UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 20th December 2023 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Bahmani Kingdom
Subject: Medieval History
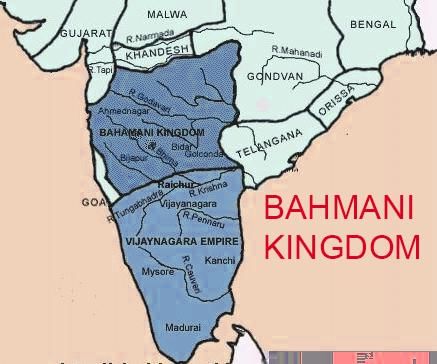
Why in News?
Recently, Karnataka HC asked authorities to remove the encroachments of Bahmani Sultans’ fort in Kalaburagi.
Background:-
- The High Court bench in Kalaburagi instructed civic authorities to clear 62 houses constructed inside the fort and 114 houses that have emerged in the surroundings of the fort.
About Bahmani Kingdom:-
- The Bahmani Sultanate was a significant medieval Muslim state in the Deccan region of South India.
- It is also known as the Bahmanid Empire.
- It was established in 1347.
- The Bahmani Sultanate was founded by Hasan Bahman Shah, a governor appointed by the Delhi Sultanate.
- He declared independence and established his capital at Gulbarga.
- It lasted until 1527 when it fragmented into five smaller states.
- The Sultanate was administratively divided into four provinces (Daulatabad, Bidar, Berar, and Gulbarga) with tarafdars or subedars governing each.
- The sultanate was governed through a decentralized feudal system.
- Trade and commerce flourished in the Bahmani Sultanate due to its strategic location. The region was a center for international trade, particularly in horses, textiles, and spices.
- Around 1518, Krishnadeva Raya of the Vijayanagar Empire defeated the last ruler of the Bahmani Empire.
Art and Architecture:-
- The Bahmanis followed the Indo-Islamic style of architecture with a few changes.
- The buildings were constructed using local materials.
- An influence of Persian architecture could be seen in the buildings of this period.
- Examples of architecture could be found at Gulbarga (Shah bazaar mosque, Hafta Gumbaz, Jama masjid), at Bijapur (Gol Gumbaz, Ibrahim Roza, Bara Kaman, etc.), and at Bidar (Rangeen mahal, Janata mahal).
- It was during this period when a new dialect, ‘Dakhini Urdu’ prevailed.
Source: AIR
Earthquake
Subject: Geography

Why in News?
Recently, an earthquake in northwestern China killed at least 131 people.
Background:-
- It has been the deadliest in 9 years.
About Earthquake:-
- An earthquake is the shaking or trembling of the earth’s surface.
- It is caused by the seismic waves or earthquake waves that are generated due to a sudden movement (sudden release of energy) in the earth’s crust (shallow-focus earthquakes) or upper mantle (some shallow-focus and all intermediate and deep-focus earthquakes).
- Earthquake are by far the most unpredictable and highly distructive of all the natural disasters
Causes of Earthquakes:-
- Fault Zones
- Plate tectonics
- Volcanic activity
- Human-Induced Earthquakes
Measurement of Earthquakes:-
- The energy from an earthquake travels through Earth in vibrations called seismic waves.
- Scientists can measure these seismic waves on instruments called
- A seismograph, or seismometer,is an instrument used to detect and record earthquakes.
- Richter magnitude scale is the scale to measure the magnitude of energy released by an earthquake.
- Hypocentre/Focus:The point where the energy is released.
- Epicentre:The point on the surface directly above the focus.
- Isoseismic line: A line connecting all points on the surface where the intensity is the same.
About China:-
- Capital: Beijing.
- Continent: Asia.
- China, lies in East Asia.
- It is the largest of all Asian countries.
- Its topography encompasses the highest and one of the lowest places on Earth.
- Its relief varies from nearly impenetrable mountainous terrain to vast coastal lowlands.
- Its climate ranges from extremely dry, desertlike conditions in the northwest to tropical monsoon in the southeast.
