JEE Mains Previous Year Questions (2025)): Laws of Motion | Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
[JEE Mains MCQs]
Q1: Two bodies of masses m1 = 5 kg and m2 = 3 kg are connected by a light string going over a smooth light pulley on a smooth inclined plane as shown in the figure. The system is at rest. The force exerted by the inclined plane on the body of mass m1 will be : [Take g = 10 ms-2]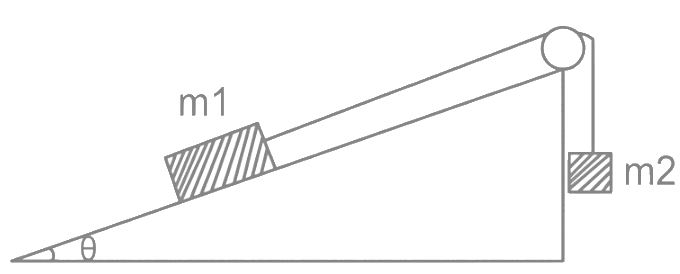 (a) 30 N
(a) 30 N
(b) 40 N
(c) 50 N
(d) 60 N
Ans: (b)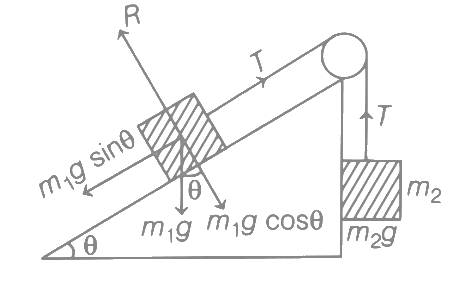 Force on equilibrium, m2g = m1g sinθ
Force on equilibrium, m2g = m1g sinθ
Normal force on m1, R = m1 g cos θ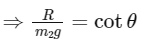
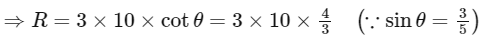
⇒ R = 40 N
Q2: A uniform metal chain of mass m and length 'L' passes over a massless and frictionless pulley. It is released from rest with a part of its length 'l' is hanging on one side and rest of its length 'L − l' is hanging on the other side of the pully. At a certain point of time, when 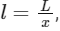 the acceleration of the chain is g/2 . The value of x is __________.
the acceleration of the chain is g/2 . The value of x is __________.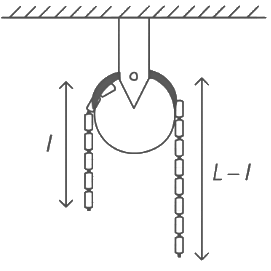 (a) 6
(a) 6
(b) 2
(c) 1.5
(d) 4
Ans: (d)
From newton's laws of motion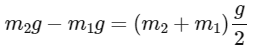
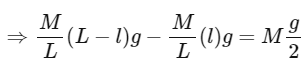
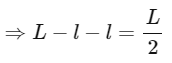
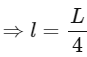
Q3: A block of mass M slides down on a rough inclined plane with constant velocity. The angle made by the incline plane with horizontal is θ. The magnitude of the contact force will be:
(a) mg
(b) Mg cos θ
(c) 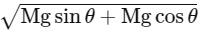
(d) 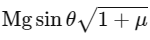
Ans: (a)
As the body is moving with constant velocity so forces acting on the body must be balanced.
⇒ Contact force from incline should balance weight of the body.
