Immunology | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
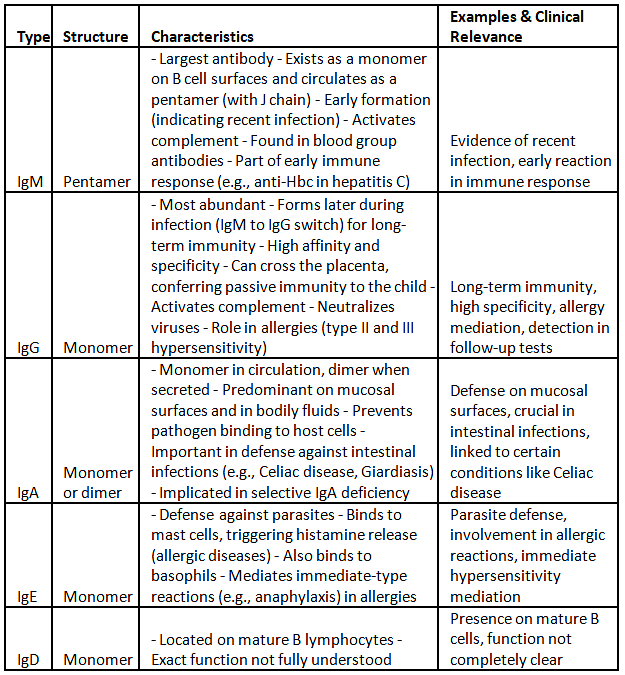
Classification of Immunoglobulins
Immunoglobulins, also known as antibodies, are glycoprotein molecules generated by the immune system in reaction to an antigenic trigger. They are present in the blood, bodily secretions, and mucous surfaces, where they attach to the specific antigen that prompted their production, leading to the inactivation of the antigen. Antibodies consist of two functional segments: the Fab region and the Fc region.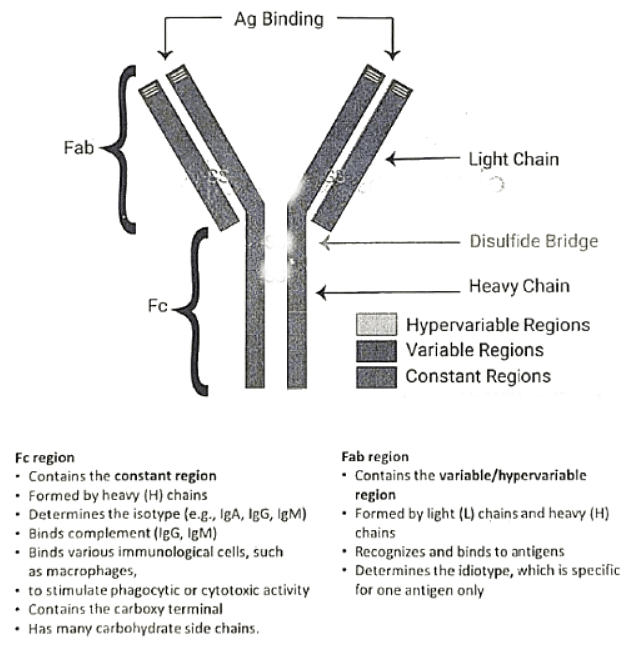
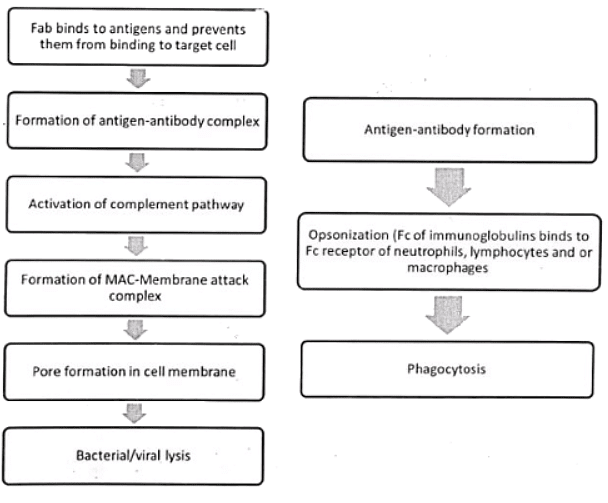
Mechanism of Action - Immunoglobulins
Complement Pathway
