UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC > Ischemic Heart Diseas (IHD)
Ischemic Heart Diseas (IHD) | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| IHD vs CAD |

|
| Syndromes - IHD |

|
| IHD - Pathogenesis |

|
| IHD - Complication |

|
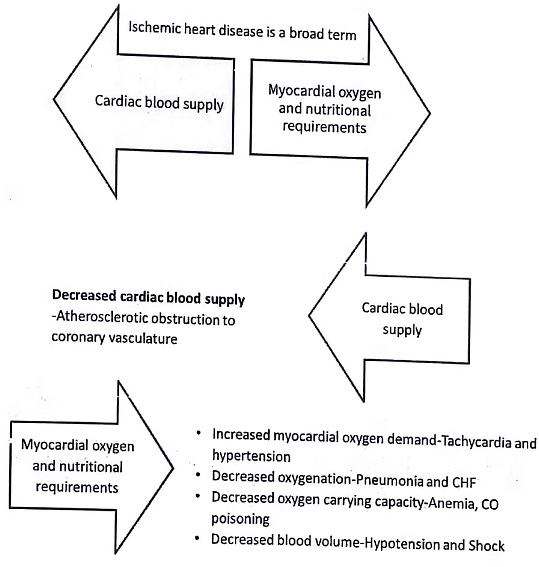
IHD vs CAD
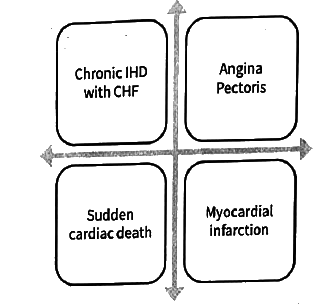
Syndromes - IHD
Atherosclerosis Risk Factors
Non-modifiable (Constitutional):
- Genetic abnormalities
- Family history
- Advancing age
- Male gender
Modifiable:
- Hyperlipidemia
- Hypertension
- Cigarette smoking
- Diabetes
- Inflammation (CRP levels)
- Hyperhomocysteinemia
- Elevated lipoprotein A levels
- Metabolic syndrome
Question for Ischemic Heart Diseas (IHD)
Try yourself:
Which of the following is a non-modifiable risk factor for atherosclerosis?View Solution
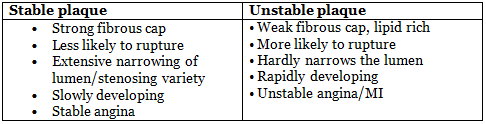
Plaque Stable vs Unstable
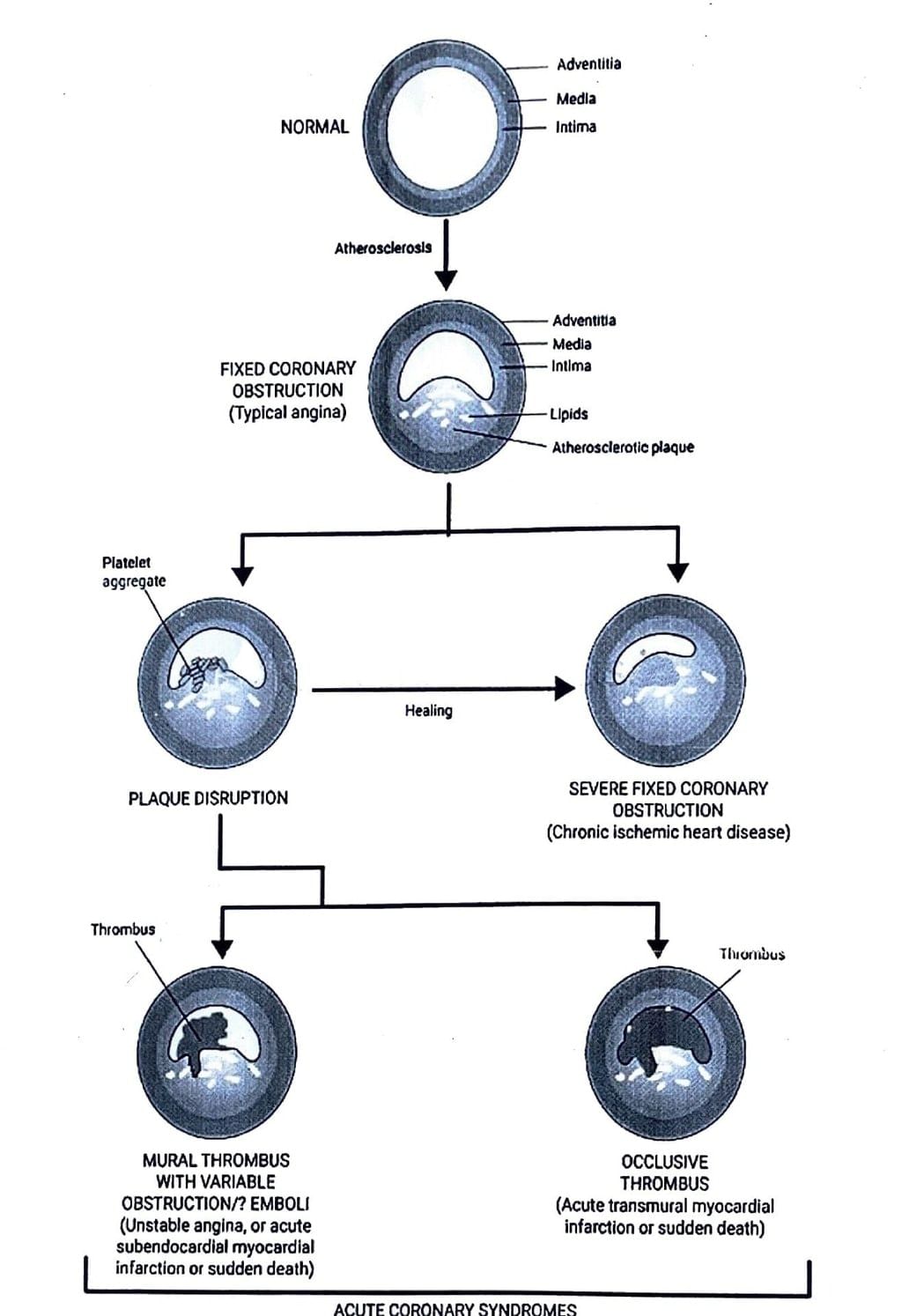
Critical stenosis >70% occlusion
IHD - Pathogenesis
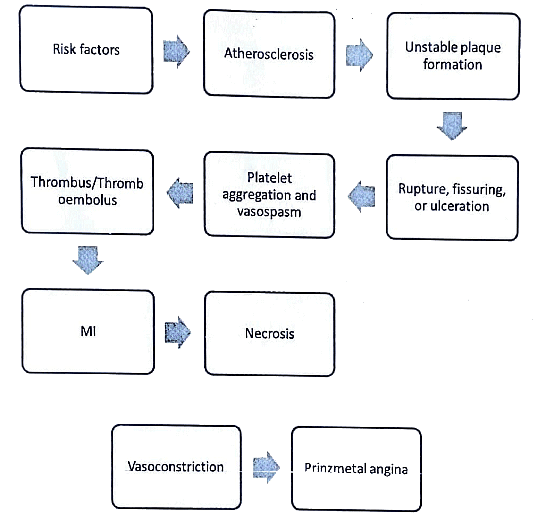
 |
Download the notes
Ischemic Heart Diseas (IHD)
|
Download as PDF |
Download as PDF
Sequential Myocardial Changes in MI
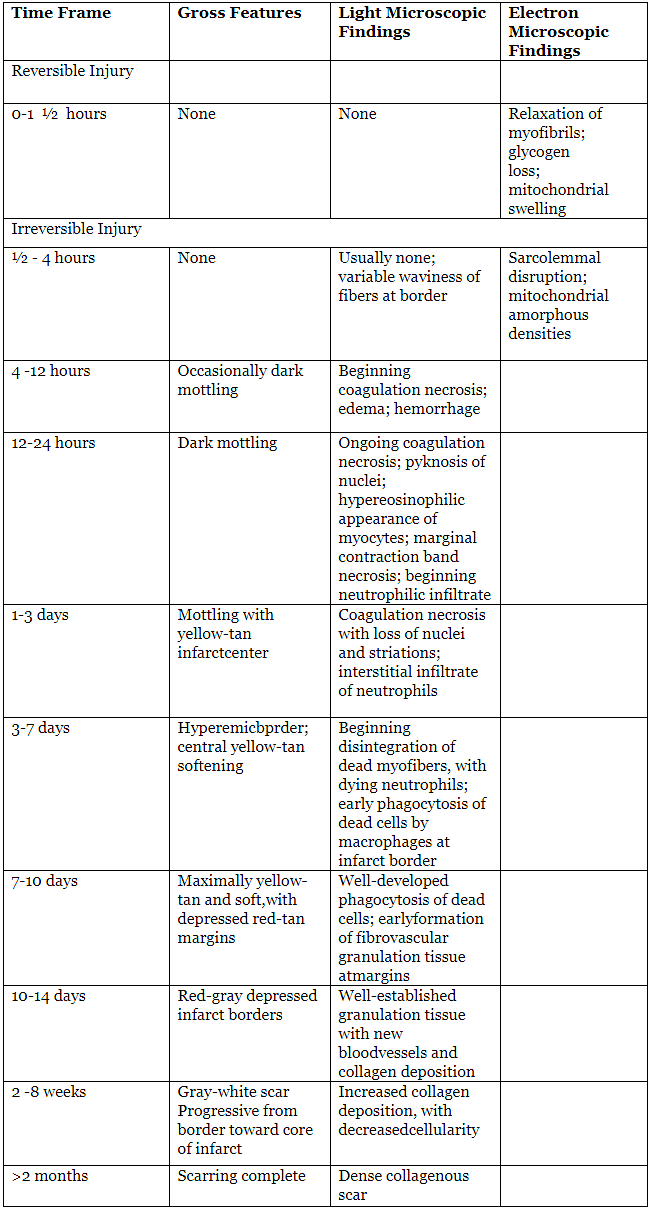
Question for Ischemic Heart Diseas (IHD)
Try yourself:
What is the main difference between stable and unstable plaques?View Solution