⇒ | Fcontact | = Mg
Q4: A block 'A' takes 2 s to slide down a frictionless incline of 30∘ and length 'l', kept inside a lift going up with uniform velocity 'v'. If the incline is changed to 45∘ , the time taken by the block, to slide down the incline, will be approximately:
(a) 2.66 s
(b) 0.83 s
(c) 1.68 s
(d) 0.70 s
Ans: (c)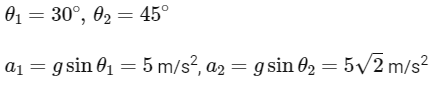
Q5: A bag is gently dropped on a conveyor belt moving at a speed of 2 m/s. The coefficient of friction between the conveyor belt and bag is 0.4 . Initially, the bag slips on the belt before it stops due to friction. The distance travelled by the bag on the belt during slipping motion, is : [Take g = 10 m/s−2]
(a) 2 m
(b) 0.5 m
(c) 3.2 m
(d) 0.8 ms
Ans: (b)
Speed of conveyor belt, v = 2 m / s
Coefficient of friction between the conveyor belt and bag, μ = 0.4
Acceleration of bag due to slipping motion,
a = μg = 0.4 × 10 = 4 m/s2 (∵ g = 10 m/s2)
If s be the distance travelled by the bag on the belt during slipping motion, then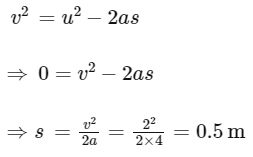
Q6: Two masses M1 and M2 are tied together at the two ends of a light inextensible string that passes over a frictionless pulley. When the mass M2 is twice that of M1 , the acceleration of the system is a1. When the mass M2 is thrice that of M1 , the acceleration of the system is a2. The ratio a1/a2 will be: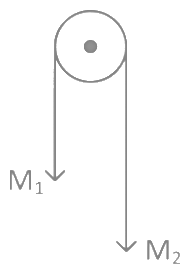 (a) 1/3
(a) 1/3
(b) 2/3
(c) 3/2
(d) 1/2
Ans: (b)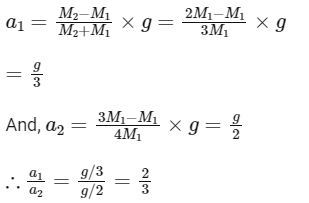
Q7: Three masses M = 100 kg , m1 = 10 kg and m2 = 20 kg are arranged in a system as shown in figure. All the surfaces are frictionless and strings are inextensible and weightless. The pulleys are also weightless and frictionless. A force F is applied on the system so that the mass m2 moves upward with an acceleration of 2 ms−2. The value of F is : (Take g = 10 ms−2)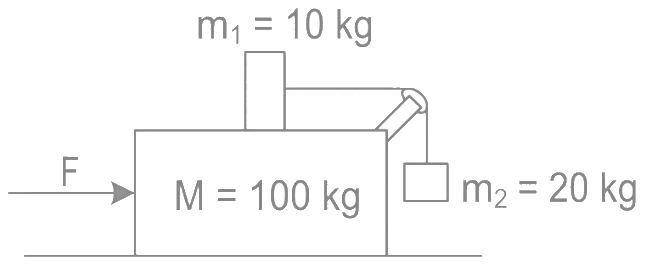 (a) 3360 N
(a) 3360 N
(b) 3380 N
(c) 3120 N
(d) 3240 N
Ans: (c)
In frame of block of mass M moving with acceleration a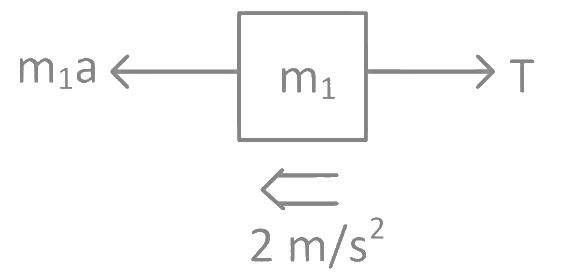
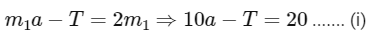
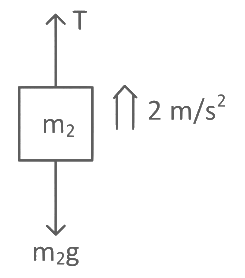
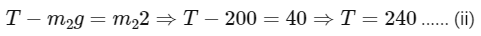
⇒ From equation 1 and 2 10a = 260 or a = 26 m/s2 for block
F (M + m2)a = 120 × 26
= 3120 N
Q8: A monkey of mass 50 kg climbs on a rope which can withstand the tension (T) of 350 N . If monkey initially climbs down with an acceleration of 4 m/s2 and then climbs up with an acceleration of 5 m/s2. Choose the correct option (g = 10 m/s2) .
(a) T = 700 N while climbing upward
(b) T = 350 N while going downward
(c) Rope will break while climbing upward
(d) Rope will break while going downward
Ans: (c)
Tdown = 50 × (10 − 4)
= 50 × 6
= 300 N
Tup = 50 × (10 + 5)
= 50 × 15
= 750 N
⇒ Rope will break while climbing up.