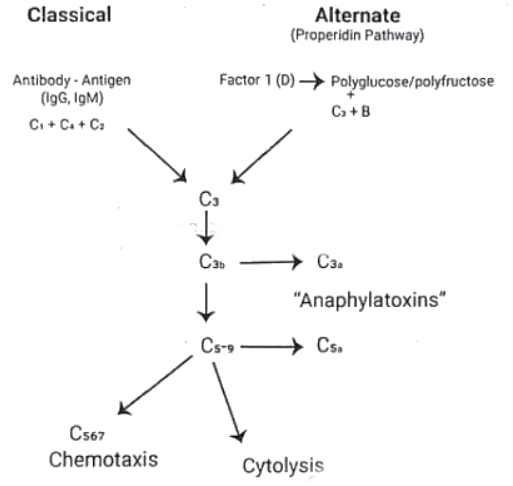
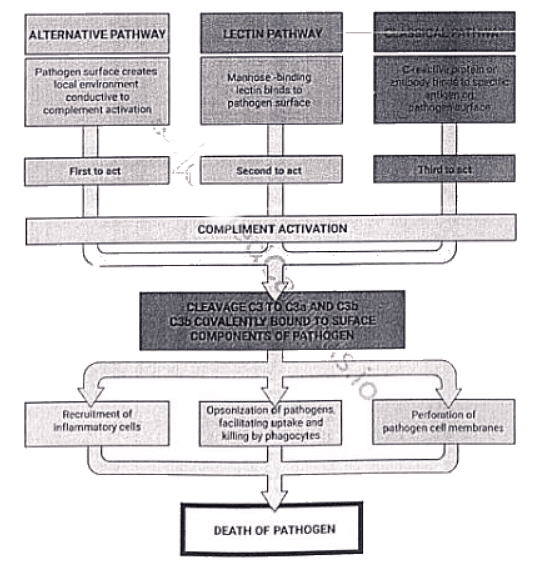
Complement Pathway
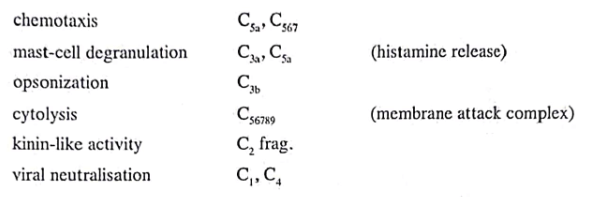
Complement deficiencies
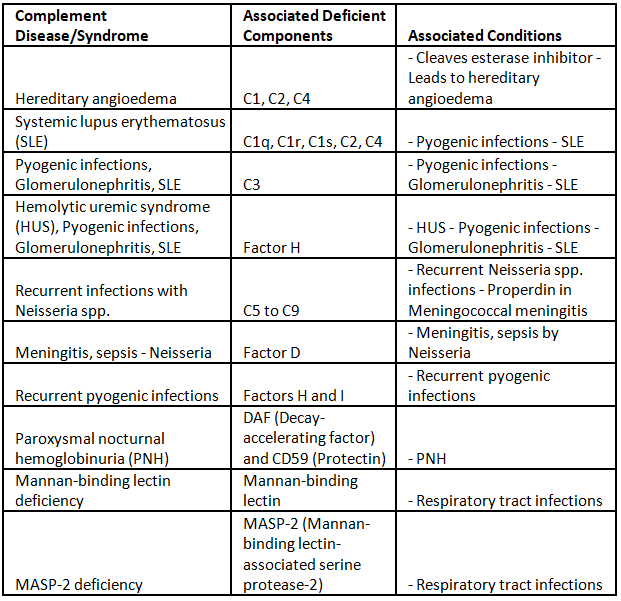
Hypersensitivity Reactions
- Normally protective immune responses can also cause harm to tissues.
- Injurious immune reactions fall under the category of hypersensitivity, leading to diseases termed hypersensitivity diseases.
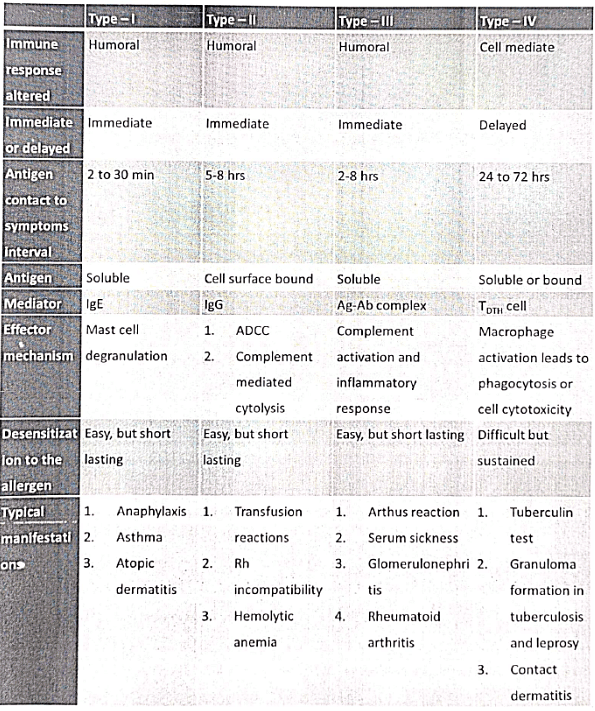
- Hypersensitivity reactions are typically classified into four types, each based on the primary immune mechanism causing injury. Three of these types involve variations of antibody-mediated harm, while the fourth involves injury mediated by T cells.

