UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC > Factors that Affect Reaction Rates
Factors that Affect Reaction Rates | Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Concentration Effects |

|
| Temperature Effects |

|
| Phase and Surface Area Effects |

|
| Solvent Effects |

|
| Catalyst Effects |

|
Introduction
- There are many factors that influence the reaction rates of chemical reactions include the concentration of reactants, temperature, the physical state of reactants and their dispersion, the solvent, and the presence of a catalyst.
- Although a balanced chemical equation for a reaction describes the quantitative relationships between the amounts of reactants present and the amounts of products that can be formed, it gives us no information about whether or how fast a given reaction will occur.
- This information is obtained by studying the chemical kinetics of a reaction, which depend on various factors: reactant concentrations, temperature, physical states and surface areas of reactants, and solvent and catalyst properties if either are present. By studying the kinetics of a reaction, chemists gain insights into how to control reaction conditions to achieve a desired outcome.
Concentration Effects
- Two substances cannot possibly react with each other unless their constituent particles (molecules, atoms, or ions) come into contact. If there is no contact, the reaction rate will be zero.
- Conversely, the more reactant particles that collide per unit time, the more often a reaction between them can occur. Consequently, the reaction rate usually increases as the concentration of the reactants increases.
Question for Factors that Affect Reaction RatesTry yourself: What is one of the factors that can influence the reaction rate of a chemical reaction?View Solution
Temperature Effects
- Increasing the temperature of a system increases the average kinetic energy of its constituent particles. As the average kinetic energy increases, the particles move faster and collide more frequently per unit time and possess greater energy when they collide. Both of these factors increase the reaction rate. Hence the reaction rate of virtually all reactions increases with increasing temperature.
- Conversely, the reaction rate of virtually all reactions decreases with decreasing temperature. For example, refrigeration retards the rate of growth of bacteria in foods by decreasing the reaction rates of biochemical reactions that enable bacteria to reproduce.
- In systems where more than one reaction is possible, the same reactants can produce different products under different reaction conditions. For example, in the presence of dilute sulfuric acid and at temperatures around 100°C, ethanol is converted to diethyl ether:

- At 180°C, however, a completely different reaction occurs, which produces ethylene as the major product:

Phase and Surface Area Effects
- When two reactants are in the same fluid phase, their particles collide more frequently than when one or both reactants are solids (or when they are in different fluids that do not mix). If the reactants are uniformly dispersed in a single homogeneous solution, then the number of collisions per unit time depends on concentration and temperature, as we have just seen.
- If the reaction is heterogeneous, however, the reactants are in two different phases, and collisions between the reactants can occur only at interfaces between phases. The number of collisions between reactants per unit time is substantially reduced relative to the homogeneous case, and, hence, so is the reaction rate. The reaction rate of a heterogeneous reaction depends on the surface area of the more condensed phase. Automobile engines use surface area effects to increase reaction rates.
- Gasoline is injected into each cylinder, where it combusts on ignition by a spark from the spark plug. The gasoline is injected in the form of microscopic droplets because in that form it has a much larger surface area and can burn much more rapidly than if it were fed into the cylinder as a stream. Similarly, a pile of finely divided flour burns slowly (or not at all), but spraying finely divided flour into a flame produces a vigorous reaction.
Question for Factors that Affect Reaction RatesTry yourself: How does the nature of the solvent affect the reaction rates of solute particles?View Solution
Solvent Effects
- The nature of the solvent can also affect the reaction rates of solute particles. For example, a sodium acetate solution reacts with methyl iodide in an exchange reaction to give methyl acetate and sodium iodide.
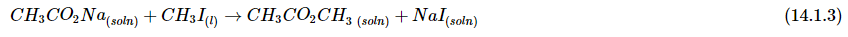
- This reaction occurs 10 million times more rapidly in the organic solvent dimethylformamide [DMF; (CH3)2NCHO] than it does in methanol (CH3OH). Although both are organic solvents with similar dielectric constants (36.7 for DMF versus 32.6 for methanol), methanol is able to hydrogen bond with acetate ions, whereas DMF cannot. Hydrogen bonding reduces the reactivity of the oxygen atoms in the acetate ion.
- Solvent viscosity is also important in determining reaction rates. In highly viscous solvents, dissolved particles diffuse much more slowly than in less viscous solvents and can collide less frequently per unit time. Thus the reaction rates of most reactions decrease rapidly with increasing solvent viscosity.
Catalyst Effects
- A catalyst is a substance that participates in a chemical reaction and increases the reaction rate without undergoing a net chemical change itself. Consider, for example, the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide in the presence and absence of different catalysts.
- Because most catalysts are highly selective, they often determine the product of a reaction by accelerating only one of several possible reactions that could occur. Most of the bulk chemicals produced in industry are formed with catalyzed reactions.
- Recent estimates indicate that about 30% of the gross national product of the United States and other industrialized nations relies either directly or indirectly on the use of catalysts.
Question for Factors that Affect Reaction RatesTry yourself: What factor influences the reaction rate of a chemical reaction?View Solution
The document Factors that Affect Reaction Rates | Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
FAQs on Factors that Affect Reaction Rates - Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What are concentration effects in relation to reaction rates? |  |
Concentration effects refer to the impact of the reactant concentration on the rate of a chemical reaction. Increasing the concentration of reactants generally leads to a higher reaction rate. This is because a higher concentration means that there are more reactant particles available to collide and react, increasing the chances of successful collisions. Conversely, decreasing the concentration of reactants will result in a slower reaction rate.
| 2. How does temperature affect reaction rates? |  |
Temperature has a significant effect on reaction rates. Generally, increasing the temperature increases the rate of a chemical reaction. This is because higher temperatures provide more kinetic energy to the reactant particles, leading to more frequent and energetic collisions. The increased collision frequency and energy increase the likelihood of successful collisions and, therefore, the reaction rate. On the other hand, decreasing the temperature slows down the reaction rate.
| 3. What is the role of phase and surface area in affecting reaction rates? |  |
The phase and surface area of reactants can greatly impact reaction rates. When reactants are in different phases, such as a solid and a gas, the rate of reaction is typically slower compared to when both reactants are in the same phase, such as gas-gas or liquid-liquid reactions. This is because intermolecular collisions are less frequent between particles in different phases.
Additionally, the surface area of solid reactants plays a crucial role. Increasing the surface area of solid reactants, such as by grinding or crushing them into smaller particles, exposes more reactant particles to the surrounding medium. This increases the frequency of collisions and, consequently, the reaction rate.
| 4. How do solvents affect reaction rates? |  |
Solvents can significantly affect reaction rates, especially in reactions involving dissolved reactants. Solvents provide a medium for the reactant particles to move and interact. The choice of solvent can impact the reaction rate due to factors such as solubility, polarity, and viscosity.
A solvent that enhances the solubility and mobility of reactant particles can increase the reaction rate. This is because more dissolved reactant particles are available for collisions. Additionally, a solvent with a suitable polarity can facilitate the formation of transition states and intermediate species, leading to a faster reaction rate.
| 5. What is the role of catalysts in affecting reaction rates? |  |
Catalysts play a crucial role in affecting reaction rates by providing an alternative reaction pathway with lower activation energy. They increase the rate of a reaction without being consumed in the process. Catalysts achieve this by providing an alternative mechanism that requires less energy for the reactant molecules to reach the transition state.
By lowering the activation energy, catalysts increase the likelihood of successful collisions and, thus, the reaction rate. They can also stabilize intermediate species and facilitate the breaking and formation of chemical bonds. Catalysts can significantly speed up reactions and are extensively used in various industrial processes.
Related Searches



