Q9: For a free body diagram shown in the figure, the four forces are applied in the 'x' and 'y' directions. What additional force must be applied and at what angle with positive x-axis so that the net acceleration of body is zero?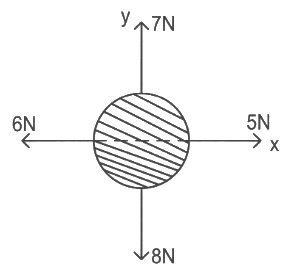 (a) √2 N, 45∘
(a) √2 N, 45∘
(b) √2 N, 135∘
(c) 2/√3 N, 30∘
(d) 2N, 45∘
Ans: (a)
Resultant of already applied forces 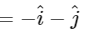
⇒ Force required to balance 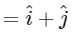
⇒ Force required = √2 N in magnitude at angle 45∘ with +ve x-axis
Q10: A 2 kg block is pushed against a vertical wall by applying a horizontal force of 50 N. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the wall is 0.5. A force F is also applied on the block vertically upward (as shown in figure). The maximum value of F applied, so that the block does not move upward, will be:
(Given : g = 10 ms−2)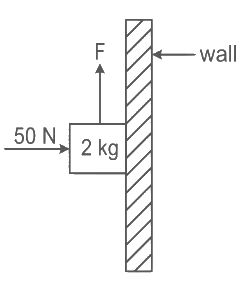 (a) 10 N
(a) 10 N
(b) 20 N
(c) 25 N
(d) 45 N
Ans: (d)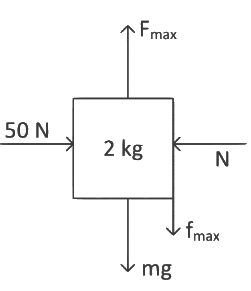 Here Fmax force is trying to move the block upward so friction force will be applied towards downward.
Here Fmax force is trying to move the block upward so friction force will be applied towards downward.
Along horizontal direction,
N = 50 N
Along vertical diretion,
Fmax = mg + fmax
= 2 × 10 + μN
= 20 + 0.5 × 50
= 20 + 25
= 45 N
Q11: A block of mass 40 kg slides over a surface, when a mass of 4 kg is suspended through an inextensible massless string passing over frictionless pulley as shown below.
The coefficient of kinetic friction between the surface and block is 0.02. The acceleration of block is. (Given g = 10 ms−2)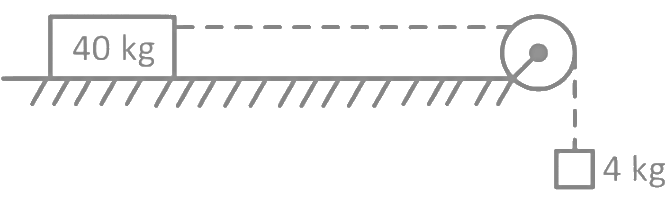 (a) 1 ms−2
(a) 1 ms−2
(b) 1/5 ms−2
(c) 4/5 ms−2
(d) 8/11 ms−2
Ans: (d)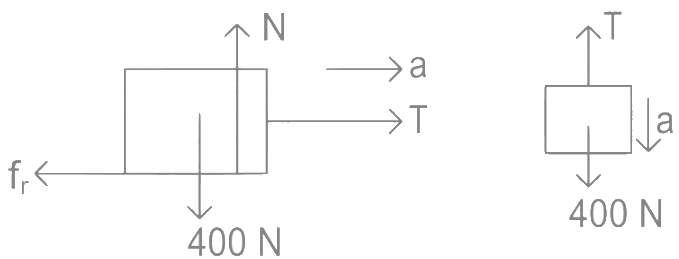
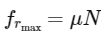
= 0.02 × 400
= 8 N
Let the acceleration is a as shown then.