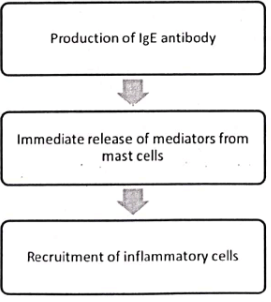
Type I Hypersensitivity
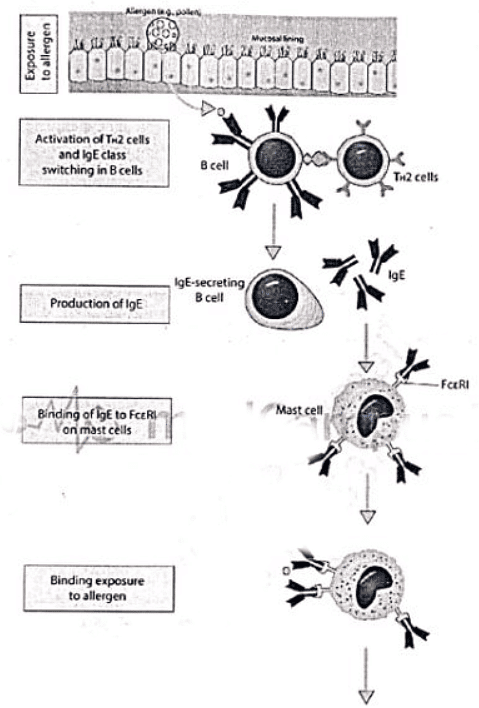
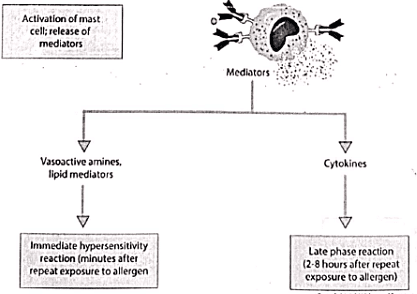
Type II Hypersensitivity
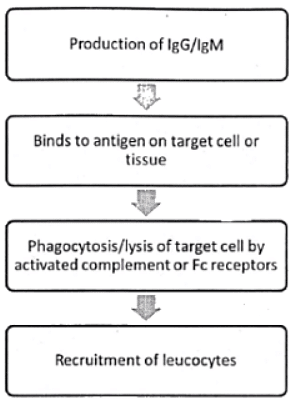
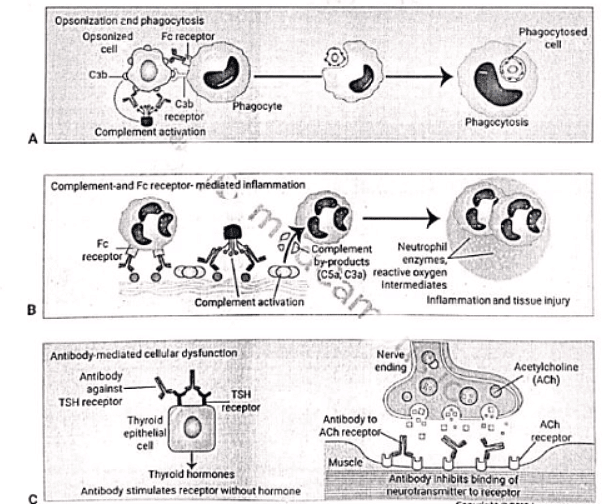
Type III Hypersensitivity
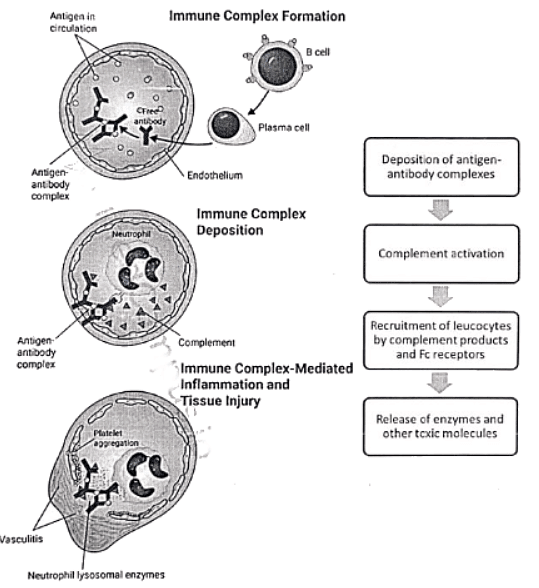
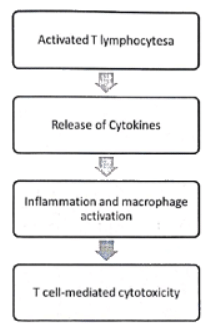
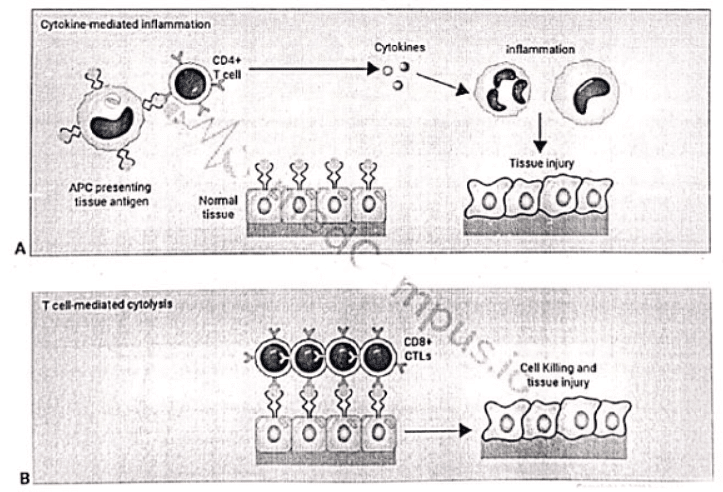
Type IV Hypersensitivity
Gell and Coombs classification of hypersensitivity reactions
Type V/VI Hypersensitivity
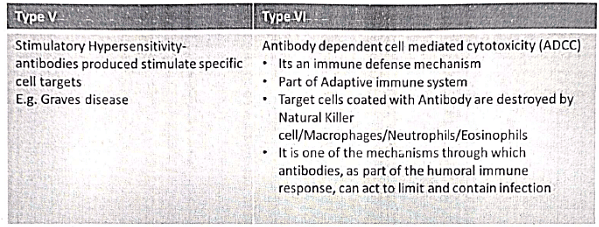
Natural Killer Cells
- Constituting 10-15% of peripheral lymphocytes, these cells lack TCR or cell surface Ig and possess abundant azurophilic granules, qualifying them as large granular lymphocytes.
