Uttar Pradesh: Agriculture - 1 | Course for UPPSC Preparation - UPPSC (UP) PDF Download
Agriculture is the base of the economy of Uttar Pradesh. About 59.3% population of the state is engaged in the agricultural sector. The state produces about 19.87% of the foodgrains in the country. Thus, it stands at the first position at all India level in terms of foodgrains production.
The state produces majorly wheat, sugarcane, oilseeds, rice, potato, maize, barley, bajra and other crops. To monitor the agricultural activities, the state has Uttar Pradesh Council of Agricultural Research which is situated at Lucknow. Agricultural activities are also dependent on irrigation which minimises the dependency of crops on rainfall. In 2016-17, Uttar Pradesh is among the top three producers in India of crops like wheat, foodgrains, sugarcane, potato and rice.
Agro-Climatic Regions of Uttar Pradesh
The state of Uttar Pradesh is divided into 9 agro-climatic regions or zones on the basis of factors affecting the agriculture. These zones are discussed below:
- Bhabar and Terai Region It includes the regions of foothills of Himalayas, like Saharanpur, Muzaffarnagar, Bijnor, Moradabad, Rampur, Bareilly, Pilibhit, Lakhimpur-Kheri, Bahraich, Shravasti, etc.
- Central Western Plains It includes regions of Bareilly and Moradabad.
- Western Plains It includes Meerut division and its surrounding area.
- Southern-Western Semi-Arid Plain It includes Agra division and its surrounding area.
- Central Plain It includes Kanpur and Lucknow divisions and Fatehpur region.
- Bundelkhand Region It includes Jhansi and Chitrakoot divisions.
- Northern-Eastern Plain It includes Gorakhpur division and regions of Gonda.
- Eastern Plain It includes Varanasi, Faizabad, Azamgarh division and few areas of Allahabad division.
- Vindhya Region It includes regions of Mirzapur, Sonbhadra and Southern Allahabad.
Crop Production in Uttar Pradesh
The main types of crops in Uttar Pradesh are Rabi crops, Kharif crops and Zaid crops. These crops are briefly discussed below:
Rabi Crops
These crops are sown in winter season in October to December and harvested in months of February to April. These crops need less water and average temperature. Important rabi crops are wheat, barley, gram, masoor, potato, pulses, etc.
Some important rabi crops are given below:
Wheat
- It is produced in the largest part of the state in about 24% agricultural land.
- It is grown almost all over the state except the Northern hilly and Southern plateau regions.
- Uttar Pradesh ranks first in wheat production.
- Generally the crop needs 50 cm to 75 cm rainfall and during sowing period it needs 10° C to 15° C temperature.
- Ganga-Yamuna and Ganga-Ghaghara doab are the largest wheat producing areas in which Gorakhpur, Meerut, Bulandshahr, Saharanpur, Agra, Aligarh, Muzaffarnagar, Moradabad,Kanpur, Etawah, Farrukhabad and Fatehpur are the main producers of wheat.
- Due to high rainfall the Eastern and North-Eastern districts of Uttar Pradesh have low yield of wheat.
Gram
- It is the largest growing crop among all cereal crops in the state. It is grown in those regions where light loam soils and arid soils are found.
- It requires 30 cm to 50 cm rainfall and during sowing period, it requires 15°C to 25°C temperature.
- Banda, Hamirpur, Jhansi, Lalitpur, Jalaun, Mirzapur, Sonbhadra, Kanpur, Fatehpur, Sitapur, Barabanki, Allahabad and Agra are the main districts where gram is grown.
- Hamirpur is the largest producer of gram in the state.
Mustard
- It is the largest growing crop in the state among all the oilseeds crops.
- Uttar Pradesh is the second largest producer of mustard in India after Rajasthan.
- Mustard is grown independently or with a combination of other crops like wheat, peas and barley.
- Gonda, Bahraich, Mirzapur, Saharanpur, Sonbhadra, Kanpur, Sitapur, Etah, Meerut, Faizabad, Etawah, Sultanpur, Mathura, Aligarh and Bulandshahr are the main districts where mustard is grown.
Barley
- It is grown best in sandy and alluvial soils. It is a short growing season crop and has good drought tolerance.
- Its geographical conditions are as same as the wheat. Uttar Pradesh is the second largest producer of barley after Rajasthan.
- Varanasi, Azamgarh, Jaunpur, Ballia, Mau, Ghazipur, Gorakhpur, Etah, Allahabad and Pratapgarh are the districts where barley is grown.
