Woodward-Fieser Rules: Conjugated Carbonyl Compounds | Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Woodward-Fieser Rules for Calculating the λmax of Conjugated Carbonyl Compounds |

|
| Core Chromophores With Base Values |

|
| Substituent Effects |

|
| Other Contributors |

|
Introduction
- As we have seen earlier in the chapter of Principle of UV-Vis Spectroscopy, absorption of a particular wavelength of light depends upon the π-electron system of the molecule. The more the conjugation of the π-electron system within the molecule, the higher the wavelength of light it can absorb.
- Robert Burns Woodward and Louis Fieser put down a set of rules which allows one to calculate the wavelength of maximum absorption (λmax) for a molecule empirically. These sets of rules to calculate the wavelength of maximum absorption or λmax of a compound in the ultraviolet-visible spectrum, based empirically have been called the Woodward-Fieser rules or Woodward’s-rules.
- These sets of article aims to guide the student on how to use these rules to calculate the wavelength of maximum absorption or λmax for different systems.
Woodward-Fieser Rules for Calculating the λmax of Conjugated Carbonyl Compounds
Woodward-Fieser rules can be extended to calculate the λmax of α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds. There is base value to which the substituent effects can be added and the λmax can be calculated using the formula:
λmax = Base value + Σ Substituent Contributions + Σ Other Contributions
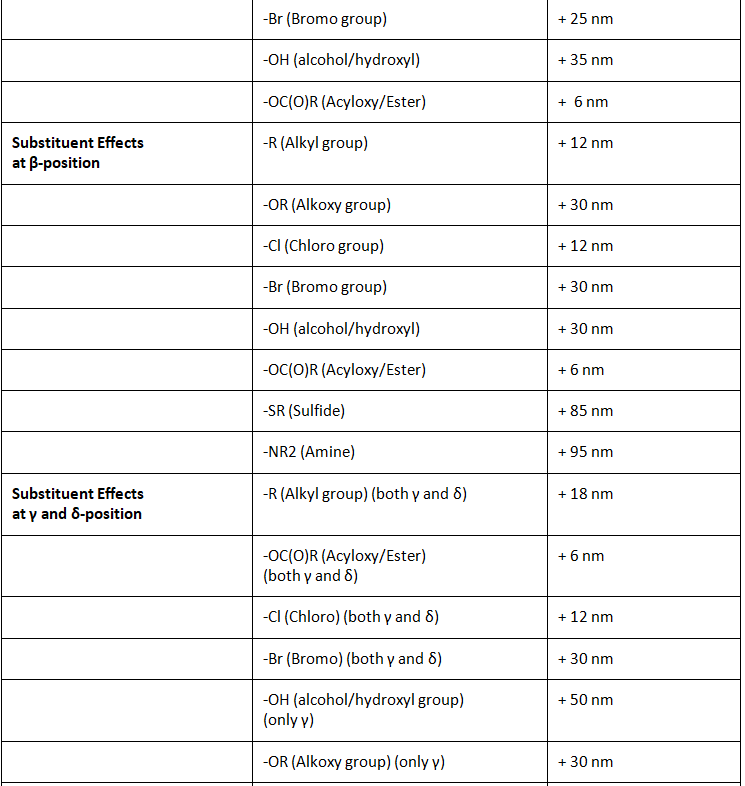
Table 2: Gives the values for the influence of different chromophores in conjugated carbonyl systems as per Woodward-Fieser rules. The usage of these will become more evident in the examples which follow.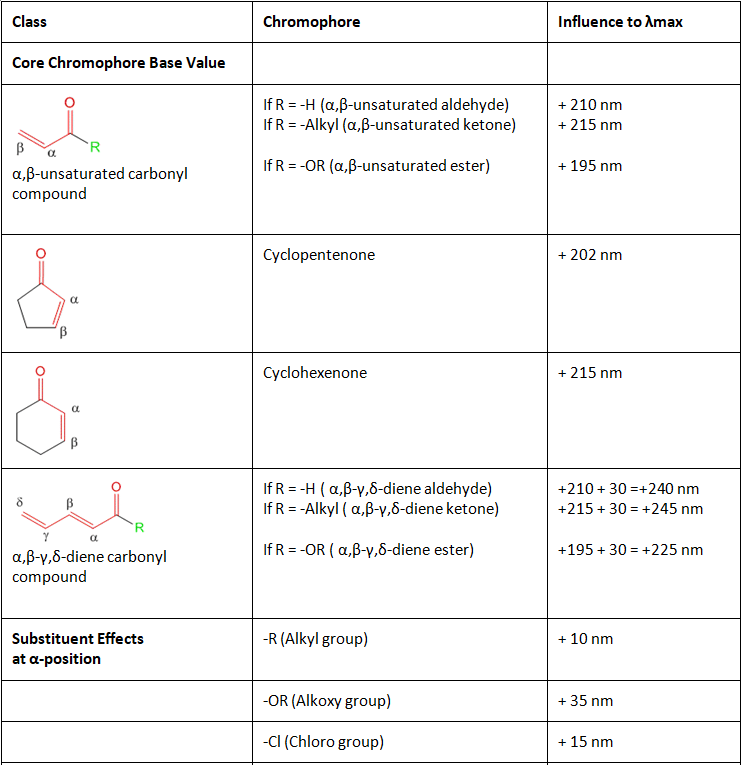