- Belonging to the innate immune system, these cells do not necessitate prior sensitization for their function.
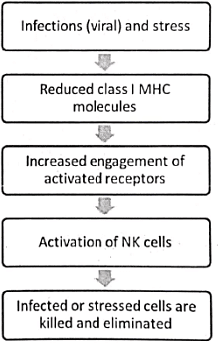
- Identified by the CD16/CD56 markers specific to natural killer (NK) cells, they exhibit the capability to lyse target cells coated with IgG through antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC).
- NK cells are equipped with two types of receptors— inhibitory and activating. Inhibitory receptors recognize self class I MHC molecules found on all healthy cells. Conversely, activating receptors recognize molecules expressed on stressed, infected, or DNA-damaged cells.
- Typically, the effects of inhibitory receptors predominate over those of activating receptors, preventing the activation of NK cells.
ADCC
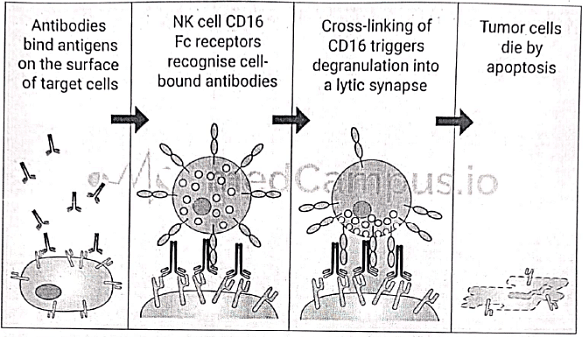
Immunological Tolerance

Immunological Tolerance
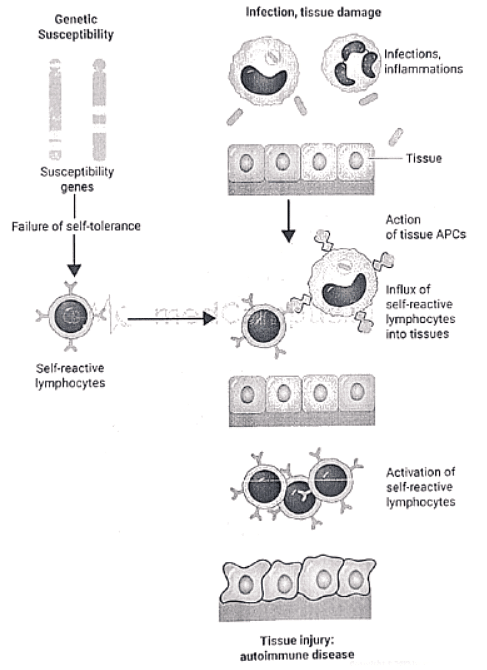
Immunological tolerance is a state in which an individual is incapable of developing an immune response against his own tissue antigens.
It is mediated by two broad mechanisms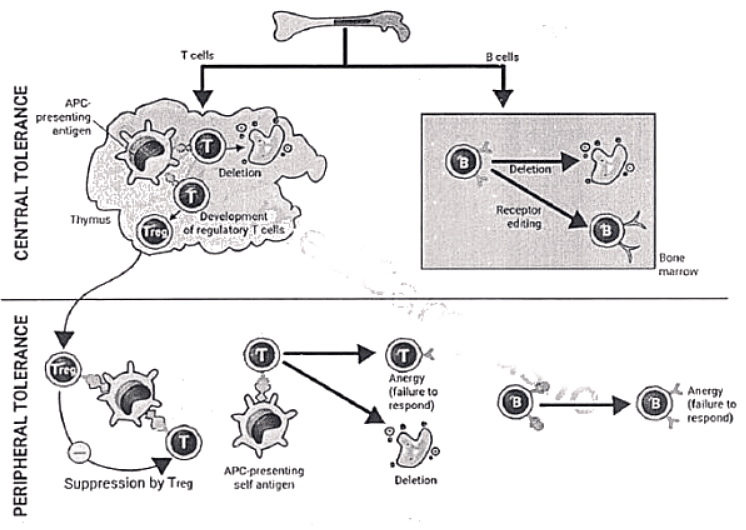
Mechanisms of Autoimmunity
Autoimmunity is a condition in which the body's own immunologically competent T-cells or Antibodies act against its self-antigens resulting in structural or functional damage.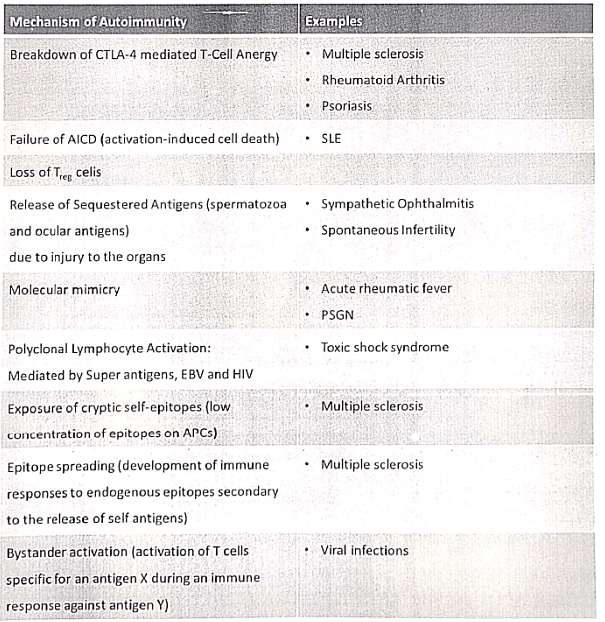
Mechanisms of Autoimmunity
Assessment of Immune Function
- Historical background and clinical assessment
- Standard diagnostic tests
- Complete Blood Picture (CBP)
- Quantitative measurement of Immunoglobulin levels
- Evaluation of B-cell functionality
- Testing for naturally occurring antibodies against rubella, influenza, tetanus, diphtheria, etc.
