Sleep | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Definition
Sleep is the inherent recurring condition of repose for the mind and body, marked by closed eyes and featuring a state of partial or complete unconsciousness.
Mechanism/Neurophysiology of Sleep:
Sleep is induced by stimulating sleep centers, leading to activation.
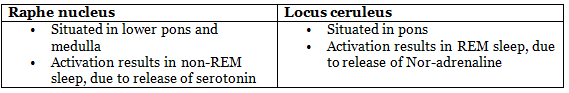
Flip-Flop Switch
The ascending arousal system and the sleep-promoting system, two crucial neural networks, operate collaboratively with mutual inhibition, creating a neural circuit comparable to what electrical engineers term a "flip-flop switch." Such a switch facilitates swift transitions between the on (wake) and off (sleep) states, avoiding intermediate states. Numerous sleep-promoting neurons experience inhibition from inputs originating in the arousal system.
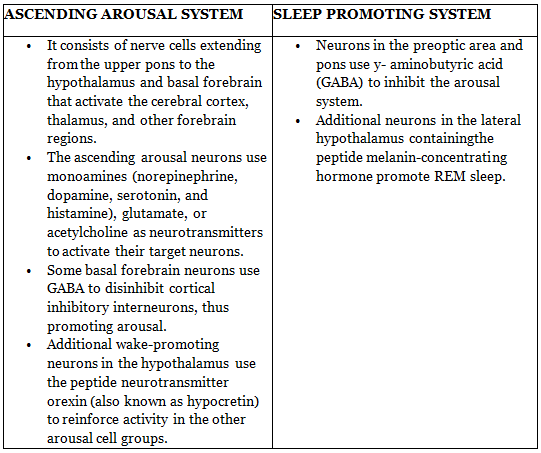
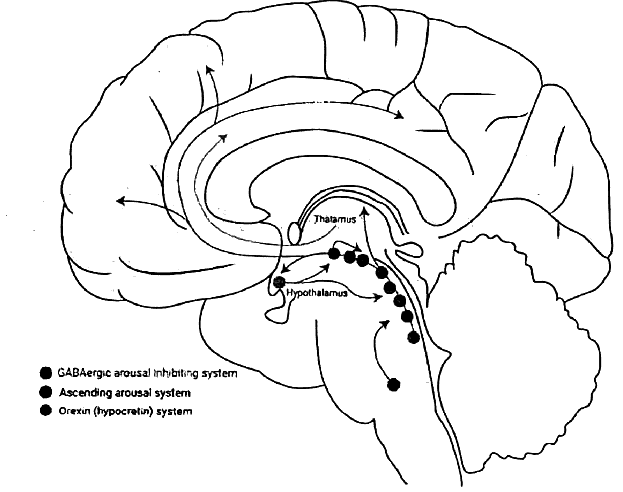
Neurons located in the ventrolateral preoptic nucleus, a crucial site for promoting sleep, diminish in number as part of the natural aging process in humans. This reduction in neurons correlates with a diminished capacity to sustain sleep, leading to sleep fragmentation. Furthermore, in Alzheimer's disease, these ventrolateral preoptic neurons are affected, potentially contributing to the compromised sleep quality observed in individuals with this condition.
Rem Sleep Switch
The shift between NREM and REM sleep seems to be regulated by a comparable switch located in the brainstem. The switch governing REM sleep receives cholinergic input, promoting transitions into REM sleep, while it also receives monoaminergic input, specifically from norepinephrine and serotonin, which inhibits REM sleep.
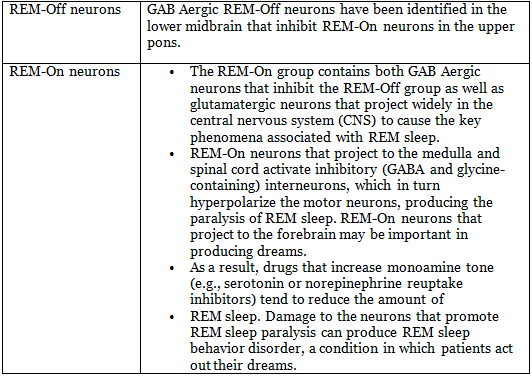
Inhibition
The wakefulness-promoting function of the Ascending Reticular Activating System (ARAS) arises from its connections with the cerebral cortex, both afferently and efferently. Sleep is induced by inhibiting the ARAS.
