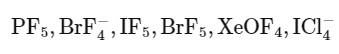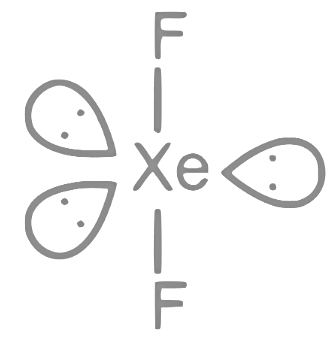[JEE Main MCQs]
Q1: The number of P − O − P bonds in H4P2O7 , (HPO3)3 and P4O10 are respectively:
(a) 1 , 3 , 6
(b) 1 , 2 , 4
(c) 0 , 3 , 4
(d) 0 , 3 , 6
Ans: (a)
Let's analyze each compound separately:
1. H4P2O7 : This compound is also known as pyrophosphoric acid. Its structure has two phosphorus atoms (P) connected by one oxygen atom (O), forming a P-O-P bond. There are no other P-O-P bonds in its structure. Number of P-O-P bonds = 1
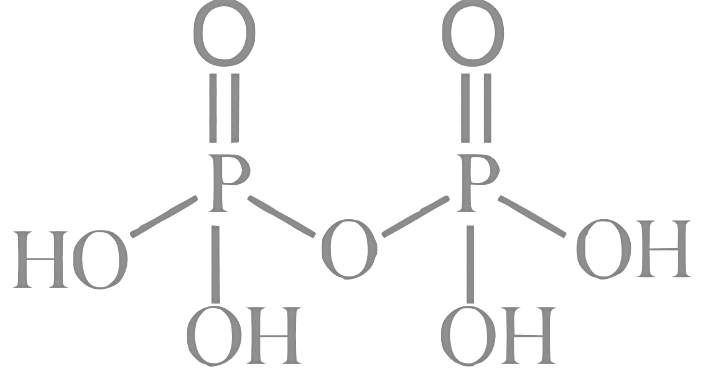
2. (HPO3)3: This compound is also known as cyclotriphosphoric acid. It has three phosphorus atoms and three oxygen atoms, arranged in a cyclic structure with each P atom connected to two O atoms, forming a six-membered ring. In this structure, there are three P-O-P bonds. Number of P-O-P bonds = 3
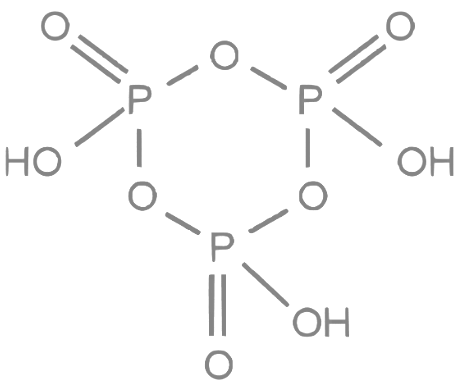 3. P4O10: This compound is also known as phosphorus pentoxide. Its structure consists of four phosphorus atoms (P) and ten oxygen atoms (O) connected in a cyclic arrangement. In the structure, each phosphorus atom is connected to four oxygen atoms, with two terminal oxygen atoms and two bridging oxygen atoms. There are six P-O-P bonds in the P4O10 structure.
3. P4O10: This compound is also known as phosphorus pentoxide. Its structure consists of four phosphorus atoms (P) and ten oxygen atoms (O) connected in a cyclic arrangement. In the structure, each phosphorus atom is connected to four oxygen atoms, with two terminal oxygen atoms and two bridging oxygen atoms. There are six P-O-P bonds in the P4O10 structure.
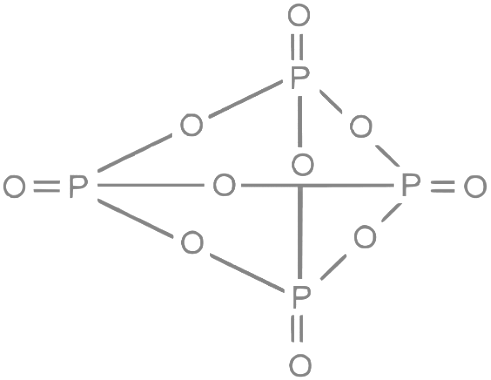 So, the number of P-O-P bonds in H4P2O7 , ( HPO3)3 , and P4O10 are 1, 3, and 6, respectively.
So, the number of P-O-P bonds in H4P2O7 , ( HPO3)3 , and P4O10 are 1, 3, and 6, respectively.
Q2: Consider the following statements:
(A) NF3 molecule has a trigonal planar structure.
(B) Bond length of N2 is shorter than O2 .
(C) Isoelectronic molecules or ions have identical bond order.
(D) Dipole moment of H2S is higher than that of water molecule.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) (C) and (D) are correct
(b) (A) and (B) are correct
(c) (B) and (C) are correct
(d) (A) and (D) are correct
Ans: (c)
The correct answer is (B) and (C).
(A) NF3 molecule has a trigonal pyramidal structure, not a trigonal planar structure. Therefore, statement (A) is false.
(B) The bond length of N2 is shorter than that of O2 due to the smaller atomic radius of nitrogen compared to oxygen. Therefore, statement (B) is true.
(C) Isoelectronic molecules or ions have the same number of electrons and hence the same bond order. Therefore, statement (C) is true.
(D) The dipole moment of water (H2O) is higher than that of H2S due to the greater electronegativity of oxygen compared to sulfur. Therefore, statement (D) is false.
Q3: Given below are two statements :
Statement I: SO2 and H2O both possess V-shaped structure.