- Assessing response to immunization for typhoid, polio, CDT, HBV, etc.
- Analysis of T-cell function
i. Utilizing skin tests (PPD, Candida, trichophyton, tetanus toxoid)
ii. Determining contact sensitivity to dinitrochlorobenzene
iii. Employing chest X-rays in children to observe the thymus shadow - Complement system assessment
- Utilizing the total hemolytic complement CH50 due to challenges in individual component assays
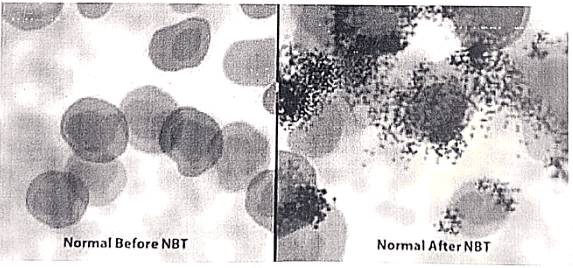
- Evaluation of phagocytic function through the Nitroblue tetrazolium test
- Lymphocyte cell culture stimulation tests and induced lymphokine assays
- Mixed lymphocyte cultures
- Applied in compatibility testing for transplantation
- Involves incubating irradiated white blood cells with a second set
- A blastogenic transformation indicates significant antigenic disparity between the two cell sets, potentially leading to clinical manifestations like graft rejection or graft versus host disease.
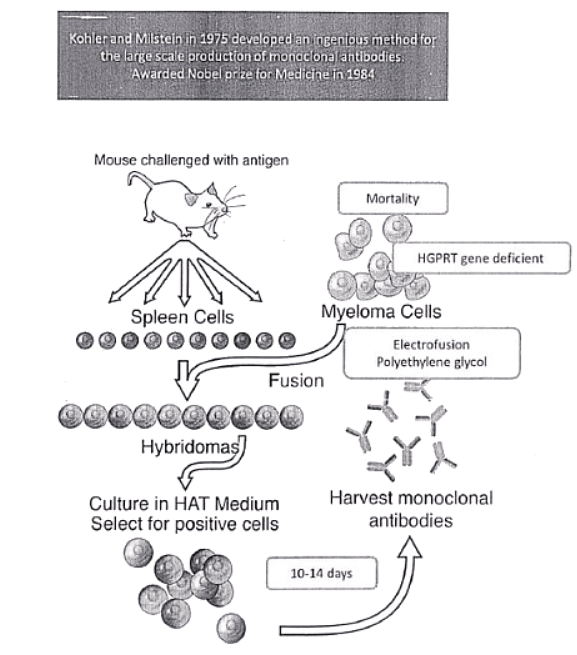
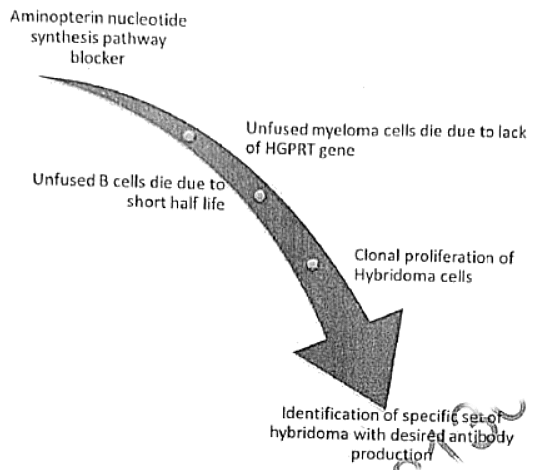
Monoclonal Antibody production by hybridoma technology
Definition of Monoclonal Antibodies
- Antibodies produced by infection have multiple epitopes or antigenic determinants, each of which generates separate clones of lymphocytes.
- This results in antisera containing immunoglobulins of different classes with specificities against different epitopes of the antigen.