40 − T = 4a
T − 8 = 40a
⇒ a = 32/44 = 8/11 m/s2
Q12: A block of mass M placed inside a box descends vertically with acceleration 'a'. The block exerts a force equal to one-fourth of its weight on the floor of the box. The value of 'a' will be
(a) g/4
(b) g/2
(c) 3g/4
(d) g
Ans: (c)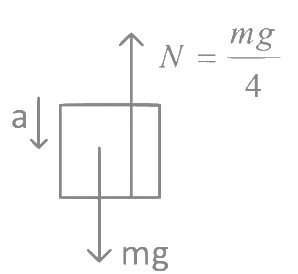 Using Newton's second law
Using Newton's second law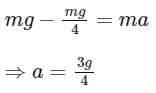
Q13: A block of mass 2 kg moving on a horizontal surface with speed of 4 ms−1 enters a rough surface ranging from x = 0.5 m to x = 1.5 m. The retarding force in this range of rough surface is related to distance by F = −kx where k = 12 Nm−1. The speed of the block as it just crosses the rough surface will be :
(a) zero
(b) 1.5 ms−1
(c) 2.0 ms−1
(d) 2.5 ms−1
Ans: (c)
F = -12x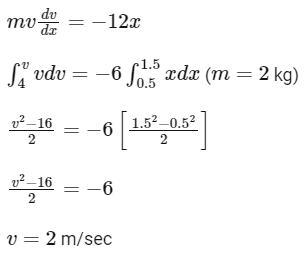
Q14: A system of two blocks of masses m = 2 kg and M = 8 kg is placed on a smooth table as shown in figure. The coefficient of static friction between two blocks is 0.5. The maximum horizontal force F that can be applied to the block of mass M so that the blocks move together will be: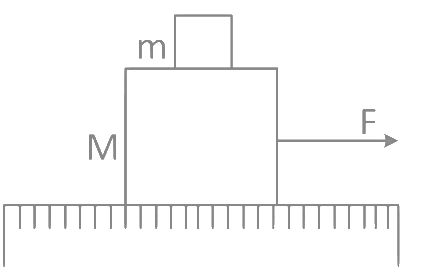 (a) 9.8 N
(a) 9.8 N
(b) 39.2 N
(c) 49 N
(d) 78.4 N
Ans: (c)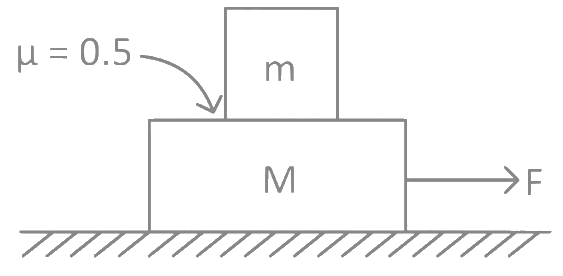 ∴ amax = μg
∴ amax = μg
= 0.5 × 9.8 = 4.9 m/s2
∴ Fmax = (8 + 2) × 4.9 = 49 N
Q15: A person is standing in an elevator. In which situation, he experiences weight loss?
(a) When the elevator moves upward with constant acceleration
(b) When the elevator moves downward with constant acceleration
(c) When the elevator moves upward with uniform velocity
(d) When the elevator moves downward with uniform velocity
Ans: (b)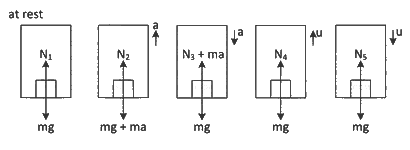 N1 = mg
N1 = mg
N2 = mg + ma
N3 = mg − ma
N4 = mg
N5 = mg
Q16: An object of mass 5 kg is thrown vertically upwards from the ground. The air resistance produces a constant retarding force of 10 N throughout the motion. The ratio of time of ascent to the time of descent will be equal to : [Use g = 10 ms−2].
(a) 1 : 1
(b) √2 : √3
(c) √3 : √2
(d) 2 : 3
Ans: (b)
Let time taken to ascent is t1 and that to descent is t2. Height will be same so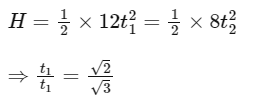
Q17: A block of mass 10 kg starts sliding on a surface with an initial velocity of 9.8 ms−1. The coefficient of friction between the surface and block is 0.5. The distance covered by the block before coming to rest is: [use g = 9.8 ms−2]
(a) 4.9 m
(b) 9.8 m
(c) 12.5 m
(d) 19.6 m
Ans: (b)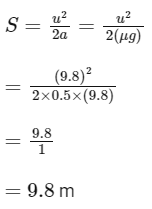
[JEE Mains Numericals]
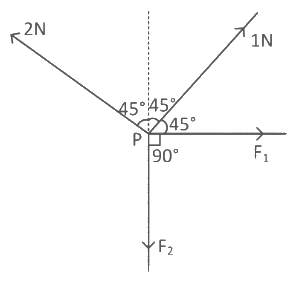
Q18: Four forces are acting at a point P in equilibrium as shown in figure. The ratio of force F1 to F2 is 1 : x where x = _____________. 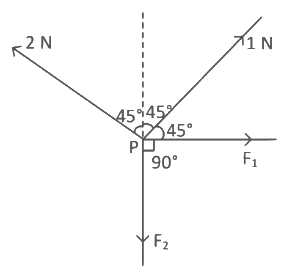 Ans: 3
Ans: 3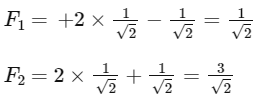
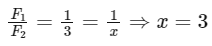
Q19: A hanging mass M is connected to a four times bigger mass by using a string-pulley arrangement, as shown in the figure. The bigger mass is placed on a horizontal ice-slab and being pulled by 2 Mg force. In this situation, tension in the string is x/5 Mg for x = ______________. Neglect mass of the string and friction of the block (bigger mass) with ice slab.