Statement II : The bond angle of SO2 is less than that of H2O . In the light of the above statements,
choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
(a) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
(b) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(c) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(d) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
Ans: (c)
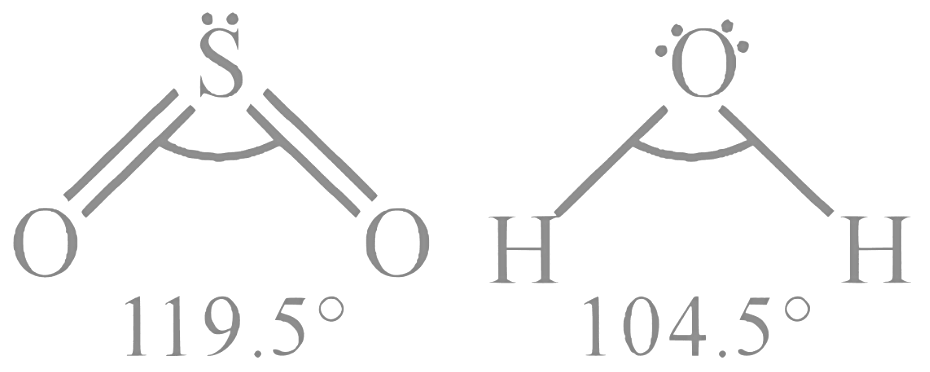
Statement I: Both SO₂ and H₂O have a V-shaped (or bent) molecular structure. SO₂ has a central sulfur atom with two oxygen atoms and one lone pair, while H₂O has a central oxygen atom with two hydrogen atoms and two lone pairs. In both cases, the repulsion between the lone pairs and the bonded electron pairs leads to a V-shaped structure.
Statement II: The bond angle in H₂O is approximately 104.5° due to the tetrahedral arrangement of electron pairs (including the lone pairs) around the central oxygen atom. In SO₂, the bond angle is approximately 119°. The presence of a lone pair and the double bonds in SO₂ results in a different electron distribution, leading to a larger bond angle compared to H₂O.
Q4: In which of the following processes, the bond order increases and paramagnetic character changes to diamagnetic one ?
(a) 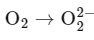
(b) 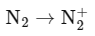
(d) NO → NO+
(d) 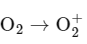
Ans: (c)
Let's analyze each option:
Option A: 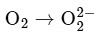
The bond order of O2 is 2 and it is paramagnetic. When two electrons are added to form 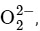 the bond order becomes 1 (decreases) and it becomes diamagnetic. This option does not meet the required conditions.Option B:
the bond order becomes 1 (decreases) and it becomes diamagnetic. This option does not meet the required conditions.Option B: 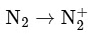
The bond order of N2 is 3 and it is diamagnetic. When one electron is removed to form 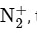 the bond order becomes 2.5 (decreases) and it remains diamagnetic. This option does not meet the required conditions.
the bond order becomes 2.5 (decreases) and it remains diamagnetic. This option does not meet the required conditions.
Option C: NO → NO+
The bond order of NO is 2.5 and it is paramagnetic. When one electron is removed to form NO+ , the bond order becomes 3 (increases) and it becomes diamagnetic. This option meets the required conditions.
Option D: 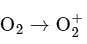
The bond order of O 2 is 2 and it is paramagnetic. When one electron is removed to form 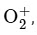 the bond order becomes 2.5 (increases) and it remains paramagnetic. This option does not meet the required conditions. Therefore, the correct answer is NO → NO+ .
the bond order becomes 2.5 (increases) and it remains paramagnetic. This option does not meet the required conditions. Therefore, the correct answer is NO → NO+ .
Q5: ClF5 at room temperature is a:
(a) Colourless liquid with square pyramidal geometry
(b) Colourless gas with square pyramidal geometry
(c) Colourless gas with trigonal bipyramidal geometry.
(d) Colourless liquid with trigonal bipyramidal geometry
Ans: (a)
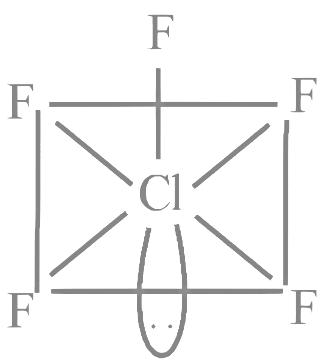 ClF5 is actually a colorless liquid at room temperature with a square pyramidal geometry.
ClF5 is actually a colorless liquid at room temperature with a square pyramidal geometry.
Q6: The bond order and magnetic property of acetylide ion are same as that of
(a) 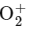
(b) 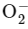
(c) 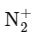
(d) NO+
Ans: (d)
The acetylide ion has the formula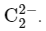 To determine its bond order, we need to first write the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for this ion.
To determine its bond order, we need to first write the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for this ion.
The MO diagram fo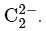 is:
is:
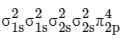
The bond order is given by the difference between the number of bonding electrons and the number of antibonding electrons, divided by 2. In this case, there are 4 bonding electrons and 2 antibonding electrons, so the bond order is:
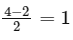
Therefore, the bond order of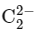 − is 1.
− is 1.
Now, we need to determine the magnetic property of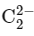 .
.
Since the bond order is 1, we know that the ion has a single unpaired electron. Therefore, it is paramagnetic.
Among the given options, the only ion with a bond order of 1 and paramagnetic property is NO+ .
Q7: Match List - I with List - II:
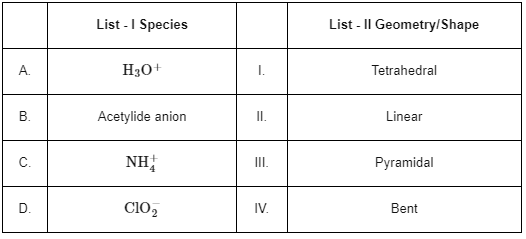 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-III, B-I, C-II, D-IV
(b) A-III, B-II, C-I, D-IV
(c) A-III, B-IV, C-I, D-II
(d) A-III, B-IV, C-II, D-I
Ans: (b)
Let's consider each species in List I and determine their geometries/shapes.