- The country is bounded by Mongolia to the north; Russia and North Korea to the northeast; the Yellow Sea and the East China Sea to the east; the South China Sea to the southeast; Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar (Burma), India, Bhutan, and Nepal to the south; Pakistan to the southwest; and Afghanistan, Tajikistan, Kyrgyzstan, and Kazakhstan to the west.
- China has more than 50,000 rivers with individual drainage areas exceeding 40 square miles (100 square km).
- Of the total annual runoff, about 95 percent drains directly into the sea (more than 80 percent into the Pacific Ocean, 12 percent into the Indian Ocean, and less than 1 percent into the Arctic Ocean and 5 percent disappears inland.
Source: Times of India
GS-II
A Blow for the Rights of the Legislature, in Law Making
Subject: Polity and Governance

Why in News?
On 10thNovember 2023, in an important judgement (State of Punjab vs Principal Secretary to the Governor of Punjab), the Chief Justice of India (CJI) pronounced an interpretation of Article 200 of the Constitution of India.
- The focus was on the first provision of Article 200, which deals with a Governor's options when presented with a Bill for assent after passage by the State Legislature.
Article 200 of the Constitution of India
- It provides for four alternative courses of action for a Governor when a Bill after being passed by the legislature is presented to him/her for his/her assent.
- The four alternative courses of action for a Governor are -
- Give his assent straightaway
- Withhold his assent
- Return the Bill to the legislature with the request to reconsider the Bill or any particular provision of the Bill.
- However, if the legislature again passes the Bill with/without accepting any of the amendments suggested by the Governor s/he is constitutionally bound to give assent to the Bill.
- Governor may also reserve it for the consideration of the President
- In this case the assent is given or withheld by the President (Article 201).
- However, there is no timeline prescribed for even the President, to decide on the outcome of the Bill.
Conventional Views on Discretionary and Absolute Nature of Governor’s Power
- Commentators, including D.D. Basu, have traditionally held that the Governor's authority to withhold assent carries finality, resulting in the demise of the Bill.
- These commentators generally asserted that the provision allowing the Governor to send the Bill back for reconsideration is discretionary, not mandatory.
- This implied an absolute power to withhold assent.
Interpretation Pronounced by the CJI of Article 200
- CJI Linked the Withholding Assent with ‘Mandatory’ Reconsideration
- The recent judgment by CJI brings a different perspective, linking withholding assent with mandatory reconsideration.
- CJI’s interpretation made it clear that there was a presumption that the Governor’s power to withhold assent from a Bill is absolute.
- Immediate Reconsideration is Required
- The CJI has essentially removed the possibility of refusing assent by connecting it to sending the Bill immediately back to the Assembly for another look.
- The judgment says that if the Governor decides to withhold assent, he has to send it back to the Assembly immediately for reconsideration, in which case he has no other option except to give assent.
The Significance of CJI’s Interpretation
- Safeguards the Legislature’s Rights: This judgement and CJI's approach safeguard the legislature's rights in law-making, protecting the constitutional system from potential misuse by unelected Governors.
- Interpretation Represents an Evolution in Views on Governor’s Power: The CJI's interpretation represents an evolution in understanding the Governor's powers, emphasising the need for ongoing assessment and refinement of constitutional interpretations.
- Provides Greater Clarity to Article 200
- The Supreme Court of India has said emphatically that Governors cannot delay the decision on the Bills.
- Thus, the decision of the top court has brought greater clarity to Article 200 and Governors will have to quickly take a decision on the Bills.
Remaining Challenges Pertaining to Governor’s Power
- Reserving Bills for President’s Consideration
- There is still an area which can be exploited by the Governors to frustrate the law-making exercise of State governments.
- Reserving a Bill for the consideration of the President is an absolute option still available to a Governor.
- The crucial question is on what kinds of Bills a Governor can send to the President for his consideration.
- The second provision to Article 200 mentions one kind of Bills which are mandatorily to be reserved for the consideration of the President.
- These are Bills which deviate from the powers of the High Court in such a way as to endanger the constitutionally designed position of that court.
- So, the Constitution requires the Governor to send all such Bills for the consideration of the President.
