Best Study Material for UPSC Exam
UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC > Von Richter reaction
Von Richter reaction | Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
- The von Richter reaction, also named von Richter rearrangement, is a name reaction in the organic chemistry. It is named after Victor von Richter, who discovered this reaction in year 1871. It is the reaction of aromatic nitro compounds with potassium cyanide in aqueous ethanol to give the product of cine substitution (ring substitution resulting in the entering group positioned adjacent to the previous location of the leaving group) by a carboxyl group.
- Although it is not generally synthetically useful due to the low chemical yield and formation of numerous side products, its mechanism was of considerable interest, eluding chemists for almost 100 years before the currently accepted one was proposed.
General reaction scheme
- The reaction below shows the classic example of the conversion of p-bromonitrobenzene into m-bromobenzoic acid.
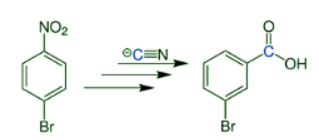
- The reaction is a type of nucleophilic aromatic substitution. Besides the bromo derivative, chlorine- and iodine-substituted nitroarenes, as well as more highly substituted derivatives, could also be used as substrates of this reaction. However, yields are generally poor to moderate, with reported percentage yields ranging from 1% to 50%.
Question for Von Richter reaction
Try yourself:
Which scientist discovered the von Richter reaction?View Solution
Reaction mechanism
- Several reasonable mechanisms were proposed and refuted by mechanistic data before the currently accepted one, shown below, was proposed in 1960 by Rosenblum on the basis of 15N labeling experiments.
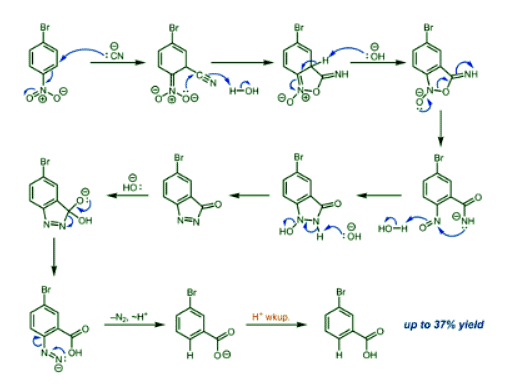
- First, the cyanide attacks the carbon ortho to the nitro group. This is followed by ring closing via nucleophilic attack on the cyano group, after which the imidate intermediate is rearomatized. Ring opening via nitrogen–oxygen bond cleavage gives an ortho-nitroso benzamide, which recyclizes to give a compound containing a nitrogen–nitrogen bond.
- Elimination of water gives a cyclic azoketone, which undergoes nucleophilic attack by hydroxide to give a tetrahedral intermediate. This intermediate collapses with elimination of the azo group to yield an aryldiazene with an ortho carboxylate group, which extrudes nitrogen gas to afford the anionic form of the observed benzoic acid product, presumably through the generation and immediate protonation of an aryl anion intermediate. The product is isolated upon acidic workup.
- Subsequent mechanistic studies have shown that the subjection of independently prepared ortho-nitroso benzamide and azoketone intermediates to von Richter reaction conditions afforded the expected product, lending further support to this proposal.
Question for Von Richter reaction
Try yourself:
What is the product formed in the von Richter reaction?View Solution
The document Von Richter reaction | Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
FAQs on Von Richter reaction - Chemistry Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is the Von Richter reaction? |  |
| 2. What is the general reaction scheme of the Von Richter reaction? |  |
The general reaction scheme of the Von Richter reaction involves the reduction of a nitrile compound (R-CN) to a primary amine (R-CH2NH2) using hydrogen gas (H2) and a metal catalyst (M). The reaction can be represented as follows:
R-CN + 2H2 -> R-CH2NH2 + NH3
| 3. What is the reaction mechanism of the Von Richter reaction? |  |
The reaction mechanism of the Von Richter reaction proceeds through a series of steps. First, the nitrile compound coordinates to the metal catalyst, forming a metal-nitrile complex. Next, hydrogen gas reacts with the metal-nitrile complex, resulting in the formation of a metal-amido intermediate. Finally, the metal-amido intermediate undergoes a protonation step, leading to the formation of the primary amine and ammonia.
| 4. What are the key factors that influence the Von Richter reaction? |  |
Several factors influence the Von Richter reaction, including the choice of catalyst, reaction temperature, reaction time, and reactant concentrations. Palladium and platinum are commonly used catalysts for this reaction. Higher temperatures and longer reaction times generally favor the conversion of the nitrile compound to the primary amine. Additionally, higher reactant concentrations can increase the reaction rate.
| 5. What are some applications of the Von Richter reaction? |  |
The Von Richter reaction has various applications in organic synthesis. It is commonly used for the preparation of primary amines, which are important building blocks in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and other fine chemicals. This reaction provides a selective and efficient method for introducing an amino group into organic molecules.
Related Searches