A. H3O+ : This ion is formed by the addition of a proton to a water molecule. The central atom (O) is surrounded by three Hydrogen atoms and one lone pair, making its shape pyramidal.
B. Acetylide anion: The acetylide ion 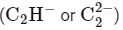 has a linear geometry as the three atoms are in a straight line.
has a linear geometry as the three atoms are in a straight line.
C. 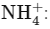 The ammonium ion has a central nitrogen atom surrounded by four hydrogen atoms, giving it a tetrahedral geometry.
The ammonium ion has a central nitrogen atom surrounded by four hydrogen atoms, giving it a tetrahedral geometry.
D. 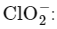 The chlorite ion has a central chlorine atom surrounded by two oxygen atoms and one lone pair, which gives it a bent or V-shaped geometry.
The chlorite ion has a central chlorine atom surrounded by two oxygen atoms and one lone pair, which gives it a bent or V-shaped geometry.
Matching these to List II, we get:
A. H3O+ - III. Pyramidal
B. Acetylide anion - II. Linear
C. 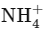 - I. Tetrahedral
- I. Tetrahedral
D. 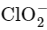 - IV. Bent
- IV. Bent
Q8: The compound which does not exist is
(a) (NH4)2BeF4
(b) PbEt4
(c) BeH2
(d) NaO2
Ans: (d)
Sodium superoxide (NaO2) is not a stable compound. It is not found in normal conditions due to its high reactivity.
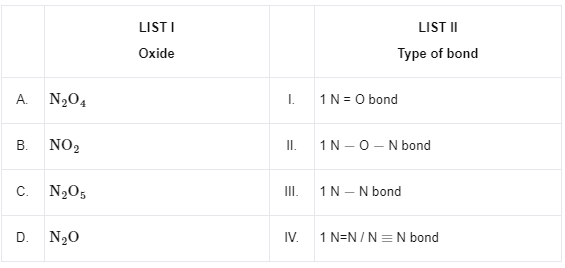
Q9: Match List I with List II
 Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
(a) A-II, B-I, C-III, D-IV
(b) A-III, B-I, C-II, D-IV
(c) A-III, B-I, C-IV, D-II
(d) A-II, B-IV, C-III, D-I
Ans: (b)
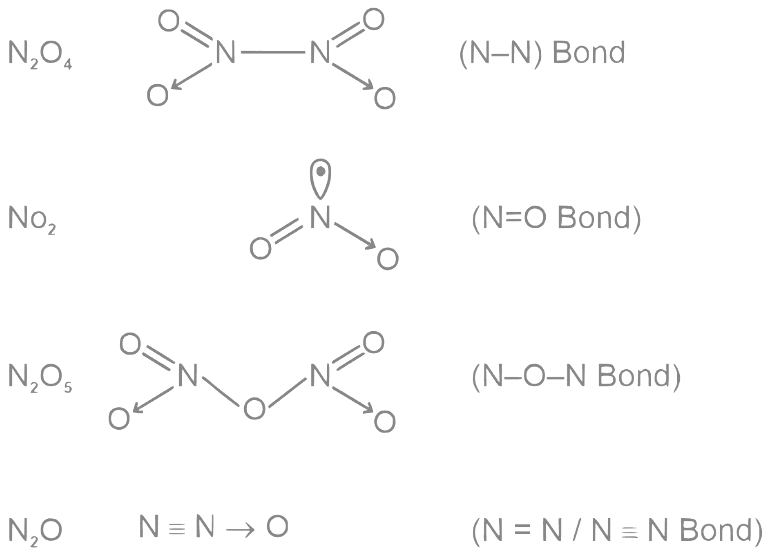
Q10: O–O bond length in H2O2 is X than the O–O bond length in F2O2. The O – H bond length in H2O2 is Y than that of the O–F bond in F2O2.
Choose the correct option for X and Y from the given below.
(a) X - shorter, Y - longer
(b) X - longer, Y - shorter
(c) X - shorter, Y - shorter
(d) X - longer, Y - longer
Ans: (b)
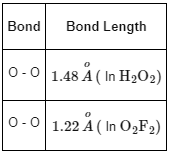
Thus, O − O bond length in H2O2 is longer than O − O bond length in O2F2 .
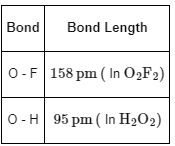
Thus, the O − H bond length in H2O2 is shorter than O − F bond length in O2F2.
Q11: Match List I with List II
 Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - II, B - I, C - III, D - IV
(b) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
(c) A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
(d) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
Ans: (b)
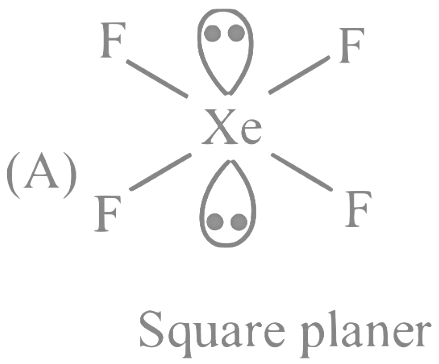
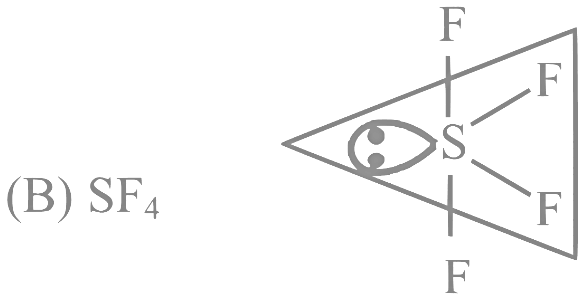
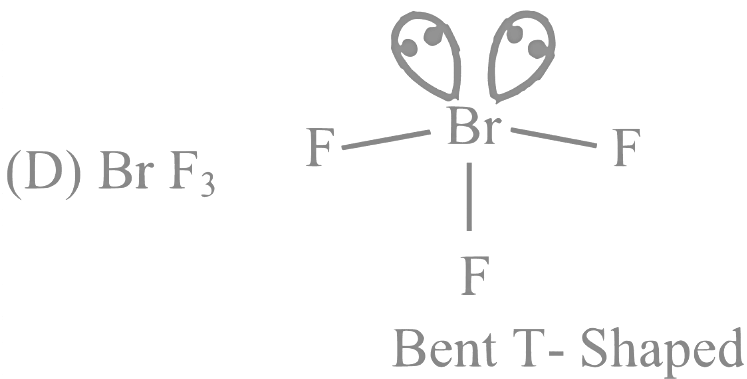
Q12: For OF2 molecule consider the following:
