UPSC Prelims Previous Year Questions 2023: Indian Polity | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Q1: In essence, what does Due Process of Law' mean?
(a) The principle of natural justice.
(b) The procedure established by law.
(c) Fair application of law.
(d) Equality before law.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- The due process of law doctrine examines not only whether a law exists to deprive a person of his or her life and personal liberty, but also whether the legislation is fair, just, and not arbitrary.
- Due process of law is a constitutional guarantee that prevents governments from impacting citizens in an abusive way. In its modern form, due process includes both procedural standards that courts must uphold in order to protect peoples’ personal liberty and a range of liberty interests that statutes and regulations must not infringe.
- It traces its origins to Chapter 39 of King John’s Magna Carta, which provides that no freeman will be seized, dispossessed of his property, or harmed except “by the law of the land,” an expression that referred to customary practices of the court. The phrase “due process of law” first appeared as a substitute for Magna Carta’s “the law of the land” in a 1354 statute of King Edward III that restated Magna Carta’s guarantee of the liberty of the subject.
Hence, option (c) is correct.
Q2: Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: In India, prisons are managed by State Governments with their own rules and regulations for the day-to-day administration of prisons.
Statement-II: In India, prisons are governed by the Prisons Act, 1894 which expressly kept the subject of prisons in the control of Provincial Governments.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I.
(b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I.
(c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect.
(d) Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- Prisons'/'persons detained therein' is a “State-List” subject under Entry 4 of List II of the Seventh Schedule to the Constitution of India.
- Administration and management of prisons and prisoners is the responsibility of respective State Governments who are competent to take appropriate action in this regard. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- However, given the significance of prisons in the Criminal Justice System, the Ministry of Home Affairs has been providing regular guidance and support to the States and UTs on diverse issues relating to prison administration.
- Under Prison act 1894, which governs the prisons, management and administration of prison falls in the domain of state governments. Hence statement 2 is correct.
Therefore, both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I.
Q3: Which one of the following statements best reflects the Chief purpose of the 'Constitution' of a country?
(a) It determines the objective for the making of necessary laws.
(b) It enables the creation of political offices and a government.
(c) It defines and limits the powers of government.
(d) It secures social justice, social equality and social security.
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- The chief purpose of a constitution is to establish the fundamental principles, structure, and functions of a government and to define the rights and freedoms of individuals within a country. Constitutions serve as the supreme law of the land and provide a framework for governance, ensuring the balance of power, protecting individual rights, and guiding the functioning of the state.
Hence, option (c) is correct.
Q4: In India, which one of the following Constitutional Amendments was widely believed to be enacted to overcome the judicial interpretations of the Fundamental Rights?
(a) 1st Amendment
(b) 42nd Amendment
(c) 44th Amendment
(d) 86th Amendment
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
1st Constitutional Amendment Act, 1951:
- Issues involved in the cases included freedom of speech, acquisition of the Zamindari land, State monopoly of trade, etc.
- Added three more grounds of restrictions on freedom of speech and expression: public order, friendly relations with foreign states and incitement to an offense. Also, it made the restrictions ‘reasonable’ and thus, justiciable in nature.
Hence, option (a) is correct.
Q5: Consider the following organizations/bodies in India:
- The National Commission for Backward Classes
- The National Human Rights Commission
- The National Law Commission
- The National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission
How many of the above constitutional bodies?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- National Commission for Backward Classes (NCBC) was initially constituted by the Central Govt by the National Commission for Backward Classes Act, 1993 and so far the Commission had been reconstituted 7 times up to 2016. The National Commission for Backward Classes Act, 1993 has been repealed through the National Commission for Backward Classes (Repeal) Act, 2018. The Commission has been accorded Constitutional Status and constituted through “The Constitution (One Hundred and Second Amendment) Act, 2018” Act.
- The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) of India was established on 12 October, 1993. The statute under which it is established is the Protection of Human Rights Act (PHRA), 1993 as amended by the Protection of Human Rights (Amendment) Act, 2006.
- The National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission (NCDRC), is a quasi- judicial commission in India which was set up in 1988 under the Consumer Protection Act of 1986.
- Law Commission of India is a non-statutory body and is constituted by a notification of the Government of India, Ministry of Law & Justice, Department of Legal Affairs with a definite terms of reference to carry out research in the field of law and the Commission makes recommendations to the Government (in the form of Reports) as per its terms of reference.
Hence, option (a) is correct.
