State Public Service Commision - UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Composition |

|
| Removal |

|
| Functions |

|
| Limitations |

|
| Joint State Public Service Commission (JSPSC) |

|
| Joint State Public Service Commission |

|
The State Public Service Commission, as defined in Article 315-323 of the Indian Constitution, is an administrative body unique to every state of India. Its primary role is to conduct examinations and interviews to recruit candidates for various services within the state's civil administration.
Each State Public Service Commission operates independently, ensuring recruitment processes adapt to the specific needs of each state. Although operating independently, SPSCs follow a structure and set of rules similar to the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC), maintaining an effective standardization of public service recruitment processes across the country.
 State Public Service Commission
State Public Service Commission
Composition
A State Public Service Commission comprises a chairman and members appointed by the state governor.
Flexibility in Commission Size: The Constitution does not specify the commission's size, leaving it to the governor's discretion.
Qualifications and Service Experience: No specific qualifications are mandated, but at least half of the members should have a minimum of 10 years of service under either the government of India or a state government.
Governor's Role in Service Conditions: The governor is responsible for determining the conditions of service for the chairman and members.
Governor's Authority for Commission Staff: The governor has the authority to establish provisions for the number of commission staff and their service conditions.
Term and Age Limit: The chairman and members hold office for 6 years or until reaching the age of 62 (65 for the UPSC), whichever comes first.