- Since consideration by the President means consideration by the Union government, the officials of the Home Ministry will in effect decide the fate of such Bills.
- Absence of Categorisation of Bills to be Sent for President’s Consideration
- The Constitution does not refer to any category of Bills which can be sent to the President for his assent.
- Therefore, taking a surface view, the Governor can use his discretion to send any Bill to the President.
- For example, the Governor of Kerala did the same thing recently. He did not act on eight Bills that were with him for over two years.
- When the Supreme Court took up the Kerala government’s petition challenging the Governor’s inaction, he gave his assent to one Bill and sent the seven Bills to the President for his consideration.
- Another example is when the Tamil Nadu Governor sent 10 Bills for reconsideration by the Assembly after many complaints by the State government.
- The Assembly after reconsideration sent the Bills to the Governor without accepting any amendments.
- But in a strange act the Governor sent all those Bills to the President for his consideration which is patently against the Constitution.
- Article 200 (First proviso) requires him to give his assent to the Bills.
Analysis of the Constitutional Provision of Governor's Discretion in Reserving Bills
- Constitutional Provision: The current political context raises a pivotal question about a Governor's discretion to reserve Bills for the President's consideration. The Constitution remains silent on this matter.
- Indirect References: Article 213 and Article 254 (2)
- Two constitutional provisions indirectly touch upon this issue: Article 213 concerning ordinance-making powers and Article 254(2) related to State laws in the Concurrent List.
- Article 213 empowers Governors to promulgate ordinances with presidential instructions if deeming it necessary to reserve a Bill's provisions.
- This implies that the Governor must exercise judgment within the constitutional scheme.
- The use of "deemed it necessary" suggests that Governors cannot act arbitrarily but must adhere to constitutional principles when deciding to reserve Bills.
- Article 254(2) instructs that State laws on Concurrent List items prevail if they have presidential assent, even if conflicting with existing central laws.
- The provision implies that a Bill on a Concurrent subject only needs presidential assent if it contradicts central laws; it does not mandate sending every such Bill to the President.
- President’s Jurisdiction and Governor’s Duty on State Subjects
- In the federal legislative division, the President lacks jurisdiction to scrutinise and assent to Bills exclusively concerning State subjects, emphasising the Governor's constitutional duty.
- Sending a Bill on State matters to the President could be seen as an abdication of the Governor's constitutional duty, as State List subjects fall outside the President's purview.
Conclusion
- The lack of explicit provisions leaves room for interpretation, creating a constitutional conundrum regarding a Governor's discretionary power in reserving Bills for the President.
- Given the evolving nature of constitutional interpretations, there is a need for clarity on the extent of a Governor's discretion in reserving Bills, ensuring alignment with the federal structure and legislative autonomy.
- A Governor is not personally responsible for anything done by the government. Further, constitutional validity of a law is decided by the court and neither the Governor nor the President has any jurisdiction over it.
Source: The Hindu
Rail Kaushal Vikas Yojana
Subject: Government Schemes

Why in News?
Recently, Railway Minister Ashwini Vaishnaw said that Indian Railways’ ‘Rail Kaushal Vikas Yojana’ graduates are not preferred for railway jobs.
Background:-
- The statement comes as a response to a query by BJP MP Narayana Koragappa regarding job preferences for the trained youth.
About Rail Kaushal Vikas Yojana:-
- Launched: September, 2021.
- Ministry: Ministry of Railway.
- Objective: imparting training skills to the youth across several trades to bring qualitative improvement.
- Rail Kaushal Vikas Yojana is a skill development scheme with a special focus on providing training for jobs that are relevant to the Railways.
- It is a sub-scheme under Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY).
Salient Features:-
- The training is imparted in fourteen (14) industry-relevant technical trades such as Electrician, Welder, Machinist, Fitter etc.
- The training is provided free of cost to the candidates.
- There is no provision for providing employment under this scheme.
- Participants will be selected from applications received online, following a transparent mechanism based on marks in matriculation.
- Candidates, who have passed class X and are aged between 18 and 35 are eligible to apply.