Q6: Consider the following statements:
- If the election of the President of India is declared voidby the Supreme Court of India, all acts done by him/her in the performance of duties of his/her office of President before the date of decision become invalid.
- Election for the post of the President of India can be postponed on the ground that some Legislative Assemblies have been dissolved and elections are yet to take place.
- When a Bill is presented to the President of India, the Constitution prescribes time limits within which he/she has to declare his/her assent.
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- If the election of a person as President or Vice President is declared void by the Supreme court, acts done by him in the exercise and performance of the powers and duties of the office of President or Vice President, as the case may be, on or before the date of the decision of the Supreme Court shall not be invalidated by reason of that declaration. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- When an assembly is dissolved, the members cease to be qualified to vote in the presidential election, even if fresh elections to the dissolved assembly are not held before the presidential election. Thus election to the president will not be postponed on the grounds that some Legislative Assemblies have been dissolved. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- Assent to Bills: When a Bill has been passed by the Houses of Parliament, it shall be presented to the President, and the President shall declare either that he assents to the Bill, or that he withholds assent therefrom Provided that the President may, as soon as possible after the presentation to him of a Bill for assent, return the Bill if it is not a Money Bill to the Houses with a message requesting that they will reconsider the Bill or any specified provisions thereof and, in particular, will consider the desirability of introducing any such amendments as he may recommend in his message, and when a Bill is so returned, the Houses shall reconsider the Bill accordingly, and if the Bill is passed again by the Houses with or without amendment and presented to the President for assent, the President shall not withhold assent therefrom Procedures in Financial Matters. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
Q7: With reference to Finance Bill and Money Bill in the Indian Parliament, consider the following statements:
- When the Lok Sabha transmits Finance Bill to the Rajya Sabha, it can amend or reject the Bill.
- When the Lok Sabha transmits Money Bill to the Rajya Sabha, it cannot amend or reject the Bill, it can only make recommendations.
- In the case of disagreement between the Lok Sabha and the Rajya Sabha, there is no joint sitting for Money Bill, but a joint sitting becomes necessary for Finance Bill.
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- Finance Bill is a Money Bill as defined under article 110(a) of the constitution.It is introduced as a part of Annual Financial Statement(Budget) under article 112.
- The Rajya Sabha has limited powers regarding the Money Bill. It cannot reject or amend the money bill after it is passed by the Lok Sabha and transmitted to the Rajya Sabha. It has to return the bill within 14 days with or without recommendations. It is at the discretion of Lok Sabha to accept or reject any or all of the recommendations made by the Rajya Sabha. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Finance bill, being subjected to all the conditions of Money bill, Rajya Sabha can only make recommendations on a finance bill. Rajya Sabha can not amend or reject finance bill(as also the case for Money bill). Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- The provision of joint sitting is applicable to ordinary bills or financial bills only and not to money bills(including Finance bills) or Constitutional amendment bills. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
Q8: With reference to Scheduled Areas in India, consider the following statements:
- Within a State, the notification of an area as Scheduled Area takes place through an Order of the President.
- The largest administrative unit forming the Scheduled Area is the District and the lowest is the cluster of villages in the Block.
- The Chief Ministers of the concerned States are required to submit annual reports to the Union Home Ministry on the administration of Scheduled Areas in the States.
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- The term “Scheduled Areas” are those that are scheduled as such by a Presidential Order under Paragraph 6 (1) of the Fifth Schedule, which states: “In this Constitution, the expression ‘Scheduled Areas’ means such areas as the President may by order declare to be “Scheduled Areas”.
- The specification of “Scheduled Areas” in relation to a State is by a notified order of the President, after consultation with the State Government concerned. The same applies in the case of any alteration, increase, decrease, incorporation of new areas, or rescinding any Orders relating to “Scheduled Areas”. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- The largest administrative unit forming the scheduled areas has been the district and the lowest the cluster of villages in the block. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- The Governor of each State having Scheduled Areas therein shall annually, or whenever so required by the President, make a report to the President regarding the administration of the Scheduled Areas in that State and the executive power of the Union shall extend to the giving of directions to the State as to the administration of the said areas. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
Q9: Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: The Supreme Court of India has held in some judgements that the reservation policies made under Article 16(4) of the Constitution of India would be limited by Article 335 for maintenance of efficiency of administration.
Statement-II: Article 335 of the Constitution of India defines the term 'efficiency of administration'.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
(b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-1
(c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
(d) Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- In the past seven decades of constitutional jurisprudence on reservations, the Supreme Court of India has consistently referred to the notions of “efficiency” and “merit,” while adjudicating the validity of various reservation policies.
