-Sale of the National Archives of India (NAI’s) publications opened recently.
About the National Archives of India (NAI):
- NAI is the custodian of the records of enduring value of the Government of India.
- Established on March 11, 1891, at Calcutta (Kolkata) as the Imperial Record Department, it is the biggest archival repository in South Asia.
- It was transferred to New Delhi in 1911.
- It functions as an attached office of the Ministry of Culture, Government of India.
- It has a vast corpus of records, viz., public records, private papers, oriental records, cartographic records, and microfilms, which constitute an invaluable source of information for scholars, administrators and users of archives.
- The Director General of Archives, heading the Department, has been given the mandate for the implementation of the Public Records Act, 1993, and the rules made there under, the Public Records Rules, 1997, for the management, administration, and preservation of public records in the Ministries, Departments, Public Sector undertakings, etc. of the Central Government.
- Access to the records in the NAI is governed by the provisions of the Public Records Rules, 1997.
- The NAI keeps and conserves records of the government of India and its organisations. It does not receive classified documents.
- Abhilekh PATAL:
- The Abhilekh PATAL (Portal for Access to Archives and Learning) is an initiative of NAI to make its rich treasure of Indian archival records available to all online.
- It is a full-featured web portal to access the NIA’s reference media and its digitised collections through the internet.
- It contains more than 2.7 million files held by the National Archives of India. The Digitized Collections contains over 71792 digitised records for online access.
Source: PIB
GS-III
Chandrayaan-3
Subject: Science and Technology

Why in News?
Recently, ISRO brought back the Chandrayaan-3 propulsion module from the Moon to Earth’s orbit.
About Chandrayaan-3:-
- Chandrayaan-3 is the successor to the Chandrayaan-2 mission.
- Launch Vehicle: Mark-III (LVM3).
- Launched site: Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC), Sriharikota, Andhra Pradesh.
- Composition: It consists of an indigenous Lander module (LM), a Propulsion module (PM), and a Rover.
- Lander: a spacecraft that descends towards and comes to rest on, the surface of an astronomical body.
- Propulsion module: a box-like structure, mounted with a large solar panel on one side and a large cylinder on top.
- Rover: a small vehicle that can move over rough ground, often used on the surface of other planets, sometimes controlled from the earth.
- The Lander and the Rover have scientific payloads to carry out experiments on the lunar surface.
- There will not be any orbiters like Chandrayaan 2 in it.
Objectives of Chandrayaan-3 mission:-
- To demonstrate a Safe and Soft Landing on the Lunar Surface.
- To demonstrate Rover roving on the moon.
- To conduct in-situ scientific experiments.
Lander payloads:-
- Chandra’s Surface Thermophysical Experiment (ChaSTE): to measure the thermal conductivity and temperature
- Instrument for Lunar Seismic Activity (ILSA): for measuring the seismicity around the landing site
- Langmuir Probe (LP): to estimate the plasma density and its variations.
- A passive Laser Retroreflector Array from NASA is accommodated for lunar laser ranging studies.
Rover payloads:-
- Alpha Particle X-ray Spectrometer (APXS) and Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscope (LIBS): for deriving the elemental composition near the landing site.
Propulsion Module Payload:-
- Spectro-polarimetry of Habitable Planet Earth (SHAPE): Future discoveries of smaller planets in reflected light would allow us to probe into a variety of Exo-planets which would qualify for habitability or for the presence of life.
About GSLV-Mk III:-
- Weighs: 641 tones.
- Capacity: GSLV can take 10,000-kg satellites to lower earth orbits.
- It is also known as the Launch Vehicle Mark 3 (LVM3).
- It is a three-stage vehicle.
- It has two solid motor strap-ons, a liquid propellant core stage, and a cryogenic stage.
- It is the heaviest and the shortest among India’s operational launch vehicles
Source: India Today
Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary
Subject: Environment and Ecology

Why in News?
Recently, the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) has recommended to the authorities that the Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary abutting the Bandipur Tiger Reserve be declared as a core critical tiger habitat.
Background:-
- This followed a site visit by Assistant Inspector General of Forests, NTCA, Ms. Harini Venugopal. The visit followed a slew of issues raised by conservation activist Giridhar Kulkarni pertaining to Bandipur.
About Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary:-
- Location: Mysuru district, Karnataka.
- Geographic Area: Nugu Wildlife Sanctuary encompasses 30.32 sq km.
- The northern part of Nugu WLS is occupied by the Nugu Reservoir.
- Nugu is a vulnerable area as far as human–elephant conflicts are concerned.
- In 1974, Nugu was declared a Wildlife Sanctuary.
- It was added to the Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve in the year 2003-2004.
- The average amount of rainfall received in this area is
- Most of the vegetation in the forests is dry, deciduous, interspersed with patches of plantations.
