Antimicrobial Agents - Mechanism of Action | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Antimicrobial Agents - Adverse Effects |

|
| MRSA Management |

|
| Inhibitors of Protein Synthesis |

|
| Antibacterial Agents - Repeats |

|
Introduction
Inhibit cell wall synthesis:
- Penicillins
- Cephalosporins
- Cycloserine
- Vancomycin
- Bacitracin
Cause leakage from cell membranes:
- Polypeptides
- Polymyxins
- Colistin
- Bacitracin
- Polyenes (Amphotericin B, Nystatin, Hamycin)
Inhibit protein synthesis:
- Tetracyclines
- Chloramphenicol
- Erythromycin
- Clindamycin
- Linezolid
Cause misreading of mRNA code and affect permeability:
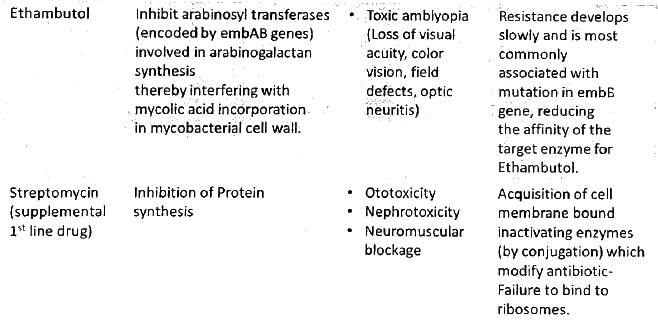
- Aminoglycosides
- Streptomycin
- Gentamicin
Inhibit DNA gyrase:
- Fluoroquinolones (Ciprofloxacin)
Interfere with DNA function:
- Rifampin
Interfere with DNA synthesis:
- Acyclovir
- Zidovudine
Interfere with intermediary metabolism:
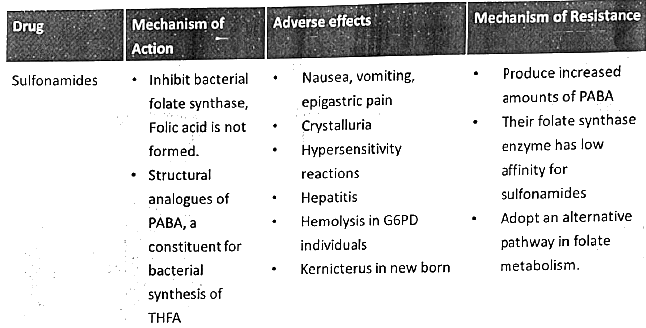
- Sulfonamides
- Sulfones
- PAS (Para-Aminosalicylic Acid)
- Trimethoprim
- Pyrimethamine
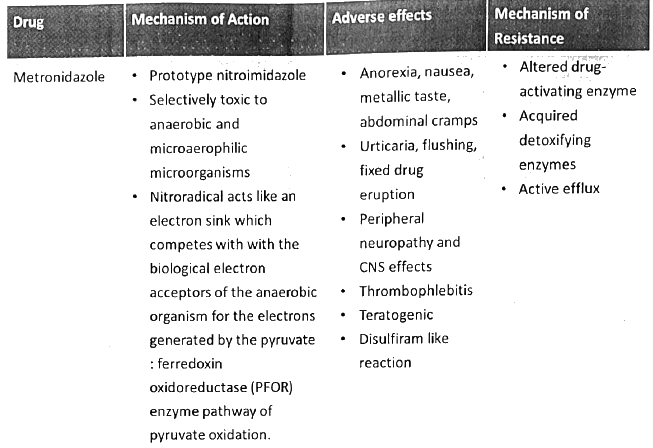
- Metronidazole
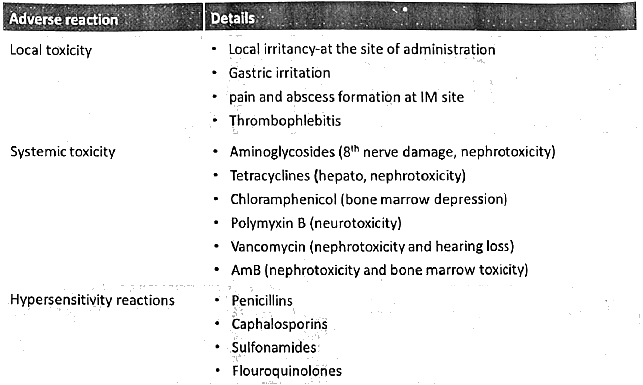
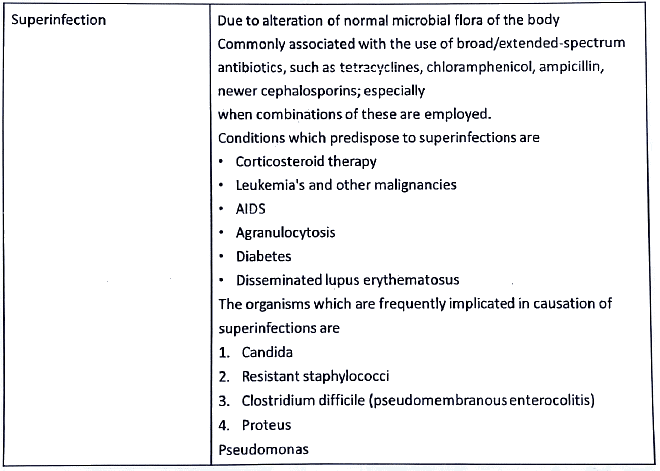
Antimicrobial Agents - Adverse Effects