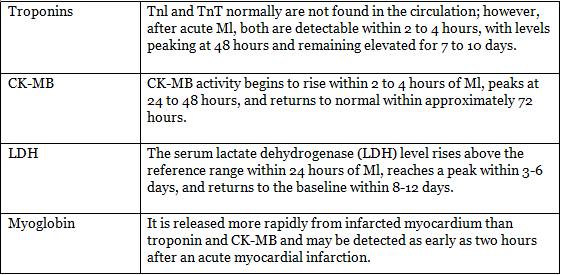
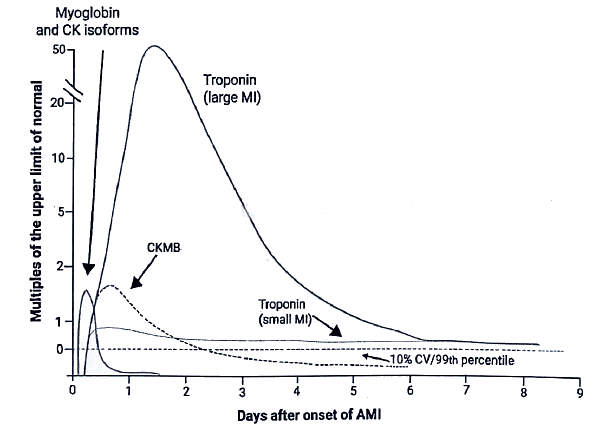
Lab Investigations in Ml
The laboratory assessment of myocardial infarction (MI) relies on measuring the blood levels of macromolecules that seep out of injured myocardial cells due to damaged cell membranes. These molecules encompass:
- Myoglobin
- Cardiac troponins T and I (TnT, TnI)
- Creatine kinase (CK), specifically the myocardial isoform, CK-MB
- Lactate dehydrogenase
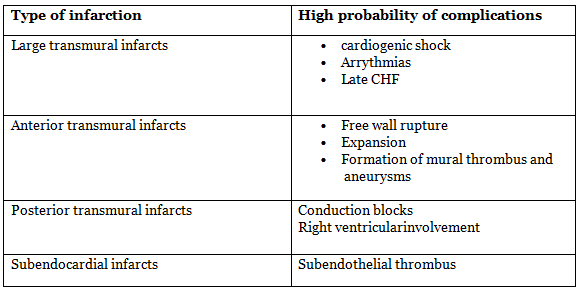
IHD - Complication
- Rupture of the myocardium
- Impaired contractile function
- Development of arrhythmias
- Onset of pericarditis
- Formation of ventricular aneurysm
- Dilatation of cardiac chambers leading to progressive late-stage heart failure (chronic IHD)
- Infarct expansion associated with mural thrombus
- Dysfunction of papillary muscles
- Involvement of the right ventricle
Question for Ischemic Heart Diseas (IHD)
Try yourself:
Which macromolecule is commonly used for the laboratory assessment of myocardial infarction (MI)?View Solution
In general, individuals experiencing anterior infarcts tend to have a more unfavorable clinical prognosis compared to those with posterior infarcts.
IHD - Repeats
- Discuss pathogenesis and pathology of ischemic heart disease (1999)