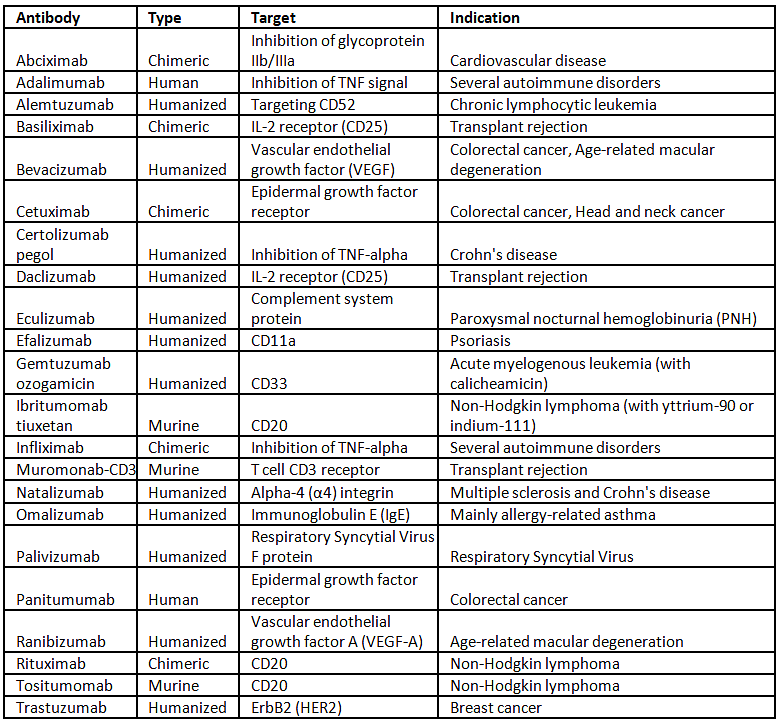
- Antibodies produced by a single clone and directed against a single antigenic determinant are called monoclonal antibodies.
- They are useful for diagnostic and research techniques.
Monoclonal Antibodies
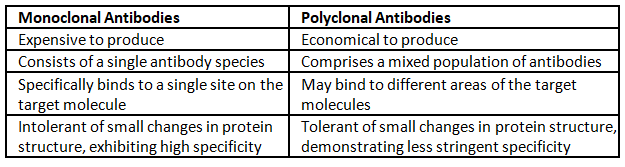
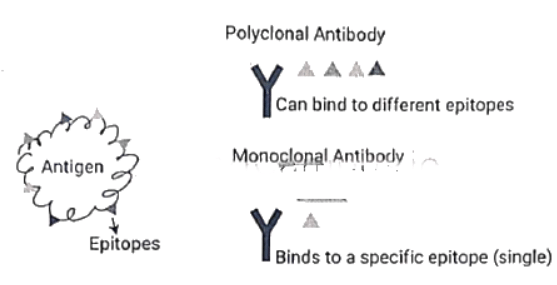
- Monoclonal antibodies (mAb) or monospecific immunoglobulins are produced from a single B-cell clone.
- These antibodies specifically recognize unique epitopes or binding sites on a single antigen.
- The distinction between monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies lies in their origin – monoclonal antibodies are derived from a single B-cell clone and target a single epitope.
- When an animal is immunized with an antigen, the resulting B cell response is polyclonal. However, from this diverse response, a specific B-cell clone can be chosen and expanded to create a supply of monoclonal antibodies.
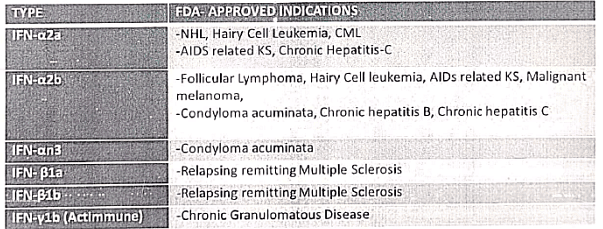
Interferons
- Categorization
- Characteristics
- Mode of Operation
- Applications
- Undesirable Outcomes
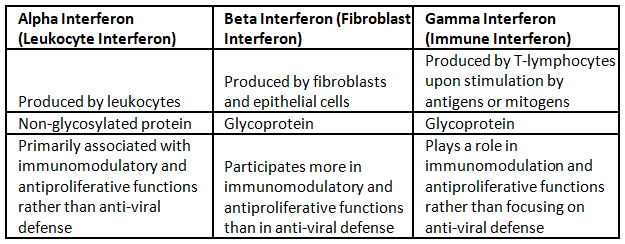
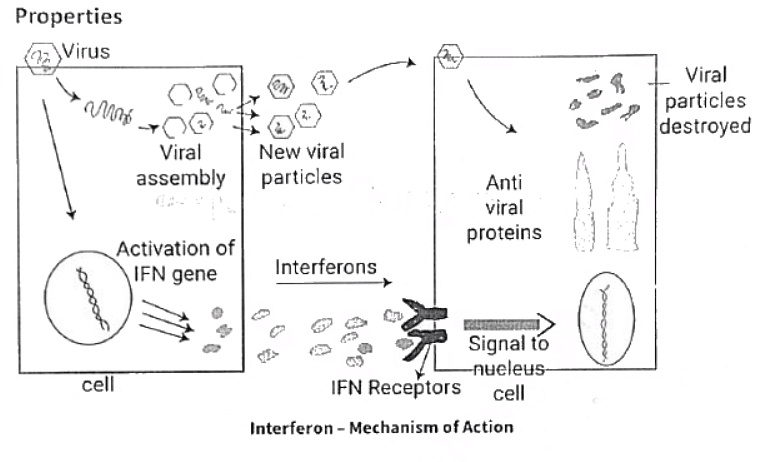
Interferon
Immunology
- Cells of Immune system
- Innate and Acquired Immunity
- Humoral and cell mediated immunity
Innate vs Adaptive immunity
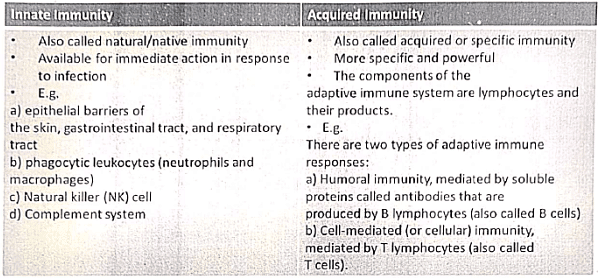
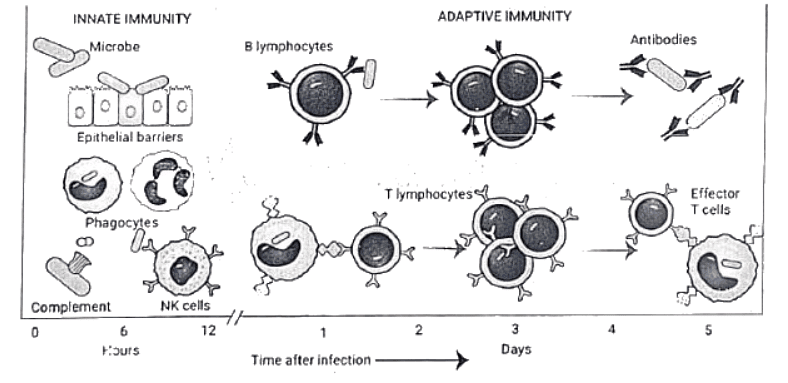
Cells of Immune System
The cells of the immune system consist of
- Lymphocytes, which recognize antigens and mount adaptive immune responses
- Specialized antigen-presentingcells (APCs), which capture and display microbial and other antigens to the lymphocytes
- Effector cells, whose function is to eliminate microbes and other antigens.
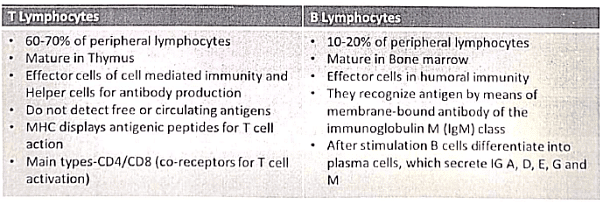
Lymphocytes
- 20-45% of DLC
- 10w in number
- Small round cells