A. Number of lone pairs on oxygen is 2 .
B. FOF angle is less than 104.5∘.
C. Oxidation state of O is − 2.
D. Molecule is bent ' V ' shaped.
E. Molecular geometry is linear.
correct options are:
(a) A, C, D only
(b) A, B, D only
(c) C, D, E only
(d) B, E, A only
Ans: (b)
 A: No. of lone pairs on oxygen = 2
A: No. of lone pairs on oxygen = 2
B:
 (θ < Bond angle in H 2 O (104.5∘)
(θ < Bond angle in H 2 O (104.5∘)
D: molecule is bent "v" shaped
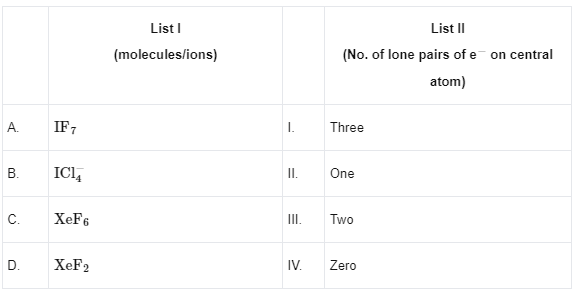
Q13: Match List I with List II
 Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A - II, B - I, C - IV, D - III
(b) A - IV, B - I, C - II, D - III
(c) A - IV, B - III, C - II, D - I
(d) A - II, B - III, C - IV, D - I
Ans: (c)
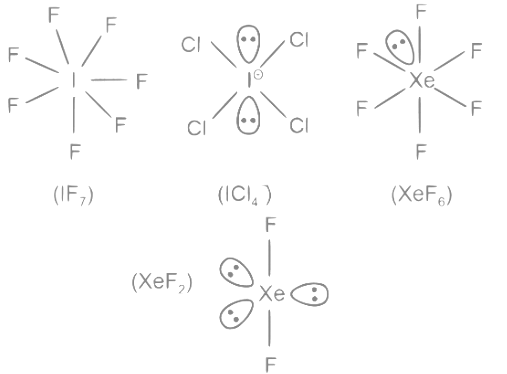
(A) IF7 − 0 lone pairs
(B) ICI4− − 2 lone pairs
(C) XeF6 − 1 lone pair
(D) XeF2 − 3 lone pairs
Q14: According to MO theory the bond orders for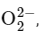 CO and NO+ respectively, are
CO and NO+ respectively, are
(a) 1, 3 and 3
(b) 2, 3 and 3
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) 1, 3 and 2
Ans: (a)
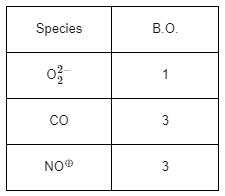
Note:
(1) Bond order = 1/2 [Nb − Na]
Nb = No of electrons in bending molecular orbital
Na = No of electrons in anti bonding molecular orbital
(4) upto 14 electrons, molecular orbital configuration is
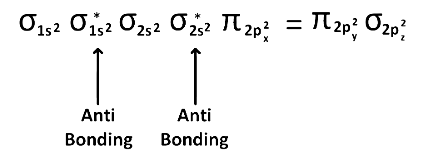
Here Na = Anti bonding electron = 4 and Nb = 10
(5) After 14 electrons to 20 electrons molecular orbital configuration is - - -
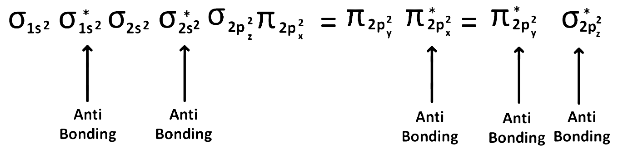
Here Na = 10
and Nb = 10 (A)
In O atom 8 electrons present, so in O2, 8 × 2 = 16 electrons present.
Then in 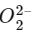 no of electrons = 18
no of electrons = 18
∴ Molecular orbital configuration of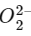 (18 electrons) is
(18 electrons) is
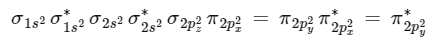
∴ Nb = 10
Na = 8
∴ BO = 1/2 [10 − 8] = 1
(B) CO has 14 electrons. Moleculer orbital configuration of CO is
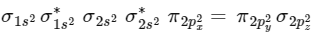
∴ Nb = 10 Na = 4
∴ BO = 1/2 [ 10 − 4] = 3
(C) NO+ has 14 electrons.
Moleculer orbital configuration of NO+ is
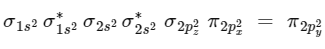
∴ Nb = 10
Na = 4
∴ BO = 1/2 [10 − 4] = 3
Q15: The magnetic behaviour of Li2O , Na2O2 and KO2 , respectively, are :
(a) paramagnetic, paramagnetic and diamagnetic
(b) paramagnetic, diamagnetic and paramagnetic
(c) diamagnetic, paramagnetic and diamagnetic
(d) diamagnetic, diamagnetic and paramagnetic
Ans: (d)
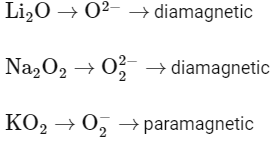
Q16: The bond dissociation energy is highest for
(a) Cl2
(b) I2
(c) Br2
(d) F2
Ans: (a)
Bond energy of F2 less than Cl2 due to lone pair – lone pair repulsions.