- Flora: Anogeissus latifolia, Tectonia grandis, Terminalia tomentosa etc.
- Fauna: elephant, leopards, jungle cats, wild pig, spotted deer, sambar deer, barking deer, etc.
Source: The Hindu
Guillain-Barre syndrome
Subject: Science and Technology
Why in News?
Recent research found out that the risk of developing ‘extremely rare’ Guillain-Barre syndrome increases due to COVID-19.
About Guillain-Barre syndrome:-
- Guillain-Barre (gee-YAH-buh-RAY) syndrome is a rare disorder in which the body’s immune system attacks your nerves.
- Weakness and tingling in your hands and feet are usually the first symptoms.
- These sensations can quickly spread, eventually paralyzing your whole body.
- In its most severe form Guillain-Barre syndrome is a medical emergency.
- Most people with the condition must be hospitalized to receive treatment.
- The exact cause of Guillain-Barre syndrome is unknown.
- But two-thirds of patients report symptoms of an infection in the six weeks preceding.
- These include COVID-19, respiratory or gastrointestinal infection or Zika virus.
Symptoms:-
- A pins and needles sensation in your fingers, toes, ankles or wrists
- Weakness in your legs that spreads to your upper body
- Unsteady walking or inability to walk or climb stairs
- Difficulty with facial movements, including speaking, chewing or swallowing
- Double vision or inability to move the eyes
- Severe pain that may feel achy, shooting or cramp-like and may be worse at night
- Difficulty with bladder control or bowel function
- Rapid heart rate
- Low or high blood pressure
- Difficulty breathing
Types:-
- Guillain-Barre syndrome has several forms. The main types are:
- Acute inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy (AIDP): the most common form in North America and Europe. The most common sign of AIDP is muscle weakness that starts in the lower part of your body and spreads upward.
- Miller-Fisher syndrome (MFS): in which paralysis starts in the eyes. MFS is also associated with unsteady gait. MFS is less common in the U.S. but more common in Asia.
- Acute motor axonal neuropathy (AMAN) and acute motor-sensory axonal neuropathy (AMSAN):are less common in the U.S. But AMAN and AMSAN are more frequent in China, Japan and Mexico.
Treatment:-
- There is no known cure for this syndrome.
- The most commonly used treatment is intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG), which is made from donated blood that contains healthy antibodies.
Source: Indian Express
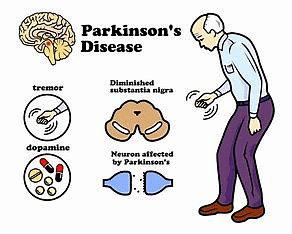
Parkinson's disease
Subject: Science and Technology
Why in News?
Recently, Researchers have developed a blood test to identify individuals at risk of developing Parkinson’s disease.
About Parkinson’s disease:-
- Parkinson’s disease is a progressive disorder that affects the nervous system and the parts of the body controlled by the nerves.
- Symptoms start slowly.
- The risk of developing it increases with age.
Symptoms:-
- uncontrollable shaking and tremors
- slowed movement (bradykinesia)
- balance difficulties and eventual problems standing up
- stiffness in limbs
- Speech changes
- Writing changes
- Loss of automatic movements
Causes:-
- Genes
- Environmental triggers
- The presence of Lewy bodies. Clumps of specific substances within brain cells are microscopic markers of Parkinson’s disease. These are called Lewy bodies.
Parkinson’s disease is often accompanied by these additional problems like:-
- Thinking difficulties
- Depression and emotional changes
- Swallowing problems.
- Chewing and eating problems.
- Sleep problems and sleep disorders
- People also may experience rapid eye movement sleep behaviour disorder, which involves acting out dreams. Medicines may improve your sleep.
- Bladder problems.
- Constipation.
Treatments:-
- Although there is no cure for Parkinson’s disease, medicines, surgical treatment, and other therapies can often relieve some symptoms.
- Medicines: Medicines can help treat the symptoms of Parkinson’s by:
- Increasing the level of dopamine in the brain
- Having an effect on other brain chemicals, such as neurotransmitters, which transfer information between brain cells
- Helping control non-movement symptoms
- Therapy: the main therapy for Parkinson’s is levodopa.
- Nerve cells use levodopa to make dopamine to replenish the brain’s dwindling supply.
- Deep brain stimulation: For people with Parkinson’s disease who do not respond well to medications, the doctor may recommend deep brain stimulation.
Source: The Hindu
|
38 videos|5264 docs|1112 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 6th December 2023 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the significance of the Painganga River? |  |
| 2. What is Section 34 of the Indian Penal Code (IPC)? |  |
| 3. What is the National Archives of India (NAI)? |  |
| 4. What is Chandrayaan-3? |  |
| 5. What is Guillain-Barre syndrome? |  |




