Kharif Crops
The crops which are grown during the monsoon (rainy season) are called kharif crops. Seeds of the crops are sown in the beginning of the monsoon season (May to July). After maturation, these crops are harvested at the end of the monsoon season from September to October. These crops require high temperature and more water.
Important crops of this season are rice, cotton, jute, sugarcane, arhar, bajra, groundnut, maize, etc. Major crops of kharif season are discussed below:
Rice
- Uttar Pradesh ranks 2nd in India in the production of rice after West Bengal.
- Rice is sown on the 18% cultivable land in the state. It requires 20°C temperature during sowing period and 27°C temperature during harvesting period.
- It requires 75 cm to 125 cm rainfall. It requires clayey soil which is very fertile for this crop.
- It is grown in the Terai region which includes Shravasti, Maharajganj, Bahraich, Kushinagar, Deoria, Balrampur, Shahjahapur, Ballia, Pilibhit, Saharanpur, Mau, Varanasi and Lucknow districts. Rice is extensively grown in Shahjahanpur.
Jute
- It is a fibre crop which is grown in Terai Belt and Saryu and Ghaghara Doab.
- Bahraich, Maharajganj, Deoria, Gorakhpur, Gonda, Sitapur and Lakhimpur-Kheri are the major centres for the cultivation of jute.
- This crop is sown in April-May and harvested in August-September.
Sugarcane
It is the most important cash crop in the state. Uttar Pradesh ranks first in terms of production of sugarcane in the country.
It is sown on the 13% of the total cultivable land in the state. It requires 20°C to 26°C temperature, 100-200 cm rainfall and clayey loam soil. It is grown in two belts:
Terai Belt
It includes Rampur, Bareilly, Pilibhit, Sitapur, Lakhimpur-Kheri, Gonda, Faizabad, Azamgarh, Mau, Jaunpur, Basti, Ballia, Maharajganj, Deoria and Gorakhpur districts.
Ganga-Yamuna Doab
It includes Meerut, Muzaffarnagar, Ghaziabad, Bulandshahar, Aligarh, Saharanpur and Moradabad districts. Muzaffarnagar is the largest producer of sugarcane. Uttar Pradesh Council of Sugarcane Research was established in 1912 in Shahjahanpur.
Cotton
- It is grown in the state in the Ganga-Yamuna Doab, Rohilkhand and Bundelkhand regions with the help of irrigation.
- In these regions, different varieties of cotton are grown like UP Deshi, Bengal cotton, Punjab cotton, American cotton, etc.
- It is sown in June-July and harvested in October-November.
- It is grown along with maithi, mung and toria. Small fibre cotton is grown at large scale instead of large fibre cotton.
- Saharanpur, Muzaffarnagar, Meerut, Ghaziabad, Bulandshahar, Aligarh, Agra, Firozabad, Etawah, Kanpur, Rampur, Bareilly, Moradabad, Mathura, Mainpuri and Farrukhabad are some districts of the state where cotton is grown.
Arhar
- It is an important cereal crop in the state.
- Bajra and barley are sown along with this crop. Varanasi, Jhansi, Lalitpur, Allahabad, Hamirpur and Lucknow are the main districts where arhar pulses are grown.
- Hamirpur is the largest producer of arhar crop.
Bajra
- It is grown in arid climatic regions where rainfall is less than 50 cm.
- It is grown in May and July and harvested in September and December.
- It is produced by Agra, Aligarh, Moradabad, Mathura, Budaun, Firozabad, Etawah, Mainpuri, Kanpur, Ghazipur, Farrukhabad and Pratapgarh districts.
- Aligarh is the largest producer of bajra in the state.
Groundnut
- It is mainly grown in the districts of Sitapur, Hardoi, Etah, Badaun, Moradabad, etc on a small scale.
- The cultivation of groundnut takes more time due to arid climate. It needs sandy soil for growth.
- It is sown in June and July and harvested in November and December.
Maize
- Uttar Pradesh ranks third in the production of maize in India.
- It is a rainy crop. It is grown in the districts like Meerut, Ghaziabad, Bulandshahar, Farrukhabad, Gonda, Jaunpur, Etah, Firozabad and Mainpuri.
- It can be grown throughout the year. It is used for starch glucose and soft drinks.
- Mainpuri is the largest producer of maize in the state.
Zaid Crops
Zaid crops are sown between Rabi and Kharif crops. These are grown in March-April and harvested in June-July.
The zaid crops require warm dry weather for growth and longer day length for flowering. The main zaid crops are watermelon, muskmelon, bitter gourd, pumpkin, cucumber and seasonal fruits and vegetables.