Physiological Changes During Sleep
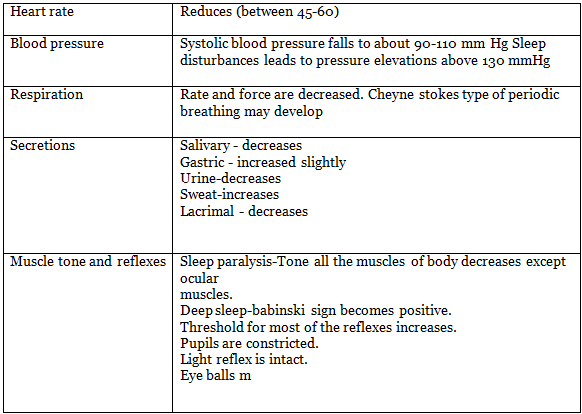
Stages/Types of sleep
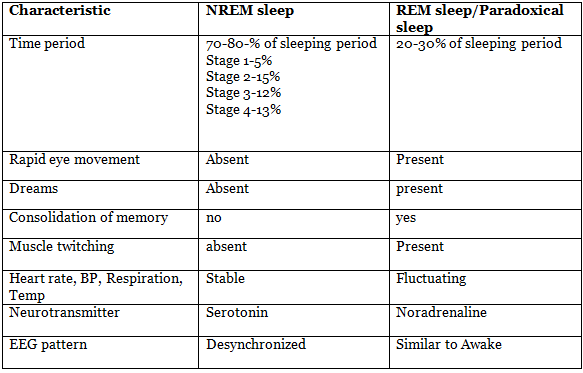
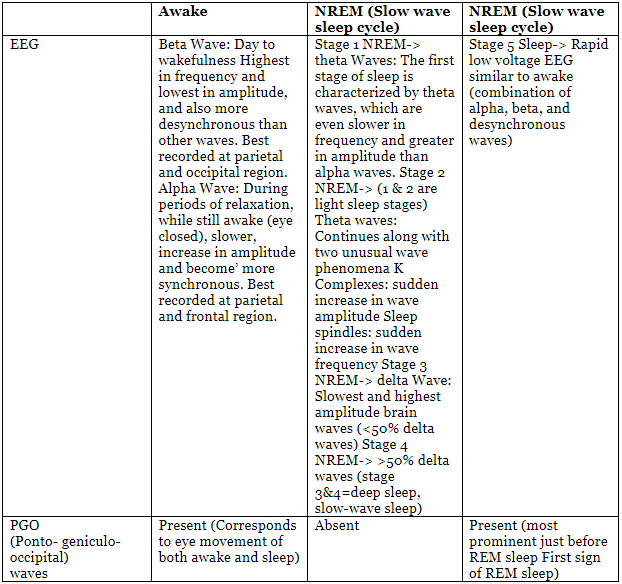
The widely accepted average duration for an adult male's sleep cycle is 90 minutes, defined as extending from the conclusion of one REM period to the conclusion of the subsequent one. A typical 7-8-hour sleep likely encompasses five cycles, with the central two cycles having a propensity for longer durations, and REM occupying an increasing portion of the cycle as the night progresses.
N1 (NREM stage 1) denotes the transitional phase from drowsiness or wakefulness to falling asleep. In this stage, both brain waves and muscle activity begin to decrease.
N2 marks a phase of light sleep where eye movement has ceased. There is a reduction in brain wave frequency and muscle tonus, accompanied by a decrease in heart rate and body temperature.
N3 or N4 are the more challenging stages to rouse from. In these stages, the entire body enters a state of relaxation, characterized by decreased breathing, lowered blood pressure, and a reduction in body temperature.
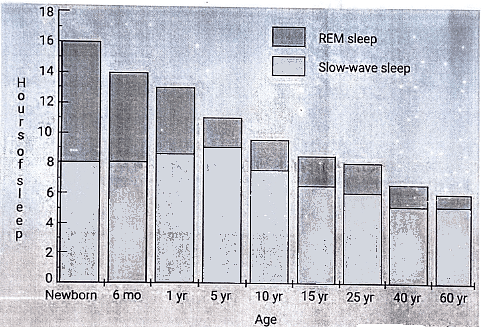
Variations of sleep cycle with age
The need for sleep is not consistent, but the average daily sleep requirement varies across different age groups:
- Newborn infants: 18 to 20 hours
- Growing children: 12 to 14 hours
- Adults: 7 to 9 hours
- Older individuals: 5 to 7 hours.
In infants, the sleep cycle typically lasts about 50-60 minutes, and its average duration increases as individuals progress into adulthood. In adults, sleep initiation involves NREM, while in infants, it commences with REM. REM-onset sleep is also observed in adults under conditions of jet lag or chronic sleep deprivation.
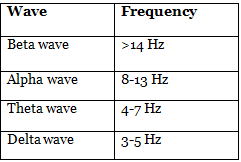
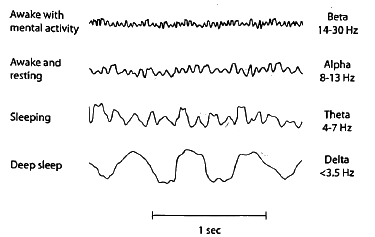
The sequence of EEG waves can be remembered as "Gay BAT Dance," representing the progression from gamma, beta, alpha, theta to delta frequencies, with a decrease in frequency and an increase in amplitude.
 |
Download the notes
Sleep
|
Download as PDF |
Normal Adult Brain Waves
Stages of sleep with EEG patterns
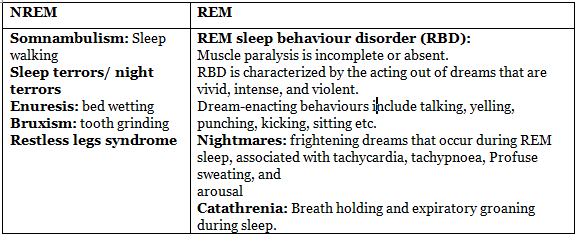
Sleep Disorders
Narcolepsy is frequently linked with excessive daytime sleepiness and may manifest with:
- Cataplexy - the sudden loss of muscle tone and paralysis of voluntary muscles.
- Hypnagogic hallucinations - dreams occurring during the pre-sleep stage.
- Automatic behaviors - engaging in activities automatically and having no recollection afterward.
Sleep and Consciousne -Repeats
- Explore the neurophysiological foundation of sleep. (2016)
- Provide a definition of sleep and delve into the various types of sleep. Examine the distinctions in the sleep patterns of a newborn in comparison to an adult. Additionally, discuss the electroencephalographic record's waveform during deep sleep. (2014)
- Define sleep and offer a concise overview of the architecture of a sleep cycle. Examine how these patterns vary with age. (2010)
- Analyze the physiology of normal sleep. (2007)
- Define consciousness and identify the key brain regions responsible for it. Explore disturbances in consciousness. (2009)
|
7 videos|219 docs
|
