- The Court has held in several judgments (Indra Sawhney and others v Union of India and Others 1993; M Nagaraj and Others v Union of India and Others 2006) that the reservation policies made under Article 16(4)1 of the Constitution would be limited by Article 335 (2) which provides for “maintenance of efficiency of administration,”. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- This was done while the Constitution does not define the term “efficiency of administration.” Hence, statement 2 is not correct. While considering the claims of the Scheduled Castes (SCs) and the Scheduled Tribes (STs) in the making of appointments to public services and posts. This was done while the Constitution does not define the term “efficiency of administration.” Hence, option (c) is correct.
Q10: Consider the following:
- Demographic performance
- Forest and ecology
- Governance reforms
- Stable government
- Tax and fiscal efforts
For the horizontal tax devolution, the Fifteenth Finance Commission used how many of the above as criteria other than population area and income distance?
(a) Only two
(b) Only three
(c) Only four
(d) All five
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
For the horizontal tax devolution, the Fifteenth Finance Commission used the following as criteria:
- Population Area
- Forest & ecology Income Distance Tax & fiscal efforts
- Demographic performance
Hence, the correct answer is b.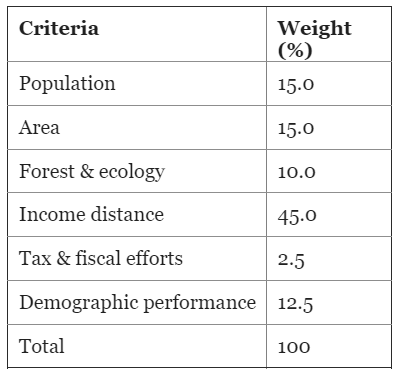
Q11: With reference to Home Guards, consider the following statements :
- Home Guards are raised under the Home Guards Act and Rules of the Central Government.
- The role of the Home Guards is to serve as an auxiliary force to the police in maintenance of internal security.
- To prevent infiltration on the international border/coastal areas, the Border Wing Home Guards Battalions have been raised in some States.
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- ‘Home Guards’ is a voluntary force, first raised in India in December 1946, to assist the police in controlling civil disturbance and communal riots.
- Subsequently, the concept of the voluntary citizen’s force was adopted by several States. In the wake of Chinese aggression in 1962, the Centre advised the States and Union Territories to merge their existing voluntary organisation into one uniform voluntary force known as Home Guards.
- Home Guards are raised under the Home Guards Act and Rules of the States/Union Territories, NOT the Central Government. Hence statement 1 is NOT correct.
- The role of Home Guards is to serve as an auxiliary Force to the Police in maintenance of internal security situations, help the community in any kind of emergency such as an air-raid, fire, cyclone, earthquake, epidemic etc., help in maintenance of essential services, promote communal harmony and assist the administration in protecting weaker sections, participate in socio-economic and welfare activities and perform Civil Defence duties. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Fifteen Border Wing Home Guards (BWHG) Battalions have been raised in the border States viz. Punjab (6 Bns.), Rajasthan ( 4 Bns.), Gujarat (2 Bns.) and one each Battalion for Meghalaya, Tripura and West Bengal to serve as an auxiliary to Border Security Force for preventing infiltration on the international border/ coastal areas, guarding of VA/VPs and lines of communication in vulnerable area at the time of external aggression. Hence statement 3 is correct.
Q12: With reference to India, consider the following pairs:

How many of the above pairs are correctly matched?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- The Official Secrets Act was first enacted in 1923 and was retained after Independence. The law, applicable to government servants and citizens, provides the framework for dealing with espionage, sedition, and other potential threats to the integrity of the nation. The law makes spying, sharing ‘secret’ information, unauthorised use of uniforms, (Under Section-6) withholding information, interference with the armed forces in prohibited/ restricted areas, among others, punishable offences. If guilty, a person may get up to 14 years’ imprisonment, a fine, or both. Hence, pair 1 is correctly matched.
- Under section 7 of Official Secrets Act 1923 No person in the vicinity of any prohibited place shall obstruct, knowingly mislead or otherwise interfere with or impede, any police officer, or any member of 21 [the Armed Forces of the Union] engaged on guard, sentry, patrol or other similar duty in relation to the prohibited place. Hence pair 2 is NOT correctly matched.