- After the end of the program, trainees have to pass a standardized assessment followed by a certificate in the allotted trade by the National Rail and Transportation Institute.
Significance:-
- It will improve the employability of the youth as well as upgrade the skills of self-employed.
- It will also cater to those who are working with contractors through re-skilling and up–skilling.
Source: Financial Express
GS-III
Discrepancies in govt report on lumpy skin disease deaths
Subject: Science and Technology

Why in News?
A Parliamentary Standing Committee has raised concerns about the accuracy of information regarding cattle deaths due to Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD).
- The committee pointed out a discrepancy between the data provided by the Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying (DAHD) and the actual situation on the ground, suggesting that the reported numbers may not align with reality.
Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD)
- LSD is caused by the lumpy skin disease virus (LSDV) of the capripoxvirus genus in the poxviridae family.
- Sheep-pox virus and goat-pox virus are the other members of this genus.
- The LSDV mainly affects cattle — cow and its progeny, and the Asian water buffaloes.
- According to a 2021 report of the Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) of the United Nations, LSD outbreaks occur in epidemics several years apart.
- As per the report, the existence of a specific reservoir for the virus is not known, nor is it known as to how and where the virus survives between epidemics.
Spread of disease
- The LSDV spreads through blood-sucking vectors like ticks and mites like houseflies, mosquitoes, etc.
- It also spreads through contaminated water, fodder and feed.
- Scientists have been advising isolation of infected animals from the healthy ones in an attempt to contain the spread of the virus.
- However, there is a problem of feral cattle in India and scientists say these free-ranging cattle could also be a reason for rapid spread of LSD.
Symptoms
- LSDV attacks the circulatory system of an animal and causes inflammation of blood vessels and lesions in various organs like liver, lungs, spleen, lymph nodes etc.
- In turn, it causes epidermis, making the outer surface of the skin to get separated from dermis – the inner layer of the skin.
- This, in turn, leads to formation of lumps or nodules on an animal’s body. Fever, increased mucus secretion, loss of appetite etc are among other symptoms.
Prevalence
- In World
- According to the FAO report, LSD was long restricted to sub-Saharan Africa. However, over the past decade, it spread to the Middle East and Turkey.
- From 2015 onward, it has impacted the Balkan (southeast Europe) countries, Caucus (eastern Europe) and Russia.
- In India
- LSD entered India, Bangladesh and China in July 2019. Since then, outbreaks of the disease have been reported from 20 Indian states.
- These states are – Assam, Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Goa, Gujarat, Haryana, Jharkhand, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Manipur, Odisha, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Uttar Pradesh and West Bengal.
- In India, as on October 30, 2.87 lakh animals were affected and 22,313 animals died during year 2023.
- LSD entered India, Bangladesh and China in July 2019. Since then, outbreaks of the disease have been reported from 20 Indian states.
News Summary: Discrepancies in govt report on lumpy skin disease deaths
- The Standing Committee on Agriculture, Animal Husbandry and Food Processing presented its report titled ‘Spread of Lumpy Skin Disease in Cattle in the Country and Issues Related There-with’ in the Lok Sabha
- The report noted that the country faced a devastating outbreak of the LSD in 2021-22 resulting in large scale death and emaciation of cattle.
- India battled the devastating LSD outbreak among cattle in 2021-22, hurting milk production and farm income.
- However, as per the report, there was a gap in data relating to number of cattle affected and died as furnished by the Department and the actual ground realities.
- The Committee also recommends the department to make comprehensive efforts to:
- ramp up disease surveillance, treatment and diagnostic infrastructure,
- improve veterinary services,
- build capacity of animal health professionals, etc. to address animal pandemic in a holistic manner in future.
Source: The Hindu
RBI Tightens Norms for Lenders Investing in AIFs
Subject: Economy

Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI has directed banks, non-banking financial companies (NBFCs) and other lenders not to invest in any scheme of Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs).
What are Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs)?
- Alternative Investment Fund is a special investment category that differs from conventional investment instruments. It is a privately pooled fund.
- Generally, institutions and High Net worth Individuals (HNIs) invest in AIFs as substantial investments are required.