Let us discuss each of the above values and when to apply them in greater detail with examples:
Core Chromophores With Base Values
- As Woodward and Fieser have listed, α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds have a range of influence on the λmax of the molecule depending upon:
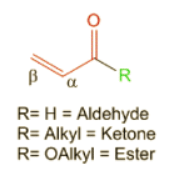
- The type of carbonyl functionality present. For example, α,β-unsaturated aldehyde contribute 210 nm while α,β-unsaturated ketones contribute 215 nm and α,β-unsaturated esters contribute 195 nm.
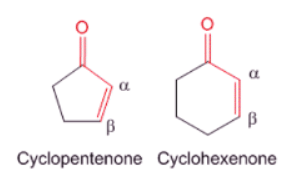
- If the core is a part of a cyclic ring. For example, cyclopentenone contribution is 202 nm while cyclohexenone is 215 nm.
- If the conjugation is extended to γ,δ-positions to form dienes. For example, in such cases, a simple addition of 30 nm to the base value of the α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound gives appropriate estimates to the observed influences.
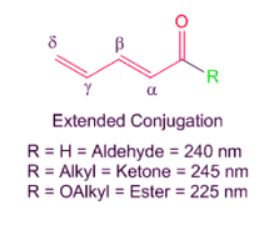
Note: In cases of α,β-γ,δ-diene carbonyl compounds like those shown above, the extended conjugation at the α,β-γ,δ-positions is accounted for in the base value of the core chromophore and need not be added separately. If however there is another substituent at the α,β-γ,δ-positions, then you must add an additional + 30 nm for each. Also the bond shown as β-γ is not counted as β substituent but as a part of the core chromophore and need not be added separately.
Substituent Effects
According to Woodward, in case of α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds, the location of the substituent is significant in determining the influence on the wavelength of maximum absorption. Substituents can be located on either α,β positions. If the conjugation is extended to γ and δ positions, then substitutions at these position also play a vital role in determining the practical λmax.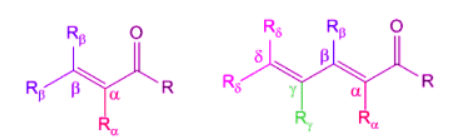
Substituents at α-Position
As we can see the from table 3 below the effect of different substituent when placed on the α-position.
Table 3: Effect of substituents on the α-position of α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds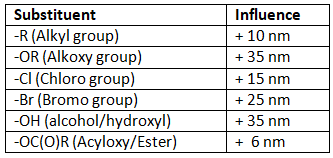
Substituents at β-Position
As we can see the from table 4 below the effect of different substituent when placed on the β-position.
Table 4: Effect of substituents on the β-position of α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compounds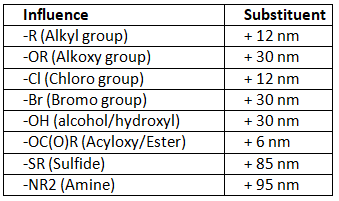
Substituents at γ and δ-position
As we can see the from table 5 below the effect of different substituent when placed on the γ or δ position.
Table 5: Effect of substituents on the γ or δ position of α,β-γ,δ-diene carbonyl compound.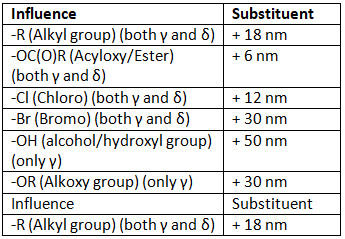
Other Contributors
Exocyclic Double Bonds
In general exocyclic double bonds add an additional + 5 nm to the base value. In order to identify exocyclic double bonds how to use Woodward-Fieser rules to calculate the λmax of conjugated dienes and polyenes. We have explained it extensively there.
Solvent Effects
Since carbonyl functional groups have polarity, solvents play an important role in how the electronics of the structure play out. The rules are simple and straight forward: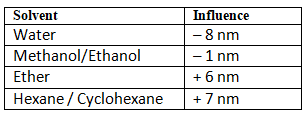
Homoannular Cyclohexadiene
In a special case where you have α,β-γ,δ-diene carbonyl compound and both the double bonds are present within one ring system you get a homoannular or homocyclic cyclohexadiene carbonyl compound. In such a case you must add an additional 35 nm to the system.
FAQs on Woodward-Fieser Rules: Conjugated Carbonyl Compounds - Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What are the Woodward-Fieser rules? |  |
| 2. How do the Woodward-Fieser rules calculate the λmax of conjugated carbonyl compounds? |  |
| 3. What are core chromophores in conjugated carbonyl compounds? |  |
| 4. How do substituents affect the λmax of conjugated carbonyl compounds? |  |
| 5. What are the applications of the Woodward-Fieser rules in organic chemistry? |  |