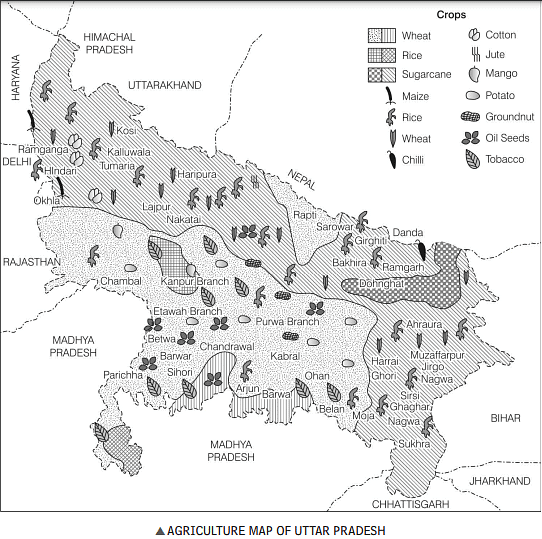
Other Crops of Uttar Pradesh
Other crops of Uttar Pradesh are as follows:
- Tea It is cultivated in Terai regions. The famous tea producing districts are Deoria, Siddharthnagar and Pilibhit.
- Opium Barabanki is the largest producer of opium in Uttar Pradesh. It is also produced in Ghazipur district. The only factory of opium is located in Ghazipur district.
- Linseed It is majorly produced in Mirzapur, Sonbhadra, Allahabad (Prayagraj), Gonda, Hamirpur, Bahraich, etc.
- Tobacco It is majorly produced in Meerut, Varanasi, Saharanpur, Ghaziabad, Bulandshahr and Mainpuri districts in Uttar Pradesh. It is used in smoking and eating.
To encourage the horticulture development, the State Government established Horticulture and Food Processing Department in 1974. India’s first Gardening Call Centre has been opened in Central Institute for Sub-Tropical Horticulture in Rehmankhera, Lucknow. State Food Processing Industrial Institution is located at Lucknow. Important horticultural crops are discussed below:
 |
Download the notes
Uttar Pradesh: Agriculture - 1
|
Download as PDF |
Fruit Production
- Mango
It is produced in Central and Western districts of Uttar Pradesh like Lucknow, Bareilly, Meerut, Ghaziabad, Kanpur, Saharanpur and Hardoi. Dasheri, Langra and Safeda are the famous varieties of Malihabadi mango in Lucknow. The mango crop which is produced in the state is known as ‘Nawab Aam’. - Guava
It is grown in Allahabad, Bareilly and Faizabad districts of Uttar Pradesh. Safeda, Dholka, Halfji Lucknow and Karela Allahabad are the main varieties of guava. - Banana
It is produced at a large scale in Varanasi, Allahabad, Gorakhpur and Kaushambi districts of the state. It requires fertile soil, heavy rain and high temperature. Few varieties are Mal-Bhog Chini, Champa, Alfan, Adheshwar, Dudhsagar and Sabja. The first ripening chamber of Uttar Pradesh is set up in Allahabad through which farmers can be benefitted by ripening their raw banana crop. - Lemon
It is produced mainly in the Bundelkhand region and generally all over the state. - Papaya
It is grown in Saharanpur, Unnao, Lucknow and Faizabad districts in the state. - Watermelon
It is a kharif crop. It is grown in Ganga, Saryu, Gomati river valleys in the state. - Orange
It is grown in Saharanpur and Bundelkhand region. The Desi Nagpuri, Empdar and Laddu varieties of orange are grown in this district. - Malta
Meerut, Varanasi and Saharanpur are the main malta producing districts of Uttar Pradesh. Mausammi and blood red are some varieties of malta. - Lichi
It is grown in Saharanpur and Meerut districts in the state. - Shaftalu
It is grown in Western part of the state and in Lucknow district. - Amla/Indian Gooseberry
Amla has medicinal values. The Indian climate is considered best in Asia for the growthof this crop. It is a cash crop in Uttar Pradesh. Pratapgarh is the largest producer of Amla crop. The other producing districts are Raebareli, Sultanpur and Jaunpur.
Vegetables and Spices Productions
Potato
- Uttar Pradesh ranks first in the production of potato. It produces around 40% potato in the country.
- The best quality of potato produced in vast farms in Agra, Firozabad, Aligarh, Hathras and Mathura districts. Production of potato is also very high in Farrukhabad, Kannauj, Etawah, Kanpur, Meerut, Hapur, Budaun and Rampur.