- These investment vehicles adhere to the SEBI (Alternative Investment Funds) Regulations, 2012.
- As of December 19, there were 1,220 AIFs registered with the SEBI.
- Total investment commitment raised by AIFs stood at Rs 8.44 lakh crore as of June 30, 2023.
- AIFs can be formed as a company, Limited Liability Partnership (LLP), trust, etc.
Types of AIFs:
- SEBI has categorised Alternative Investment Funds into 3 categories:
- Category 1: These funds invest in SMEs, start-ups, and new economically viable businesses with high growth potential.
- Venture Capital Fund:
- New-age entrepreneurial firms that require large financing during their initial days can approach VCF.
- VCF can help them in overcoming the financial crunch. These funds invest in start-ups with high growth prospects.
- HNIs investing in VCFs adopt a high-risk, high-return strategy while allocating their resources.
- Angel Funds:
- These invest in budding start-ups and are called angel investors.
- They bring early business management experience with them.
- These funds invest in those start-ups that do not receive funding from VCF.
- The minimum investment by each angel investor is Rs 25 lakh.
- Infrastructure Funds:
- This fund invests in infrastructure companies, i.e., those involved in railway construction, port construction, etc.
- Investors who are bullish on infrastructure development invest their money in these funds.
- Social Venture Funds:
- Funds investing in a socially responsible business are social venture funds.
- They are a kind of philanthropic investment but have a scope of generating decent returns for investors.
- Venture Capital Fund:
- Category-2:
- Private Equity Funds:
- A private equity fund invests in unlisted private companies.
- It is difficult for unlisted companies to raise funds by issuing equity and debt instruments.
- Usually, these funds come with a lock-in period which ranges from 4 to 7 years.
- Debt Funds:
- This fund primarily invests in debt securities of unlisted companies.
- Usually, such companies follow good corporate governance models and have high growth potential.
- They have a low credit rating, which makes them a risky option for conservative investors.
- As per SEBI guidelines, money accumulated by debt funds cannot be used to give loans.
- Fund of Funds:
- Such funds invest in other Alternative Investment Funds.
- They do not have an investment portfolio but focus on investing in different AIFs.
- Private Equity Funds:
- Category-3:
- Private Investment in Public Equity Fund (PIPE):
- A PIPE invests in shares of publicly traded companies. They acquire shares at a discounted price.
- Investment through PIPE is more convenient than going for a secondary issue owing to less paperwork and administration.
- Hedge Funds:
- Hedge funds pool money from accredited investors and institutions.
- These funds invest in both domestic and international debt and equity markets.
- They adopt an aggressive investment strategy to generate returns for investors.
- However, hedge funds are expensive as fund managers can charge an asset management fee of 2% or more.
- They can also levy 20% of the returns generated as their fees.
- Private Investment in Public Equity Fund (PIPE):
Benefits of Investing in AIFs:
- High Return Potential:
- AIFs generally have a higher return potential than other investment options.
- The massive pooled amount gives the fund managers enough room to prepare flexible strategies for maximising returns.
- Low Volatility:
- AIFs are not directly related to stock markets. Volatility in these funds is less, particularly when compared with traditional equity investments.
- So, it might be suitable for risk-averse investors looking for stability.
- Diversification:
- These funds allow much-needed diversification in an investment portfolio.
- They act as a cushion at the time of financial crisis or market volatility.
News Summary:
- In a move aimed at curbing evergreening of stressed loans, the RBI has directed banks, Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) and other lenders not to invest in any scheme of Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs).
Key highlights
- In order to address concerns relating to possible evergreening through this route, the RBI said the REs should not make ‘investments in any scheme of AIFs which has downstream investments either directly or indirectly in a debtor company of the RE’.
- Evergreening of loans is a process whereby a lender tries to revive a loan that is on the verge of default or in default by extending more loans to the same borrower.
- The process of evergreening of loans is typically a temporary fix for a bank.
- Downstream investments mean the actual investment by the AIF in a company using the funds they have raised from AIF investors.