- Spherical nucleus

Cells of Immune system

MHC-the peptide display system of adaptive immunity
*The human MHC, known as the human leukocyte antigen (HLA) complex, consists of a cluster of genes on chromosome 6
Several other proteins are encoded in the MHC locus, some of which have been called "class III molecules." These include complement components (C2, C3, and Bf) and the cytokines tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and lymphotoxin. These molecules do not form a part of the peptide display system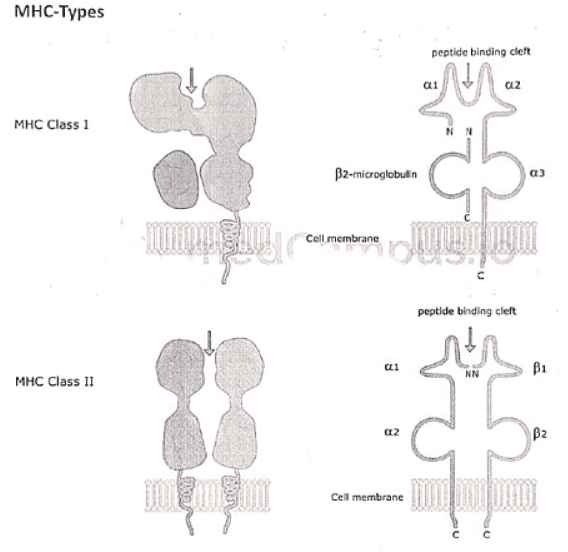
MHC RESTRICTION
T cells within an individual can identify and respond solely to peptides presented by the individual's MHC molecules. These encountered MHC molecules are the only ones T cells typically interact with. This specific recognition phenomenon is termed MHC restriction.
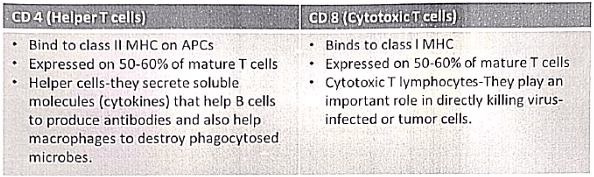
CD4 vs CD8
Th1 vs Th2

Other types of T cells

Antigen-Presenting Cells (APCs)
- Dendritic Cells:
- Interdigitate dendritic cells are strategically positioned beneath epithelial layers to capture and display antigens to T cells, exemplified by Langhans cells.
- Plasmacytoid DCs, found in blood and lymphoid organs, generate the major antiviral cytokine Interferon type I.
- Follicular dendritic cells (FDCs) reside in germinal centers within lymphoid follicles in the spleen and lymph nodes. They enhance secondary antibody responses by capturing antigens bound to antibodies and complement, presenting them to activated D-lymphocytes in lymphoid follicles.
- Macrophages: Engaged in the ingestion of microbes, macrophages present antigenic peptides to T lymphocytes, contributing to cell-mediated immunity.
- B Cells: Involved in presenting antigens to helper T cells, B cells receive signals that trigger antibody responses to protein antigens.