- Central Potato Research Institute is located in Meerut.
- The state has three agricultural export zones, namely, Lucknow, Saharanpur and Agra, in which Agra has been established for potato export. The potato of this zone is known as Taj Brand.
- Aaloo Vikas Neeti, 2014 has been implemented in the state. The main objective of this scheme is to provide liable rate to potato farmers of their products and for overall development of potato farming. The other main objectives of this scheme are as follows:
- To promote production of quality potato.
- To promote advanced technology of potato farming.
- To assure the stores for seeds and potato in state.
- Promotion of marketing and export of potato out of state.
- To promote potato based processing industry establishment.
- Skill development and technical transfer of scientific methods to farmers for production.
Turmeric and Ginger
- Uttar Pradesh ranks first in the production of turmeric and ginger in India. Turmeric and ginger are mainly grown in Bundelkhand region.
Onion and Garlic
- Both of these crops are mainly produced in Farrukhabad, Budaun, Mainpuri, Etawah, Kannauj, Etah, Firozabad, etc.
Coriander and Aniseed
- Both of these crops are produced in Deoria, Gorakhpur, Kushinagar, Azamgarh, Mau, Jaunpur, Sultanpur, Ambedkar Nagar and Faizabad districts in the state.
Floriculture in Uttar Pradesh
- In Uttar Pradesh, flower production is done in Varanasi, Lucknow, Allahabad (Prayagraj), Mirzapur and Jaunpur districts.
- In Kannauj district, flowers are used to produce perfumes. Lucknow is one of the nine ideal flower producing centres in the country.
Medical and Scented Plant Production
- The state produces some important medical and scented plants like Alovera, Basil, Satawari, Sarpgandha, Shankhpushpi, Arjun, Khus, etc.
- Mentha plant is similar to mint plant. Mentha oil is extracted from its leaves which are used for medicines and other products.
- It is produced in Western districts like Barabanki, Budaun, Rampur, Kannauj, Jalaun, Auraiya, Etawah and Etah districts.
- Uttar Pradesh produces around 90% mentha oil of the country. Mentha oil industry has been established in Rampur, Budaun and Barabanki districts.
- Under Herbal Garden scheme, the State Government is going to establish Herbal Garden in many districts of the state like Gorakhpur, Varanasi, Mathura, Ballia, Jhansi, Gonda, Hardoi, Maharajganj, etc.
Betal Production
- Betal is produced in the state in 21 districts like Mahoba, Banda, Unnao, Pratapgarh, Sultanpur, Raebareli, Ballia, Lucknow, Hardoi, Gorakhpur, Azamgarh, Barabanki, Kanpur, etc. The Betal Research and Training Centre was established in 1981 in Mahoba.
- Mahoba, Barinanpur of Banda district and Pali region of Lalitpur district are famous for betal production.
- Mahoba Deshawari, Kalkatiya Kapuri Bangla, Magahi Sanchi, Banarasi, Sophiya, Ramtek and Mitha are main varieties of betal plant.
Jatropha
- Oil extracted from the seed of Jatropha is used as an alternating of diesel oil. Thus, Uttar Pradesh Government is giving main emphasis on its production.
- Jatropha Cloning Garden Scheme is being implemented by Biotech Park at Bakshi Ka Talab region in the state.
List of Important Horticultural Crops of Uttar Pradesh
- Mango - Kanpur, Lucknow,Bareilly, Meerut, Ghaziabad, Saharanpur, Hardoi
- Banana - Varanasi, Gorakhpur, Allahabad
- Guava - Kausambi, Allahabad, Bareilly, Unnao, Faizabad
- Lichi - Saharanpur, Meerut
- Malta - Varanasi, Meerut, Saharanpur
- Papaya - Saharanpur, Unnao, Lucknow, Faizabad
- Saftalu/Peach - Western district of Uttar Pradesh, Lucknow
- Watermelon - Valley of Ganga, Gomti, Saryu river
- Orange - Saharanpur, Bundelkhand regions
- Lemon - Saharanpur, Meerut, Bundelkhand, Eastern regions
- Turmeric - Bundelkhand region
- Ginger - Bundelkhand region
- Flowers - Varanasi, Kannauj, Mirzapur, Jaunpur, Allahabad, Lucknow
- Mentha - Barabanki, Auraiya, Etawah, Rampur, Kannauj, Jalaun, Budaun
|
113 videos|360 docs|105 tests
|