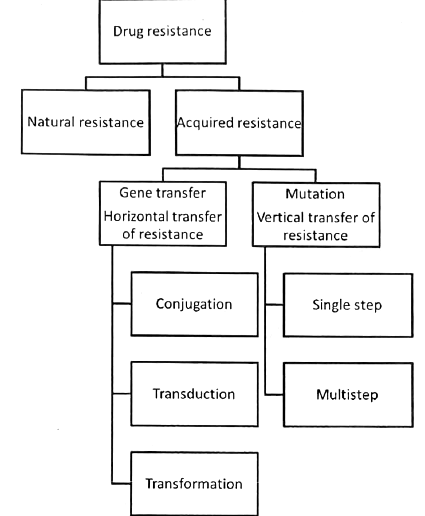
Antimicrobial Agents - Mechanisms of Resistance
Three fundamental mechanisms include:
- Modifying or bypassing targets that experience diminished drug binding,
- Changing the drug's access to its target through decreased uptake or heightened active efflux,
- Modifying the drug itself to diminish its activity.
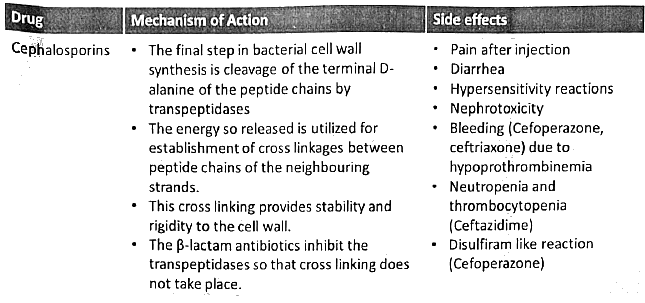
Beta Lactam Antibiotics

MRSA Management
Methicillin resistance signifies resistance to all semisynthetic penicillinase-resistant penicillins (SPRPs), including oxacillin or nafcillin, as well as resistance to all cephalosporins (except ceftaroline). The emergence of methicillin resistance is attributed to the production of a novel penicillin-binding protein (PBP2a) synthesized by the mecA gene. It is hypothesized that this genetic material was acquired through horizontal transfer from a related staphylococcal species, such as Staphylococcus sciuri.
Vancomycin and daptomycin are currently recommended as the drugs of choice for treating Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
Vancomycin:
- A glycopeptide antibiotic that inhibits bacterial cell wall synthesis.
- It binds to the terminal dipeptidic 'D-ala-D-ala' sequence of peptidoglycan units, preventing their release from the bactoprenol lipid carrier. This action inhibits the assembly of units at the cell membrane and their cross-linking to form the cell wall.
- Systemic use is restricted to serious MRSA infections, with recommended doses of 500 mg every 6 hours or 1 g every 12 hours infused intravenously over 1 hour.
- Vancomycin has the potential to release histamine, causing adverse reactions such as chills, fever, urticaria, and intense flushing known as 'Red man syndrome.'
Daptomycin:
- A lipopeptide antibiotic that disrupts multiple aspects of bacterial cell membrane.
- The recommended dosage is 4-6 mg/kg intravenously once daily.
- It binds avidly to pulmonary surfactant, rendering it ineffective in respiratory infections.
- Common adverse reactions include rash, hypersensitivity, alterations in blood pressure, swelling, insomnia, and eosinophilia.
Antimicrobial Agents

Antimicrobial Agents - Mechanism of Action

Antimycobacterial Agents

Inhibitors of Protein Synthesis

Antibacterial Agents - Repeats
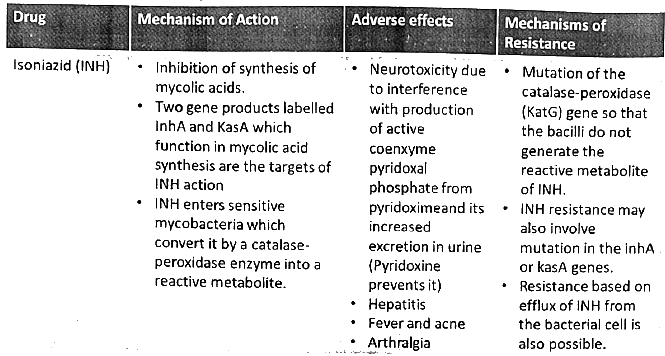
- Explore the primary anti-mycobacterial drugs, focusing on their mechanism of action, side effects, and the development of resistance. (2013)
- Outline the general mechanism of action of antimicrobial drugs and delve into the specific mechanism of action and adverse reactions of penicillins. (2014)
- Examine the pharmacotherapy for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infection. (2016)
- Elaborate on the mechanism of action of sulfonamides and elucidate the methods bacteria employ to develop resistance to them. (2017)
- Clarify the reasons behind using Imipenem, a beta-lactam antibiotic, in combination with cilastatin. (2018)
- Review the adverse effects associated with the utilization of antimicrobial agents. (2018)
|
7 videos|236 docs
|
FAQs on Antimicrobial Agents - Mechanism of Action - Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What are the adverse effects of antimicrobial agents? |  |
| 2. How can MRSA be managed? |  |
| 3. What are inhibitors of protein synthesis? |  |
| 4. How do antibacterial agents work? |  |
| 5. What is the mechanism of action of antimicrobial agents? |  |