Bond energy order Cl2 > Br2 > F2 > I2
Q17: Statement I : Dipole moment is a vector quantity and by convention it is depicted by a small arrow with tail on the negative centre and head pointing towards the positive centre.
Statement II : The crossed arrow of the dipole moment symbolizes the direction of the shift of charges in the molecules.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :
(a) Statement I is correct but Statement II is incorrect
(b) Statement I is incorrect but Statement II is correct
(c) Both Statement I and Statement II are correct
(d) Both Statement I and Statement II are incorrect
Ans: (b)
The dipole moment is a vector quantity and is depicted by an arrow with tail on the positive centre and head pointing towards the negative centre. So, Statement-I is incorrect.
The crossed arrow of the dipole moment symbolizes the direction of the shift of charges in the molecules. So, Statement-II is correct.
For example,
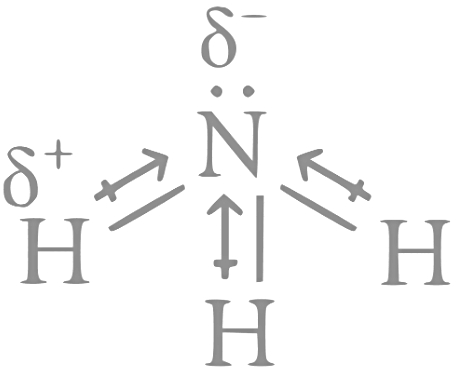
Q18: What is the number of unpaired electron(s) in the highest occupied molecular orbital of the following species : 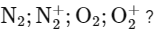
(a) 0, 1, 0, 1
(b) 2, 1, 0, 1
(c) 0, 1, 2, 1
(d) 2, 1, 2, 1
Ans: (c)
Q19: Decreasing order of the hydrogen bonding in following forms of water is correctly represented by
A. Liquid water
B. Ice
C. Impure water
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
(a) A = B > C
(b) B > A > C
(c) A > B > C
(d) C > B > A
Ans: (b)
Extent of hydrogen bonding :
Ice > liquid water > impure water
- In ice, 4 molecules of H2O are connected to H2O molecule.
- Impure water will have less hydrogen bonding.
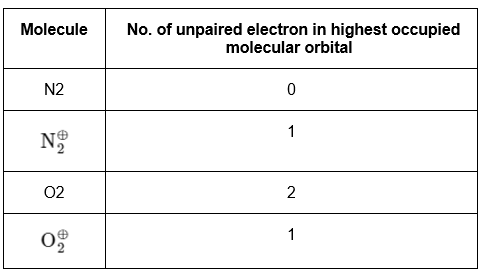
Q20: Order of Covalent bond;
A. KF > KI; LiF > KF
B. KF < KI; LiF > KF
C. SnCl4 > SnCl2; CuCl > NaCl
D. LiF > KF; CuCl < NaCl
E. KF < KI; CuCl > NaCl
(a) B, C only
(b) A, B only
(c) C, E only
(d) B, C, E only
Ans: (d)
[JEE Main Numericals]
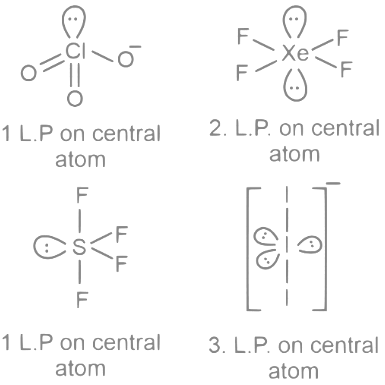
Q21: Which species has the maximum number of lone pair of electrons on the central at ?
ClO3-, XeF4, SF4, I3-
Ans: 3
Q22: The number of molecules from the following which contain only two lone pair of electrons is _______.
H2O, N2, CO, XeF4, NH3, NO, CO2, F2
Ans: 3
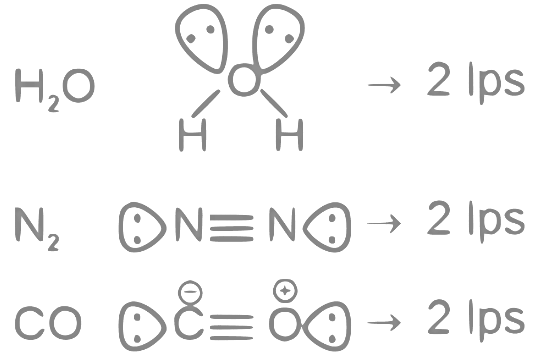
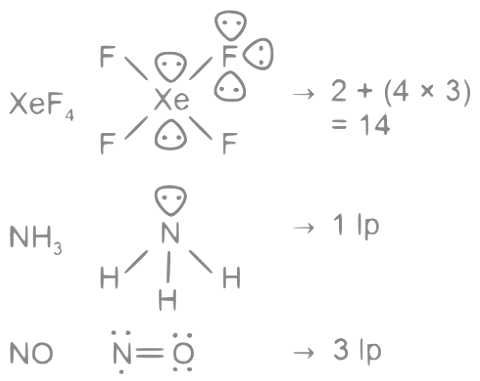
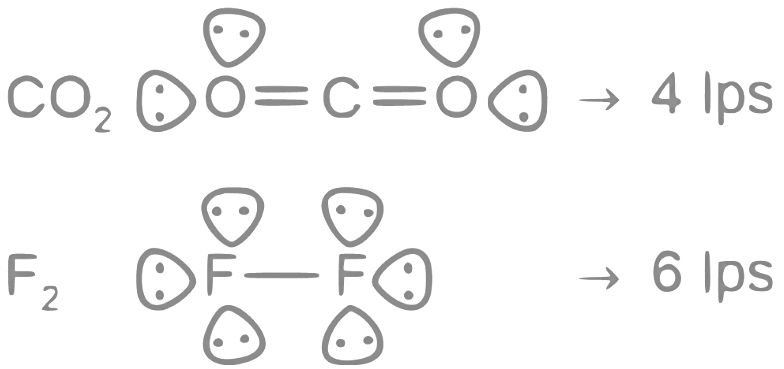 The number of molecules having only 2 lone pair of electrons = 3
The number of molecules having only 2 lone pair of electrons = 3
Which are H2O, N2 and CO
Note:- XeF4 have 2 lps on central atom, but we are asked about lone pair in molecule
Q23: The number of bent-shaped molecule/s from the following is __________
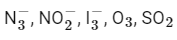
Ans: 3
A bent-shaped molecule has a molecular geometry with a central atom bonded to two other atoms and one or two pairs of non-bonding electrons. The VSEPR (Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion) theory helps us predict the shapes of molecules.