Effector cells

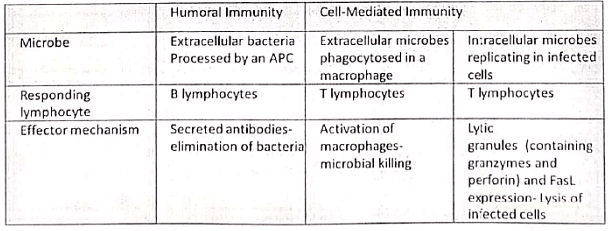
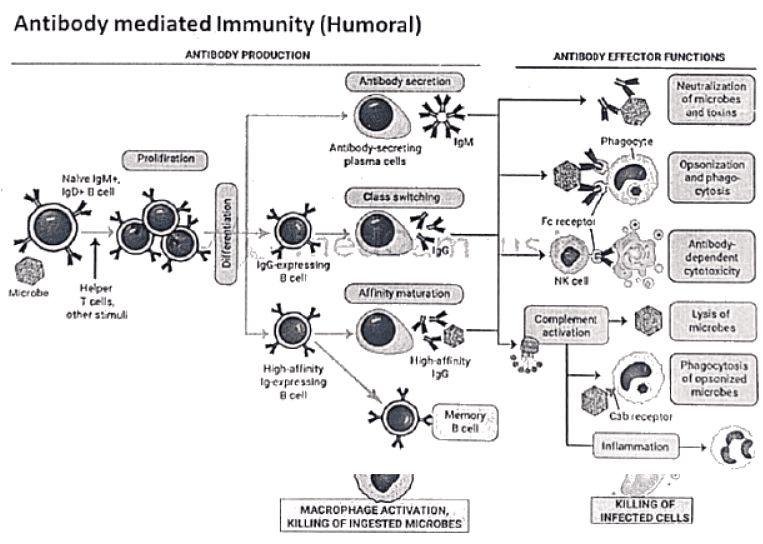
Humoral And Cell Mediated Immunity (CMI)
- The nature of immune response depends on depends on whether the lymphocyte is a B or T cell.
- T cells induce CMI while stimulated B cells produce antibodies (Humoral mediated immunity).
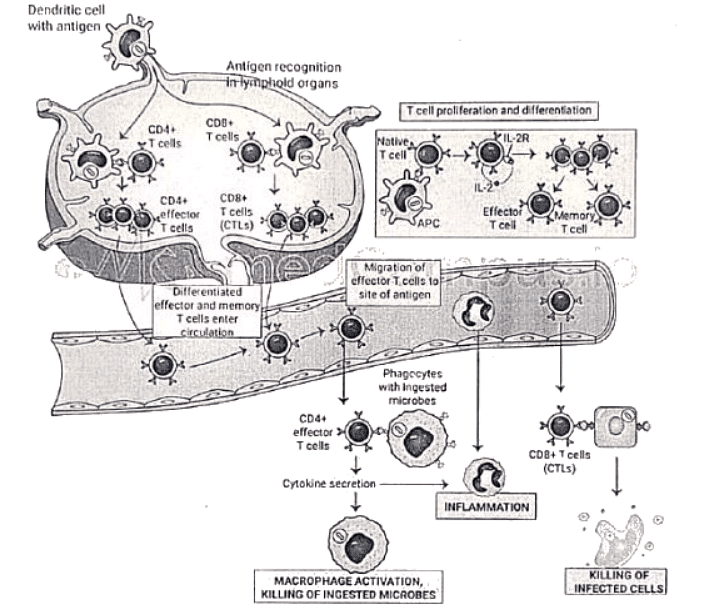
Cell Mediated Immunity (CMI)
Immunology-Repeats
Q1: What are Immunoglobulins? Classify Immunoglobulins. Describe their role in host defense against communicable diseases. What are the modes by which immunoglobulins act on antigens? (2010)
Q2: What is the mechanism involved in Type I hypersensitivity reaction? What types of agents can induce it? Describe the laboratory evaluation and management of allergic reactions. (2011)
Q3: Briefly describe various cells of immune system. Discuss classification systems to differentiate lymphocytes. Discuss cell-mediated immunity. (2012)
Q4: Discuss the role of Natural Killer (NK) cells and Antibody Dependent Cytotoxic Cells (ADCC). (2014)
Q5: What are the features of innate and acquired immunity? What is the mechanism of action of immunoglobulins? (2015)
Q6: Define and classify hypersensitivity. Describe type I hypersensitivity. (2015)
Q7: Define immunological tolerance and discuss its role in autoimmunity, with one example. (2017)
Q8: Write short note on Monoclonal antibody and its application. (2018)
Q9: Write short notes on Interferons and their uses. (2018)
Q10: Briefly describe various cells of immune system. Discuss classification systems to differentiate lymphocytes. Discuss cell-mediated immunity. (2012)
Q11: What are the features of innate and acquired immunity?
|
7 videos|236 docs
|
FAQs on Immunology - Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What are the different classifications of immunoglobulins? |  |
| 2. What is the Gell and Coombs classification of hypersensitivity reactions? |  |
| 3. What are natural killer cells and their role in the immune system? |  |
| 4. What is immunological tolerance and how is it maintained in the immune system? |  |
| 5. What are the mechanisms of autoimmunity? |  |




















