UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC > Acute pyelonephritis
Acute pyelonephritis | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Acute pyelonephritis-Etiology |

|
| Acute pyelonephritis-Presentation |

|
| Acute pyelonephritis-Diagnosis |

|
| Acute pyelonephritis-Management |

|
| Chronic pyelonephritis |

|
Acute pyelonephritis-Etiology
Pyelonephritis is an infection of the renal pelvis and parenchyma.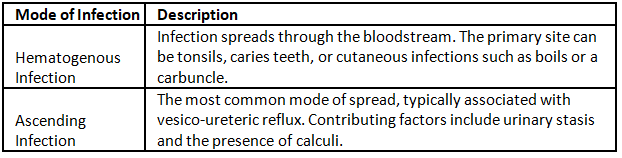
Pathogens
- Most commonly Enterobacteriaceae (gram-negative rods)
- Escherichia coli (~ 75-90% of cases)
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Proteus mirabilis
- Gram-positive bacteria (e.g., Enterococcus faecalis, Staphylococcus aureus)
- Candida infection (esp. in immunocompromised patients) is possible
Risk Factors
- Most common in women because they have shorter urethras
- Pregnancy (presents between 20-28 weeks, more commonly affects the right kidney because of dilated right ureter, might present with premature labor)
- Urinary tract obstruction
- Foreign bodies (e.g., catheters or other urologic instrumentation)
- Anatomical abnormalities (e.g., benign prostatic hyperplasia, vesicoureteral reflux, nephrolithiasis, ureteral strictures)
- Cystitis
- Recent administration of antibiotics (possible antibiotic resistance)
- Immunosuppression (e.g., HIV, diabetes)
- Acute kidney injury
Question for Acute pyelonephritisTry yourself: Which pathogen is the most common cause of acute pyelonephritis?View Solution
Acute pyelonephritis-Presentation
Clinical Presentation
- Acute pyelonephritis is indicated by symptoms such as fever (temperature >38°C), rigors, flank pain, nausea and vomiting, and costovertebral angle tenderness.
- The severity of symptoms can range from a mild illness to a severe condition involving septic shock, renal failure, and a life-threatening situation.
- Pyuria, the presence of pus in the urine, is almost always observed.
Differentiation and Complications
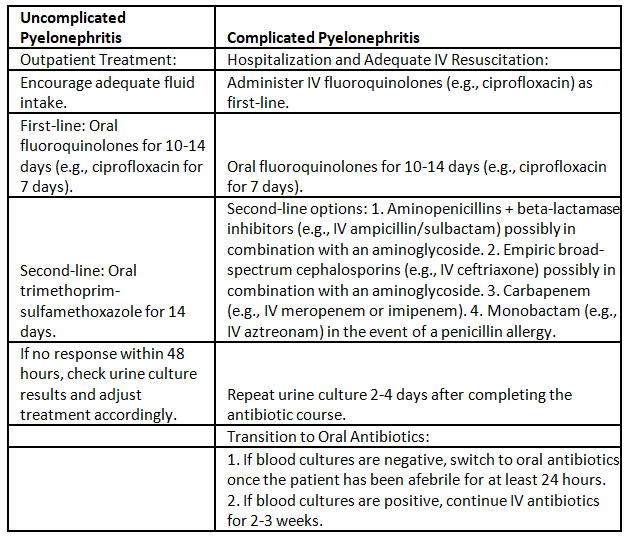
- It is crucial to distinguish between complicated and uncomplicated pyelonephritis due to differing management approaches.
- Complicated pyelonephritis is characterized by the following factors:
- Urinary tract abnormalities (e.g., obstruction, indwelling catheter)
- Recent surgery on the urinary tract
- Renal impairment
- Immunosuppression and/or severe comorbidities
- High-risk patients despite an uncomplicated clinical presentation (e.g., elderly)
Complications
- Urosepsis: Systemic infection originating from a urinary tract infection.
- Perinephric Abscess: Collection of pus in the tissue surrounding the kidney.
- Papillary Necrosis: Degeneration of renal papillae, often associated with severe pyelonephritis.
- Emphysematous Pyelonephritis: Severe infection causing the presence of gas within the renal parenchyma.
- Renal Abscess: Formation of a localized collection of pus within the kidney.
- Recurrent Bacterial Pyelonephritis:
- If recurrence is due to the same organism despite adequate treatment, extend the antibiotic course for 6 weeks.
- If a new pathogen is identified, adjust the antibiotic and treat for 2 weeks.
- Atrophic Kidneys: Reduction in the size of the kidneys.
- End-Stage Renal Disease (ESRD): Occurs if both kidneys are affected, the patient has a single kidney, or the other kidney has been damaged by a different pathology.
Question for Acute pyelonephritisTry yourself: Which of the following is a symptom of acute pyelonephritis?View Solution
Acute pyelonephritis-Diagnosis
- Urinalysis: Examination of urine for pyuria, leucocyte casts, bacteriuria, and hematuria.
- Inflammatory Markers: Elevated levels of C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
- Cultures: Collection of urine and blood samples for microbial cultures.
- Imaging:
- Renal Ultrasound: Detects urinary obstruction, calculi, or abscess.
- CT KUB (Kidneys, Ureters, Bladder): Identifies hemorrhage, renal, and bladder stones.
- Retrograde Cystourethrogram: Useful for detecting vesicoureteral reflux (VUR).
Acute pyelonephritis-Management
Emphysematous pyelonephritis
- Life-Threatening Variant:
- Description: Fulminant and necrotizing.
- Causative Organisms: Gas-forming organisms such as E. coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Proteus mirabilis.
- Risk Factors: Mainly associated with diabetes (90%) and urinary tract obstruction.
- Diagnosis:
- Gas presence can be detected through imaging techniques such as X-ray, ultrasound (USG), or computed tomography (CT).
- Management:
- Specific management strategies are not provided in the original text.