Let's consider the given molecules:
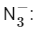 The azide ion has a linear shape, not bent. The nitrogen in the middle is connected to two other nitrogens and there are no lone pairs on the central atom.
The azide ion has a linear shape, not bent. The nitrogen in the middle is connected to two other nitrogens and there are no lone pairs on the central atom.
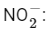 The nitrite ion has a bent shape. The central nitrogen atom is connected to two oxygen atoms and has one lone pair of electrons, giving it a bent geometry.
The nitrite ion has a bent shape. The central nitrogen atom is connected to two oxygen atoms and has one lone pair of electrons, giving it a bent geometry.
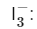 The triiodide ion has a linear shape, not bent. The central iodine atom is connected to two other iodine atoms and there are no lone pairs on the central atom.
The triiodide ion has a linear shape, not bent. The central iodine atom is connected to two other iodine atoms and there are no lone pairs on the central atom.
O3: Ozone has a bent shape. The central oxygen atom is connected to two other oxygen atoms and has one lone pair of electrons, giving it a bent geometry.
SO2: Sulfur dioxide has a bent shape. The central sulfur atom is connected to two oxygen atoms and has one lone pair of electrons, giving it a bent geometry.
Therefore, there are 3 bent-shaped molecules: 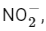 O3 , and SO2 .
O3 , and SO2 .
Q24: The sum of lone pairs present on the central atom of the interhalogen IF5 and IF7 is _________.
Ans: 1
Interhalogen compounds are the substances that consist of two different halogens. The most common type of interhalogen compounds are binary, containing only two different elements.
In IF5, iodine (I) is the central atom. Iodine has 7 valence electrons, 5 of which are used for bonding with the 5 fluorine (F) atoms. This leaves 2 electrons, or 1 lone pair on the iodine atom.
In IF7, iodine (I) is the central atom again. Iodine has 7 valence electrons, all of which are used for bonding with the 7 fluorine (F) atoms. So, there are no lone pairs on the iodine atom.
Therefore, the sum of lone pairs present on the central atom of the interhalogens IF 5 and IF7 is 1.
Q25: The number of species from the following carrying a single lone pair on central atom Xenon is ___________.
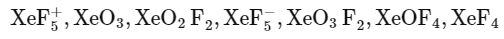
Ans: 4
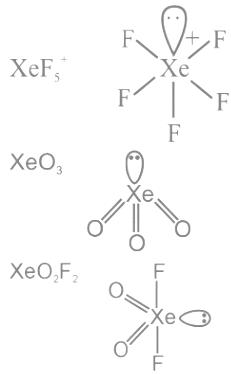
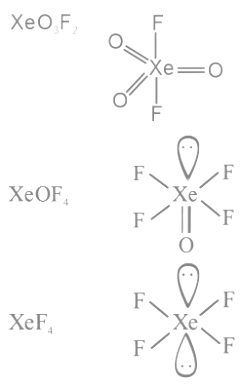
Q26: The number of following factors which affect the percent covalent character of the ionic bond is _________
(a) Polarising power of cation
(b) Extent of distortion of anion
(c) Polarisability of the anion
(d) Polarising power of anion
Ans: 3
The covalent character of an ionic bond is largely determined by the polarization of the ions involved in the bond. Polarization refers to the distortion of the electron cloud of an anion by a cation. This distortion leads to a shift in electron density towards the cation, thereby increasing the covalent character of the bond.
Here's a breakdown of the options:
(a) Polarising power of cation: The greater the polarising power of a cation, the greater the distortion of the anion, and therefore, the greater the covalent character of the bond. Thus, this statement is correct.
(b) Extent of distortion of anion: The more an anion is distorted, the more the electron density is shifted towards the cation, and the greater the covalent character of the bond. This statement is also correct.
(c) Polarisability of the anion: The greater the polarisability of an anion, the more it can be distorted, and therefore, the greater the covalent character of the bond. Thus, this statement is also correct.
(d) Polarising power of anion: This statement is incorrect. It is not the polarising power of the anion, but the polarisability of the anion and the polarising power of the cation that influence the covalent character of the bond.
Therefore, three of the factors listed (A, B, C) affect the percent covalent character of the ionic bond.
Q27: The number of species having a square planar shape from the following is __________.
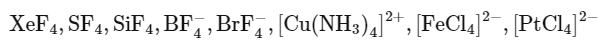
Ans: 4
XeF4→ Square planar
SF4 → See saw
SiF4 → Tetrahedral
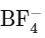 → Tetrahedral
→ Tetrahedral
[Cu(NH3)4]2+ → Square planar
[FeCl4]2− → Tetrahedral
[PtCl4]2− → Square planar
BrF4− → Square planar
So, 4 square planer shape compounds are present.
