Atomic & Nuclear Physics | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Prerequisites for Further Exploration |

|
| Use of Atomic and Nuclear Physics |

|
| Atomic Physics |

|
| Photoelectric Effect |

|
| De Broglie’s Hypothesis |

|
| Nuclear Physics |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Prerequisites for Further Exploration
- The world is made up of combinations of fundamental or subatomic particles, forming the basis of matter.
- A typical atom consists of an atomic nucleus and a subatomic cloud.
- The properties or nature of an atom's nucleus are determined by the number of protons and neutrons present.
- The Standard Model in physics provides a theoretical summary of fundamental particles and their interactions.
- Nuclear decay occurs when an unstable atom loses energy and emits ionizing radiation.
- A nuclear reaction is the process through which two nuclear particles interact to emit gamma rays.
- Separate studies are required for each particle to understand their unique interactions in nuclear reactions.
Use of Atomic and Nuclear Physics
- Essential Knowledge: Nuclear and atomic physics is vital for engineers in nuclear reactor operations.
- Societal Applications: In contemporary times, nuclear physics has permeated various societal applications.
- Technological Advancements: The field contributes to the development of new and advanced technologies.
- Innovation Catalyst: Nuclear physics plays a pivotal role in fostering innovation in various sectors.
Atomic Physics
Atomic physics is the study of the atom structure and deals with atoms as an isolated system of electrons and the atomic nucleus. This field of study deals with the structure of atoms, the arrangement of electrons around the nucleus and the procedure by how the arrangements undergo several changes. The study provides the base for quantum physics, a celebrated cornerstone in modern physics.
Following concepts form the base of atomic physics:
Thomson’s Experiment to find the charge/mass ratio
- Experimental Technique: In 1896, Thomson employed a combination of electric and magnetic fields to determine the charge-to-mass ratio of a particle.
- J.J. Thomson's Observation: Thomson noted the deflection of cathode rays by the electrical field during his experiment.
- Control and Balance: The experiment involved manipulating and balancing the effects of both magnetic and electrical fields on cathode rays.
- Results: The outcome of the experiment provided the charge-to-mass ratio of the particles under investigation.
Important formulas to remember:
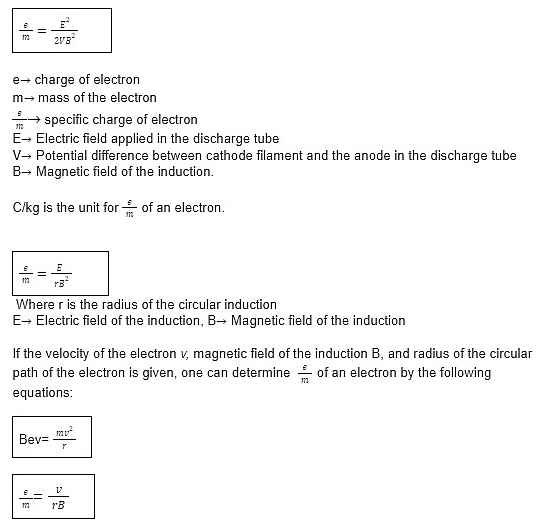
The formula used when after both electronic field E and the magnetic field B are applied mutually perpendicular to the electron beam and the electron beam does not deflect is
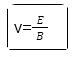
Millikan’s Oil Drop Experiment
In 1909, the scientist Milikan tried to measure the charge of electrons by balancing the gravitational and electric forces on the tiny suspended droplets of oil. After further experimentations, he concluded that in the presence of a light source, the velocity of the droplets can be observed from a microscope and timing the droplets as they travelled the predetermined distance of the experimentation. As the electric forces are controlled, knowing the electric field can help determine the charge being carried by the droplet.
The important formula for calculating the charge:

Photoelectric Effect
At the end of the 19th century, scientists discovered that after coming in contact with some light source, some metals emit electrons from the surface. This experiment was termed the photoelectric effect and the electrons emitted were known as photoelectrons. This theory was further improved by Einstein who stated that the ray of light should be perceived not only as a wave but as made up of tiny packets of energy. The frequency of the single-photon was proportional to the frequency of light.
The important formula for Einstein’s photoelectric equation:

De Broglie’s Hypothesis
In 1923, De Broglie hypothesised the wave-particle duality in which he stated that if light can display the behaviour of both wave and particles, then perhaps matter can also display such behaviour. While Broglie’s matter waves were rejected after further experimentation, evidence was found for the electron waves.
Important formulas:
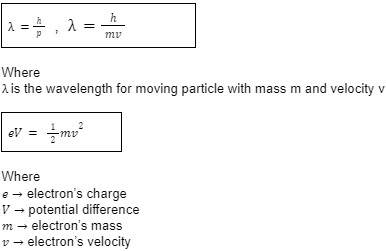
Nuclear Physics
Nuclear physics is involved with the study of the protons, neutrons and their nuclear interactions. The primary research tool of nuclear physics involves the use of beams and particles directed towards nuclear targets. If there is a detection of recoiling particles or nuclear fragments, their direction and energies are analysed and studied to extract information about their nuclear and strong force.
Conclusion
Atomic and nuclear physics are vast subjects that further take inspiration from particle physics and form the base of one of the most celebrated cornerstones of modern-day physics, namely, quantum physics. The article summarises important concepts and experiments to revisit before diving deep into the topic.
|
743 videos|1444 docs|633 tests
|
FAQs on Atomic & Nuclear Physics - Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests)
| 1. What is atomic physics? |  |
| 2. What is the photoelectric effect? |  |
| 3. What is De Broglie's hypothesis? |  |
| 4. What is nuclear physics? |  |
| 5. What are the applications of atomic and nuclear physics? |  |