Question for Acute pyelonephritisTry yourself: Which imaging technique is useful for detecting vesicoureteral reflux (VUR) in patients with acute pyelonephritis?View Solution
Chronic pyelonephritis
Xanthogranulomatous Pyelonephritis (Chronic Pyelonephritis)
- Etiology: Unknown.
- Severe chronic destructive granulomatous inflammation affects the renal parenchyma.
- Associated with urinary tract obstruction and infection.
- Predominantly observed in middle-aged women, displaying chronic symptoms such as flank pain, pyrexia, malaise, and a palpable mass.
- Differential diagnosis includes renal cell carcinoma.
- Diagnosis:
- Culture typically reveals E. coli, Gram-negative bacilli, or S. aureus.
- CT scans often indicate an enlarged, non-functioning kidney, the presence of calculi, low-density masses (xanthomatous tissue), and occasional involvement of adjacent structures.
- Histology:
- Histological examination reveals lipid-laden foamy macrophages and multinucleated giant cells.
- Gross examination displays large, irregular, yellow masses throughout the kidney.
- Treatment:
- Nephrectomy is the recommended treatment.
Pyelonephritis (Acute/Chronic)
Q: What are the symptoms of acute pyelonephritis? Name the organisms that commonly cause acute pyelonephritis. List the antibiotics commonly used to treat severe pyelonephritis. (2012)
The document Acute pyelonephritis | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
7 videos|236 docs
|
FAQs on Acute pyelonephritis - Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is the main cause of acute pyelonephritis? |  |
Ans. The main cause of acute pyelonephritis is a bacterial infection, most commonly caused by the bacteria Escherichia coli (E. coli). Other bacteria such as Klebsiella, Proteus, and Enterococcus can also cause the condition.
| 2. What are the typical symptoms of acute pyelonephritis? |  |
Ans. The typical symptoms of acute pyelonephritis include fever, chills, flank pain (pain in the lower back or side), frequent urination, painful urination, blood in the urine, and cloudy or foul-smelling urine.
| 3. How is acute pyelonephritis diagnosed? |  |
Ans. Acute pyelonephritis is typically diagnosed through a combination of clinical evaluation, medical history, physical examination, and laboratory tests. Urine analysis, urine culture, blood tests, and imaging studies such as ultrasound or CT scan may be done to confirm the diagnosis.
| 4. What is the recommended management for acute pyelonephritis? |  |
Ans. The management of acute pyelonephritis usually involves antibiotic therapy to treat the underlying bacterial infection. Hospitalization may be necessary for severe cases or for individuals who are unable to take oral antibiotics. Fluid intake, pain management, and supportive care are also important aspects of the management.
| 5. What is the difference between acute and chronic pyelonephritis? |  |
Ans. Acute pyelonephritis is a sudden and severe infection of the kidneys, usually caused by bacteria. It typically presents with symptoms such as fever, flank pain, and urinary symptoms. Chronic pyelonephritis, on the other hand, is a long-standing inflammation of the kidneys that may result from recurrent or untreated acute infections. It can lead to kidney damage and eventually kidney failure if left untreated.
Related Searches



