Removal
- Appointment and Authority: The chairman and members of a State Public Service Commission (SPSC) are appointed by the governor, but the authority to remove them lies solely with the President, not the governor.
- Grounds for Removal: Removal can take place on grounds similar to those for the UPSC chairman or members, including being declared insolvent, engaging in paid employment outside official duties, or being deemed unfit by the President due to mental or physical infirmity.
- Misbehaviour and Supreme Court Inquiry: In such cases, the President must refer the matter to the Supreme Court for an inquiry. If the Supreme Court upholds the cause of removal, the President can proceed with removal, and the Court's advice is binding.
- Specified Misbehaviour: The Constitution specifies that misbehaviour includes being concerned or interested in any contract or agreement made by the Government of India or a state government, or participating in the profit or benefit of such contracts, except as a member of an incorporated company alongside other members.
- Governor's Authority During Inquiry: During the Supreme Court's inquiry, the governor has the authority to suspend the concerned chairman or member until the President issues the final removal order upon receiving the Court's report.
Functions
- Conducting Examinations: The SPSC conducts examinations to facilitate appointments to various state services.
- Advisory Role: The SPSC serves as an advisory body, offering guidance on crucial matters such as:
- Methods of recruitment for civil services and posts.
- Principles guiding appointments, promotions, transfers, and the assessment of candidates' suitability.
- Disciplinary issues involving individuals in civil service, including related petitions.
- Claims for reimbursement of legal expenses incurred by civil servants in defending legal proceedings related to official duties.
- Claims for pension awards related to injuries sustained during service, including the determination of award amounts.
Key Role of the State Public Service Commission (SPSC)
The SPSC is also known as the ''Watchdog of the Merit System''
Functional Scope of SPSC:
- Recruitment Focus
- Advisory Role in Promotion and Disciplinary Matters
Administrative Division of Responsibilities:
- Department of Personnel and General Administration Department
Advisory Nature of SPSC Recommendations:
- Advisory Status
- Government's Discretion and Rule Regulation
Influence of State Vigilance Commission (SVC):
- Impact on Disciplinary Matters
- SPSC's Advantage as an Independent Constitutional Body
Governor's Consultation for Judicial Service Appointments:
- SPSC's Role in Judicial Service Appointments
- Consultation with the High Court
Limitations
- Exclusion of Matters from SPSC Jurisdiction: Certain matters are excluded from the functional jurisdiction of the SPSC. In other words, the SPSC is not consulted on the following issues:
Reservations and Backward Classes:
- While reserving appointments or posts in favour of any backward class of citizens.
Consideration of Claims:
- When considering the claims of scheduled castes and scheduled tribes in making appointments to services and posts.
2. Governor's Authority to Exclude: The governor has the authority to exclude posts, services, and matters from the purview of the SPSC. According to the Constitution, the governor, concerning state services and posts, can create regulations specifying matters where consultation with the SPSC is not necessary.
3. Legislative Oversight: All such regulations made by the governor must be presented before each House of the state legislature for a minimum of 14 days. The state legislature holds the power to amend or repeal these regulations.
Joint State Public Service Commission (JSPSC)
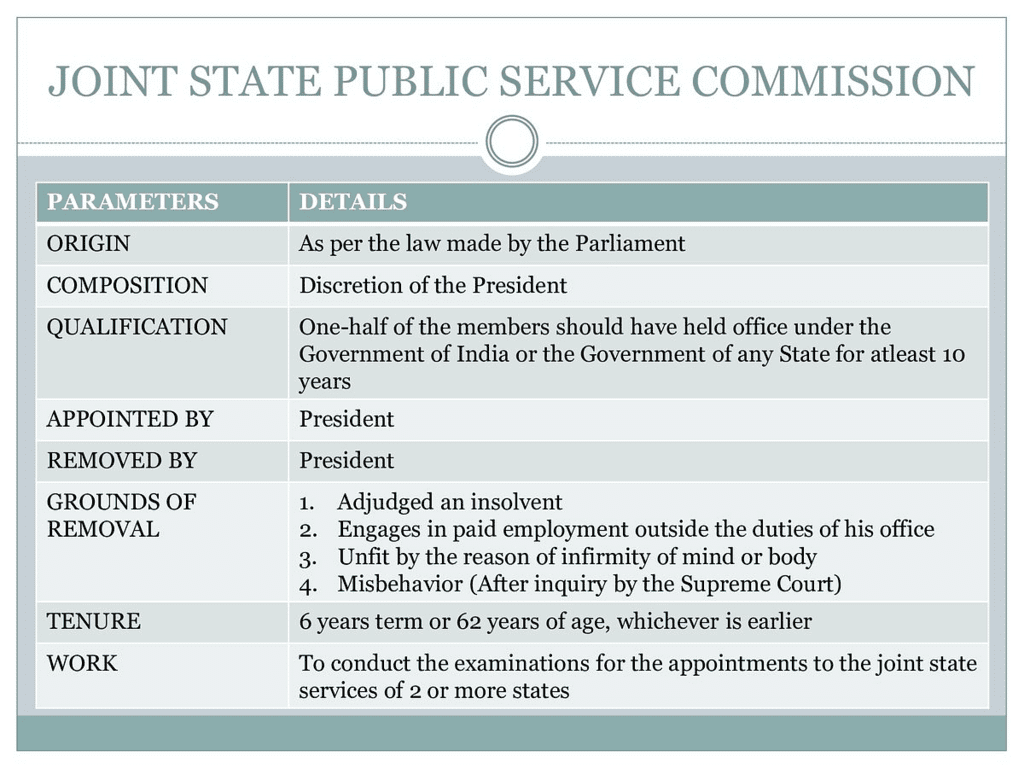 Joint State Public Service Commission
Joint State Public Service Commission
Constitutional Provision :
- The Constitution allows for the establishment of a Joint State Public Service Commission (JSPSC) to serve two or more states.
Statutory Nature :
- Unlike the UPSC and SPSC directly created by the Constitution, a JSPSC is formed through an act of Parliament upon the request of the concerned state legislatures. Consequently, a JSPSC is a statutory, not a constitutional, body.
Appointment and Tenure:
- The chairman and members of a JSPSC are appointed by the President and hold office for a term of six years or until they reach the age of 62, whichever comes earlier.
Authority of the President:
- The President has the authority to suspend or remove JSPSC members, and they can also resign by submitting their resignation letters to the President.
Determination of Membership and Conditions:
- The President determines the number of JSPSC members and their conditions of service.
Reporting and Accountability:
- A JSPSC submits its annual performance report to the governors of the concerned states, and each governor presents the report before the respective state legislature.
FAQs on State Public Service Commision - UPSC
| 1. What is the composition of the State Public Service Commission (SPSC)? |  |
| 2. What is the role of the State Public Service Commission (SPSC)? |  |
| 3. How does the removal process of the State Public Service Commission (SPSC) work? |  |
| 4. What are the functions of the State Public Service Commission (SPSC)? |  |
| 5. What are the limitations of the State Public Service Commission (SPSC)? |  |