Q28: In an ice crystal, each water molecule is hydrogen bonded to ____________ neighbouring molecules.
Ans: 4
In an ice crystal, each water molecule is hydrogen bonded to four neighbouring molecules.
Q29: The number of species from the following which have square pyramidal structure is _________
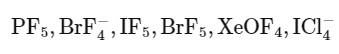
Ans: 3
A square pyramidal structure has five bonds and one lone pair, making a total of six electron pairs around the central atom. The geometry of such a molecule can be analyzed using the VSEPR theory.
PF5: 5 bond pairs and 0 lone pairs, so its geometry is trigonal bipyramidal, not square pyramidal.
BrF4−: 4 bond pairs and 2 lone pairs, so its geometry is square planar, not square pyramidal.
IF5: 5 bond pairs and 1 lone pair, so its geometry is square pyramidal.
BrF5: 5 bond pairs and 1 lone pair, so its geometry is square pyramidal.
XeOF4: 5 bond pairs and 1 lone pair, so its geometry is square pyramidal.
ICl4−: 4 bond pairs and 2 lone pairs, so its geometry is square planar, not square pyramidal.
So the number of species from the given list that have a square pyramidal structure is 3.
Q30: Amongst the following, the number of species having the linear shape is _________.
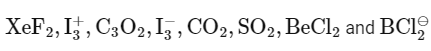
Ans: 5
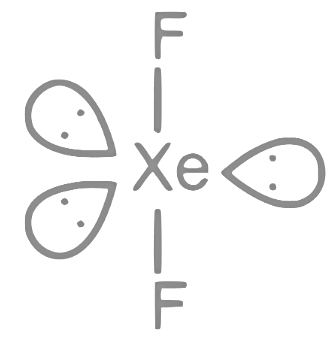

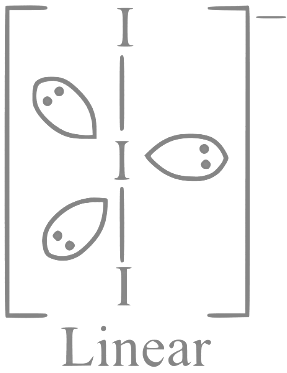
Q31: The number of molecules or ions from the following, which do not have odd number of electrons are _________.
(A) NO2
(B) ICl4−
(C) BrF3
(D) ClO2
(E) NO2+
(F) NO
Ans: 3
Only ICl4−, BrF3 and NO2+ have even number of electrons.
NO2 ⇒ 23e−;
ICl4− ⇒ 122e−;
BrF3 ⇒ 62e−;
ClO2 ⇒ 33e−;
NO2+ ⇒ 22e−;
NO ⇒ 15e−
Q33: The total number of lone pairs of electrons on oxygen atoms of ozone is __________.
Ans: 6
Total no, of lone pairs on oxygen atoms = 6
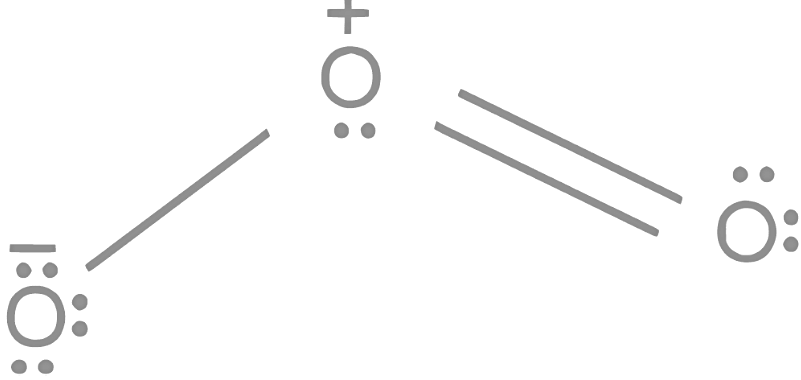

 3. P4O10: This compound is also known as phosphorus pentoxide. Its structure consists of four phosphorus atoms (P) and ten oxygen atoms (O) connected in a cyclic arrangement. In the structure, each phosphorus atom is connected to four oxygen atoms, with two terminal oxygen atoms and two bridging oxygen atoms. There are six P-O-P bonds in the P4O10 structure.
3. P4O10: This compound is also known as phosphorus pentoxide. Its structure consists of four phosphorus atoms (P) and ten oxygen atoms (O) connected in a cyclic arrangement. In the structure, each phosphorus atom is connected to four oxygen atoms, with two terminal oxygen atoms and two bridging oxygen atoms. There are six P-O-P bonds in the P4O10 structure. So, the number of P-O-P bonds in H4P2O7 , ( HPO3)3 , and P4O10 are 1, 3, and 6, respectively.
So, the number of P-O-P bonds in H4P2O7 , ( HPO3)3 , and P4O10 are 1, 3, and 6, respectively.
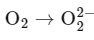
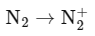
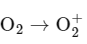
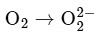
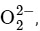 the bond order becomes 1 (decreases) and it becomes diamagnetic. This option does not meet the required conditions.Option B:
the bond order becomes 1 (decreases) and it becomes diamagnetic. This option does not meet the required conditions.Option B: 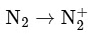
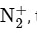 the bond order becomes 2.5 (decreases) and it remains diamagnetic. This option does not meet the required conditions.
the bond order becomes 2.5 (decreases) and it remains diamagnetic. This option does not meet the required conditions.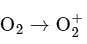
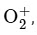 the bond order becomes 2.5 (increases) and it remains paramagnetic. This option does not meet the required conditions. Therefore, the correct answer is NO → NO+ .
the bond order becomes 2.5 (increases) and it remains paramagnetic. This option does not meet the required conditions. Therefore, the correct answer is NO → NO+ . ClF5 is actually a colorless liquid at room temperature with a square pyramidal geometry.