- Give the morphological changes and complications in myocardial infarction (2007).
- What are sequential myocardial changes in myocardial infarction?
Discuss the laboratory investigations in a case of myocardial infarction. (2016)
The document Ischemic Heart Diseas (IHD) | Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
7 videos|219 docs
|
FAQs on Ischemic Heart Diseas (IHD) - Medical Science Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is the difference between IHD and CAD? |  |
| 2. What are the common syndromes associated with IHD? |  |
Ans. The common syndromes associated with IHD include angina pectoris, myocardial infarction (heart attack), and silent ischemia. Angina pectoris is characterized by chest pain or discomfort due to reduced blood flow to the heart muscle. Myocardial infarction occurs when there is a complete blockage of a coronary artery, leading to the death of a part of the heart muscle. Silent ischemia refers to a lack of symptoms despite reduced blood flow to the heart.
| 3. What is the pathogenesis of IHD? |  |
Ans. The pathogenesis of IHD involves the development of atherosclerosis, which is the buildup of fatty deposits (plaques) within the walls of the coronary arteries. These plaques gradually narrow the arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart muscle. In some cases, a plaque can rupture, leading to the formation of a blood clot that further blocks the artery and causes a heart attack.
| 4. What are the complications of IHD? |  |
Ans. The complications of IHD include heart failure, arrhythmias, and sudden cardiac death. Heart failure can occur when the heart muscle becomes weakened due to reduced blood supply, leading to difficulties in pumping blood effectively. Arrhythmias refer to abnormal heart rhythms, which can range from mild palpitations to life-threatening irregularities. Sudden cardiac death is an unexpected loss of heart function, usually caused by a severe arrhythmia.
| 5. How is IHD diagnosed and treated? |  |
Ans. IHD is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, electrocardiogram (ECG), stress tests, cardiac catheterization, and imaging tests (such as angiography or CT scans). Treatment options for IHD include lifestyle modifications (such as quitting smoking and adopting a healthy diet), medications (such as antiplatelet drugs and beta-blockers), invasive procedures (such as angioplasty and stenting), and in severe cases, coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery. The choice of treatment depends on the severity and specific characteristics of the individual case.
Related Searches





