- The debtor company of the Regulated entities (REs), for this purpose, means any company to which the RE currently has or had a loan or investment exposure anytime during the preceding 12 months.
- Evergreening of loans is a process whereby a lender tries to revive a loan that is on the verge of default or in default by extending more loans to the same borrower.
Rationale behind this step
- There have been a few instances where some of the regulated entities used the AIF route to evergreen loans that are under stress, thereby delaying classification of such loans as non-performing assets (NPA).
- In such a case, the RE creates an AIF structure to provide funding to its borrower which is likely to become an NPA.
- The AIF, created by the RE along with other investors, invests in the stressed company, which uses the same money to repay to the lender.
Source: The Hindu
TEMPO satellite
Subject: Science and Technology

Why in News?
NASA's new satellite TEMPO measures air pollution hourly has shown significant progress and now the space agency officials are already thinking about ways to extend its life.
About the TEMPO satellite:
- Tropospheric Emissions Monitoring of Pollution (TEMPO) monitors major air pollutants across North America.
- Its monitoring range extends from Canada’s oil sands to the Yucatán Peninsula and across the Atlantic to the Pacific Ocean.
- It is part of a virtual constellation with South Korea's Geostationary Environment Monitoring Spectrometer (GEMS) and the European Space Agency’s upcoming satellite, aiming for comprehensive air pollution monitoring over the Northern Hemisphere.
- It will make important scientific observations, including that of ozone, nitrogen oxide, sulphur dioxide and formaldehyde levels.
- It is capable of measuring air quality over North America hourly during the daytime with a resolution of several square miles.
- It monitors the effects of everything from rush-hour traffic to pollution from forest fires and volcanoes.
- The present pollution-monitoring satellites are in low Earth orbit (LEO), but this new monitoring instrument is hosted in geostationary orbit.
- It was designed for a 20-month operation.
Source: Hindustan Times
Indian Coast Guard
Subject: Defence

Why in News?
Recently, the Indian Coast Guard has deployed its ships, aircraft and disaster relief teams in flood-affected areas of South Tamil Nadu.
Background:-
- Coast Guard said, they have saved 200 lives stranded in flood waters of Tuticorin and adjoining areas.
About the Indian Coast Guard:-
- Established: August 1978.
- HQ: New Delhi.
- Ministry: Ministry of Defense.
- ICG was established by the Coast Guard Act, of 1978 as an independent Armed force of India.
- It is the fourth largest Coast Guard in the world.
- It has jurisdiction over the territorial waters of India, including its contiguous zone and exclusive economic zone.
- It is an Armed Force, Search and Rescue and Maritime Law Enforcement agency .
- For effective command and control, the Maritime Zones of India are divided into five Coast Guard Regions, namely:
- North-West ( Regional Headquarters in Gandhinagar)
- West (Regional Headquarters at Mumbai)
- East (Regional Headquarters at Chennai)
- North-East (Regional Headquarters at Kolkata)
- Andaman & Nicobar (Regional Headquarters at Port Blair)
Functions:-
- Preventing Smuggling.
- It is responsible for marine environment protection in maritime zones of India and is the coordinating authority for response to oil spills in Indian waters.
- It has also rescued approximately 13,000 personnel till date during various ‘Aid to Civil Authority’ operations viz. assistance provided to civil authorities during floods, cyclones and other natural calamities; most recently during the recent floods in Maharashtra, Karnataka and Goa.
- It is also working in close coordination with Central and State agencies to put in place a robust coastal security mechanism.
- It is responsible for marine environment protection in maritime zones of India.
Source: AIR
|
38 videos|5293 docs|1118 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 20th December 2023 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What was the significance of the Bahmani Kingdom in Indian history? |  |
| 2. How did the Earthquake impact the affected region? |  |
| 3. What is the Rail Kaushal Vikas Yojana and how does it benefit the railway sector? |  |
| 4. What are the discrepancies in the government report on lumpy skin disease deaths? |  |
| 5. How do the tightened norms for lenders investing in AIFs impact the RBI's regulations? |  |
