ClF5 is actually a colorless liquid at room temperature with a square pyramidal geometry.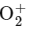
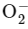
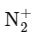
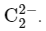 To determine its bond order, we need to first write the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for this ion.
To determine its bond order, we need to first write the molecular orbital (MO) diagram for this ion.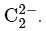 is:
is: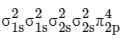
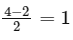
 − is 1.
− is 1. .
. Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below: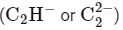 has a linear geometry as the three atoms are in a straight line.
has a linear geometry as the three atoms are in a straight line.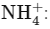 The ammonium ion has a central nitrogen atom surrounded by four hydrogen atoms, giving it a tetrahedral geometry.
The ammonium ion has a central nitrogen atom surrounded by four hydrogen atoms, giving it a tetrahedral geometry.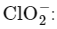 The chlorite ion has a central chlorine atom surrounded by two oxygen atoms and one lone pair, which gives it a bent or V-shaped geometry.
The chlorite ion has a central chlorine atom surrounded by two oxygen atoms and one lone pair, which gives it a bent or V-shaped geometry. - I. Tetrahedral
- I. Tetrahedral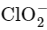 - IV. Bent
- IV. Bent Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:


 Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :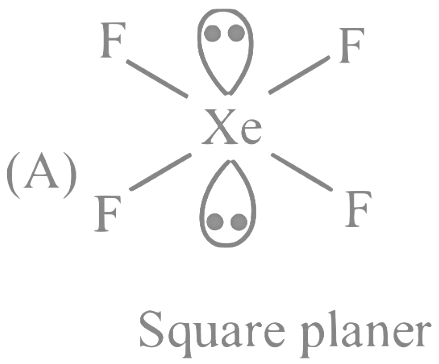



 A: No. of lone pairs on oxygen = 2
A: No. of lone pairs on oxygen = 2 (θ < Bond angle in H 2 O (104.5∘)
(θ < Bond angle in H 2 O (104.5∘) Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
 CO and NO+ respectively, are
CO and NO+ respectively, are

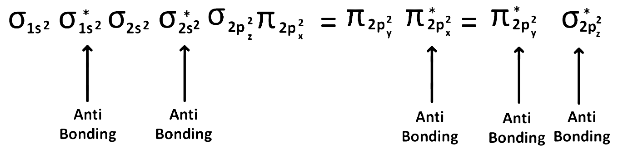
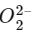 no of electrons = 18
no of electrons = 18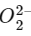 (18 electrons) is
(18 electrons) is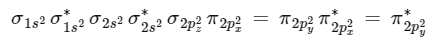
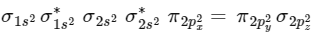
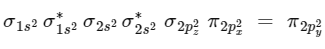
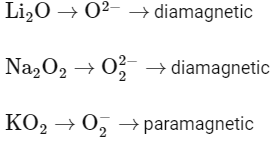

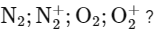

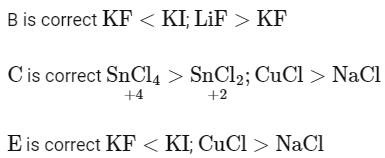

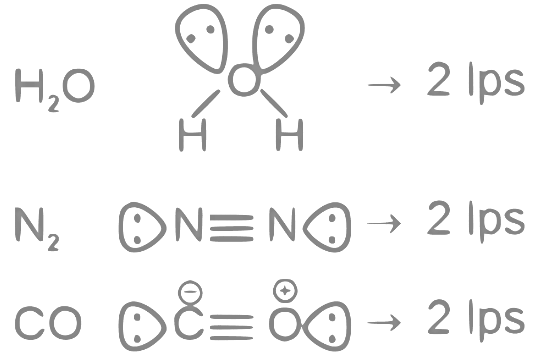
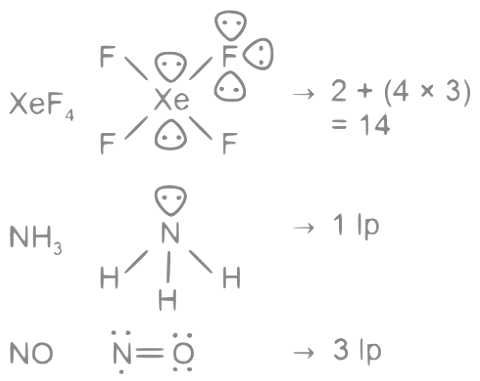
 The number of molecules having only 2 lone pair of electrons = 3
The number of molecules having only 2 lone pair of electrons = 3
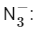 The azide ion has a linear shape, not bent. The nitrogen in the middle is connected to two other nitrogens and there are no lone pairs on the central atom.
The azide ion has a linear shape, not bent. The nitrogen in the middle is connected to two other nitrogens and there are no lone pairs on the central atom.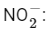 The nitrite ion has a bent shape. The central nitrogen atom is connected to two oxygen atoms and has one lone pair of electrons, giving it a bent geometry.
The nitrite ion has a bent shape. The central nitrogen atom is connected to two oxygen atoms and has one lone pair of electrons, giving it a bent geometry.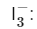 The triiodide ion has a linear shape, not bent. The central iodine atom is connected to two other iodine atoms and there are no lone pairs on the central atom.
The triiodide ion has a linear shape, not bent. The central iodine atom is connected to two other iodine atoms and there are no lone pairs on the central atom.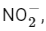 O3 , and SO2 .
O3 , and SO2 .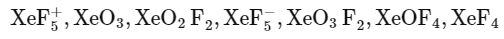


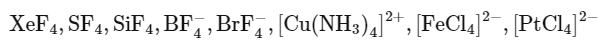
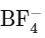 → Tetrahedral
→ Tetrahedral