(Given g = acceleration due to gravity)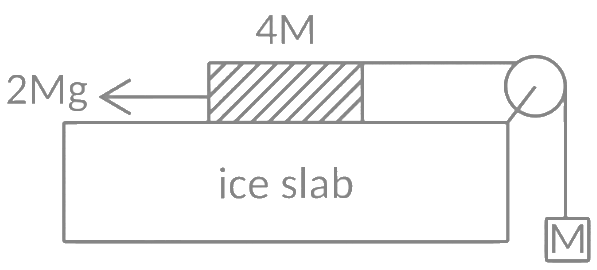 Ans: 6
Ans: 6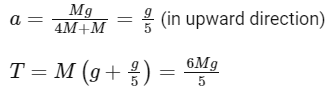
⇒ x = 6
Q20: A mass of 10 kg is suspended vertically by a rope of length 5 m from the roof. A force of 30 N is applied at the middle point of rope in horizontal direction. The angle made by upper half of the rope with vertical is θ = tan−1 (x × 10−1). The value of x is ____________.
(Given, g = 10 m/s2)
Ans: 3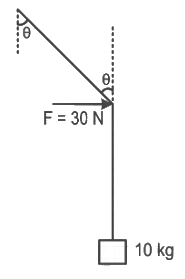
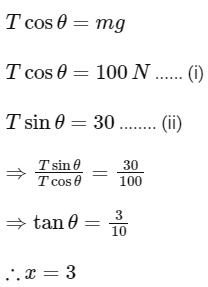
Q21: A system to 10 balls each of mass 2 kg are connected via massless and unstretchable string. The system is allowed to slip over the edge of a smooth table as shown in figure. Tension on the string between the 7th and 8th ball is __________ N when 6th ball just leaves the table.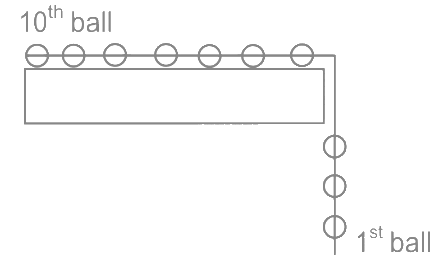 Ans: 36
Ans: 36
At given instant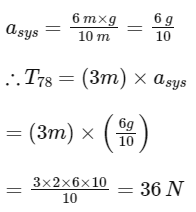
Q22: A block of mass 200 g is kept stationary on a smooth inclined plane by applying a minimum horizontal force F = √xN as shown in figure.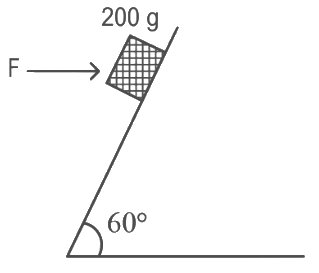 The value of x = _____________.
The value of x = _____________.
Ans: 12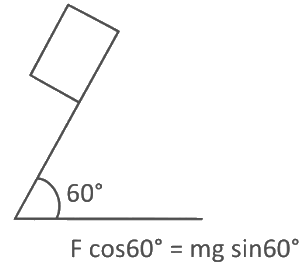
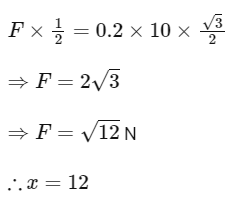
Q23: A force on an object of mass 100 g is 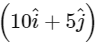 N. The position of that object at t = 2s is
N. The position of that object at t = 2s is 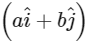 m after starting from rest. The value of a/b will be
m after starting from rest. The value of a/b will be
Ans: 2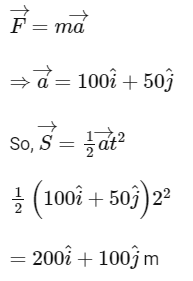
so a = 200 m and b = 100 m
so = a/b = 2
|
446 docs|929 tests
|
FAQs on JEE Mains Previous Year Questions (2025)): Laws of Motion - Chapter-wise Tests for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What are the fundamental laws of motion? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between mass and weight? |  |
| 3. How does friction affect the motion of objects? |  |
| 4. How does Newton's third law of motion apply to everyday situations? |  |
| 5. How does the mass of an object affect its motion? |  |




