- THE ARMS (AMENDMENT) ACT, 2019 says Whoever uses firearm in a rash or negligent manner or in celebratory gunfire so as to endanger human life or personal safety of others shall be punishable with an imprisonment for a term which may extend to two years, or with fine which may extend to rupees one lakh, or with both. Hence pair 3 is correctly matched.
Q13: Consider the following statements in respect of the National Flag of India According to the Flag Code of India, 2002:
Statement-I: One of the standard sizes the National Flag of India of 600 mm × 400 mm.
Statement-II: The ratio of the length to the height (width) of the Flag shall be 3 : 2.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
(b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
(c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
(d) Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
The standard sizes of national flag shall be as follows:
- Hence, statement 1 is incorrect.
- The National Flag shall be rectangular in shape. The ratio of the length to the height (width) of the flag shall be 3 : 2. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
Q14: Consider the following statements in respect of the Constitution Day:
Statement-I: The Constitution Day is celebrated on 26th November every year to promote constitutional values among citizens.
Statement-II: On 26th November, 1949, the Constituent Assembly of India set up a Drafting Committee under the Chairmanship of Dr. B.R. Ambedkar to prepare a Draft Constitution of India.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
(b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
(c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
(d) Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
- It is celebrated on 26th November every year. It is also known as National Law Day. On this day in 1949, the Constituent Assembly of India formally adopted the Constitution of India that came into force on 26th January 1950. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- On 29 August, 1947, the Constituent Assembly set up a Drafting Committee under the Chairmanship of Dr. B.R. Ambedkar to prepare a Draft Constitution for India. Hence, statement 2 is incorrect.
- On 13 December 1946, the Constituent Assembly formally commenced its task of framing the Constitution of India. Jawaharlal Nehru moved the Objectives Resolution, which aimed to declare India as an Independent Sovereign Republic and create a Constitution to govern its future. The Resolution established general principles to guide the work of the Constituent Assembly. On January 22, 1947, the Constituent Assembly adopted the Resolution.
Q15: Consider the following statements in relation to Janani Suraksha Yojana:
- It is a safe motherhood intervention of the State Health Departments.
- Its objective is to reduce maternal and neonatal mortality among poor pregnant women.
- It aims to promote institutional delivery among poor pregnant women.
- Its objective includes providing public health facilities to sick infants up to one year of age.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Janani Suraksha Yojana:
- The Yojana, launched on 12th April 2005, is being implemented in all states and UTs with special focus on low performing states.
- It is a safe motherhood intervention under the National Rural Health Mission (NRHM). Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- It was implemented with the objective of reducing maternal and neo-natal mortality by promoting institutional delivery among the poor pregnant women. Hence, statements 2 and 3 are correct.
- Providing public health facilities to sick infants up to one year of age is not an objective of the scheme. Hence, statement 4 is not correct.
Q16: Consider the following statements in the context interventions being undertaken under Anaemia Mukt Bharat Strategy:
- It provides prophylactic calcium supplementation for pre-school children, adolescents and pregnant women.
- It runs a campaign for delayed cord clamping at the time of child-birth.
- It provides for periodic deworming to children and adolescents.
- It addresses non-nutritional causes of anaemia in endemic pockets with special focus on malaria, hemoglobinopathies and fluorosis.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Interventions of Anaemia Mukt Bharat:
- Not Prophylactic calcium supplementation but Prophylactic Iron and Folic Acid Supplementation is provided to children, adolescents and women of reproductive age and pregnant women irrespective of anemia. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- Appropriate Infant and Young Child Feeding (IYCF) with emphasis on adequate and age-appropriate complementary foods for children 6 months and above. Increase intake of iron-rich, protein-rich and vitamin C-rich foods through dietary diversification/quantity/frequency and food fortification
- Promoting practice of delayed cord clamping (by atleast 3 minutes or until cord pulsations cease) in all health facility deliveries followed by early initiation of breastfeeding within 1 hour of birth. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Bi-annual mass deworming for children in the age groups between 1-19 years is carried out every year under National Deworming Day (NDD) programme. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- The Anemia Mukt Bharat, also integrates deworming of women of reproductive age and for pregnant women as part of the NDD strategy.
- Addressing non-nutritional causes of anemia in endemic pockets, with special focus on malaria, haemoglobinopathies and fluorosis. Hence, statement 4 is correct.
Q17: Consider the following statements:
Statement-I: India's public sector health care system largely focuses on curative care with limited preventive, promotive and rehabilitative care.
Statement-II: Under India's decentralized approach to health care delivery, the States are primarily responsible for organizing health services.
Which one of the following is correct in respect of the above statements?
(a) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is the correct explanation for Statement-I
(b) Both Statement-I and Statement-II are correct and Statement-II is not the correct explanation for Statement-I
(c) Statement-I is correct but Statement-II is incorrect
(d) Statement-I is incorrect but Statement-II is correct
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
- The Ayushman Bharat - Health and Wellness Centres (ABHWCs) were launched under the Ayushman Bharat Programme in a bid to move away from selective health care to a more comprehensive range of services spanning preventive, promotive, curative, rehabilitative and palliative care for all ages. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- In AB, HWCs at the Sub Health Centre (SHC) level, Multi-Purpose Workers (male & female) & ASHAs and Primary Health Centre / Urban Primary Health Centre are organized by state govt but in case of tertiary Health services Central govt is also a key stakeholders. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
Q18: Consider the following statements:
- According to the Constitution of India, the Central Government has a duty to protect States from internal disturbances.
- The Constitution of India exempts the States from providing legal counsel to a person being held for preventive detention.
- According the Prevention of Terrorism Act, 2002, confession of the accused before the police cannot be used as evidence.
How many of the above statement are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) All three
(d) None
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
- As per Article 355, it shall be the duty of the Union to protect every State against external aggression and internal disturbance and to ensure that the government of every State is carried on in accordance with the provisions of this Constitution. Hence, Statement 1 is correct.
- Article 22 (1) of the Constitution, for example, guarantees the right to legal counsel, but Article 22 (3) (b) strips this right from persons arrested or detained under preventive detention law. Relying on these provisions, the Supreme Court stated, in A.K. Roy v. Union of India, that detainees do not have the right to legal representation or cross-examination in Advisory Board hearings. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- The Terrorist and Disruptive Activities (Prevention) Act, 1987 and the Prevention of Terrorism Act, 2002 (commonly known as TADA and POTA respectively) had made provisions to admit the confessions made by the accused before the police authorities. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
- The Indian Evidence Act, 1872 provides that confession made before police authority or under police custody is inadmissible.
Q19: Consider the following statements in respect of election to the President of India:
- The members nominated to either House of the Parliament or the Legislative Assemblies of States are also eligible to be included in the Electoral College.
- Higher the number of elective Assembly seats, higher is the value of vote of each MLA of that State.
- The value of vote of each MLA of Madhya Pradesh is greater than that of Kerala.
- The value of vote of each MLA of Puducherry is higher than that of Arunachal Pradesh because the ratio of total population to total number of elective seats in Puducherry is greater as compared to Arunachal Pradesh.
How many of the above statements are correct?
(a) Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All four
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
- The President is elected not directly by the people but by members of electoral college consisting of: 1. the elected members of both the Houses of Parliament; 2. the elected members of the legislative assemblies of the states; and 3. the elected members of the legislative assemblies of the Union Territories of Delhi and Puducherry1. Thus, the nominated members of both of Houses of Parliament, the nominated members of the state legislative assemblies, the members (both elected and nominated) of the state legislative councils (in case of the bicameral legislature) and the nominated members of the Legislative Assemblies of Delhi and Puducherry do not participate in the election of the President. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- Is the value of vote of each elector the same?
- Answer: No. The value of votes of MLAs would differ from State to State as the value of each such vote is calculated by the process explained below. However, the value of votes of all MPs is the same. Statements 2 and 3 are not correct.
- Ratio of total population to total number of elective seats in Puducherry = 471707/30 =
- 15,723.56.
- Ratio of total population to total number of elective seats in Arunachal Pradesh = 467511/60 = 7,791.85.
The value of vote of each MLA of Puducherry is higher than that of Arunachal Pradesh because the ratio of total population to total number of elective seats in Puducherry is greater as compared to Arunachal Pradesh. Hence, statement 4 is correct.
|
142 videos|779 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Prelims Previous Year Questions 2023: Indian Polity - Indian Polity for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the significance of the UPSC Prelims exam in the Indian Polity? |  |
| 2. What are some important topics in Indian Polity for the UPSC Prelims exam? |  |
| 3. How can I prepare for Indian Polity for the UPSC Prelims exam? |  |
| 4. Are there any specific sources or books recommended for studying Indian Polity for the UPSC Prelims exam? |  |
| 5. What is the weightage of Indian Polity in the UPSC Prelims exam? |  |

















