Lewis Model of Economic Development | NABARD Grade A & Grade B Preparation - Bank Exams PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction to the Lewis Model |

|
| Assumptions of the Lewis Model |

|
| Slowing of the Pace of expansion of the Capitalist Sector |

|
| Critical Review of the Lewis’s Model |

|
Introduction to the Lewis Model
Lewis published his model entitled
- “Economic Development with Unlimited Supplies of Labour” in 1954. In his model Lewis divides the economy in an underdeveloped country in two sectors namely the Subsistence sector and the capitalist sector. Subsistence is identified with the agricultural sector of the economy while the capitalist sector implies mainly the manufacturing sector of the economy.
- Capitalist sector also includes plantations and mining where hired labour is employed for purposes of production. The capitalist sector can either be private or public in nature. Subsistence sector, that the agricultural sector is considered to be labour intensive. It does not use reproducible capital. It uses poor techniques of production and has very low productivity.
Assumptions of the Lewis Model
(A) Surplus Labour in the Subsistence Sectors
- The basic assumption of the model is that there exists surplus labour in the subsistence sectors. It includes labour whose marginal productivity is zero as well as that whose marginal productivity is positive but is less than the institutional wage. This labour comprises farmers, agricultural labourers, petty traders domestic servants and women.
- The surplus labour in the agriculture sector acts as a source of unlimited supply of labour for the manufacturing sector. By unlimited supply of labour. Lewis means that the supply of labour is perfectly elastic at a particular wages. This particular wage is somewhat higher than the institutional wage which each worker in the agricultural sector gets.
- Lewis calls it as institutional wage because every worker gets this wage because of some institutional arrangements. This wages is equal to an average share of each worker in the total output in the subsistence sector. If market forces were allowed to operate in the subsistence sector labourers with zero margin productivity or those with a very low marginal productivity would not have received this wage.
(B) Importance of Saving
- Another important assumption that Lewis makes is about the savings generated in the capitalist sector and in the subsistence sector. The capitalist sector invests all its savings for its further expansion.
- Those in the subsistence sector, on the other hand squander away their savings, if any in purchase of jewellery & for construction of temples etc. The propensity to save of the people in subsistence sector is also lower when compared with that of those in the capitalist sector.
- Lewis in fact so much fascinated by the higher propensity to save of the capitalist sector that he even advocates a transfer of income from the subsistence sector to the capitalist sector. He feels that steps have to be taken to raise the rate of savings from 10% to 15% if the development of the economy has to be smooth.
Slowing of the Pace of expansion of the Capitalist Sector
According to Lewis, expansion of the capitalist sector will continue unhindered so long as the supply curve for labour from the subsistence sector is perfectly elastic i.e. so long as the labour can be transferred to the capitalist sector at a constant wage. Lewis, of course is conscious of the fact that under certain circumstances, the supply curve for labour can turn upwards.
These circumstances are:
- The pace of expansion of the capitalist sector is more rapid when compared with the rate of growth of population in the subsistence sector. The surplus labour in that case will ultimately be fully exhausted.
- Technological development in the subsistence sector raise the productivity of labour with in that case will rise. We too will have to be raised them.
- As population increase due to law of decreasing marginal return, prices of food and raw materials will rise.
- When workers in the capitalist sector start imitating the living pattern of the capitalist themselves, they may ask for higher wages.
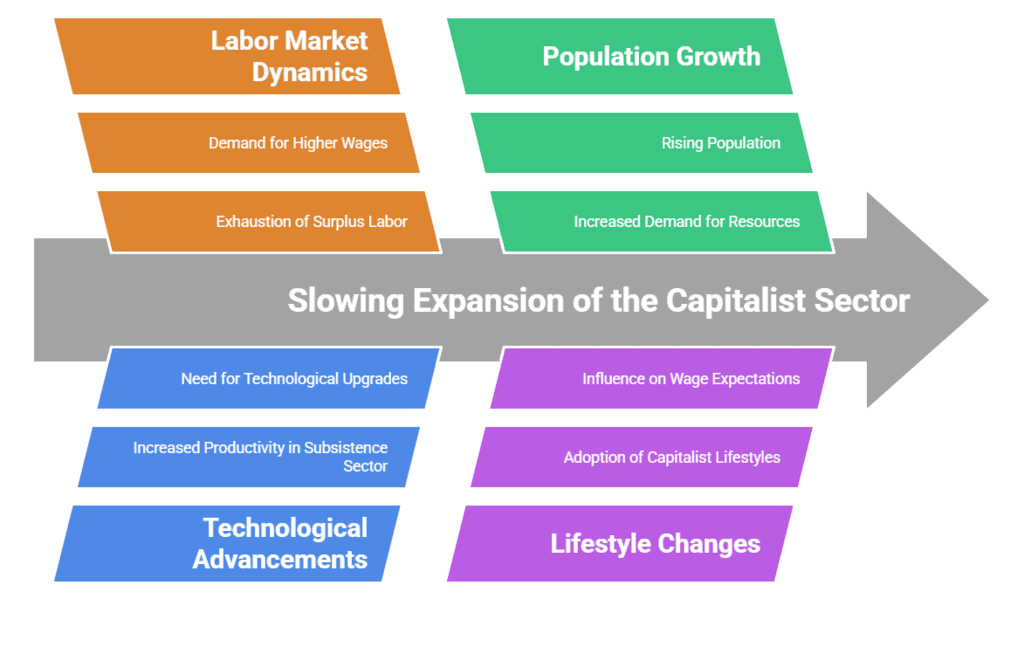
If any of the above four factors start operating, then according to Lewis, the expansion of the capitalist sector will be slow down.
Impact of the Open Economy
The open economy can encourage the immigration of labour. If this happens, it will help in the expansion of the capitalist sector. But immigration may not be so easy. If in that case the pace of expansion of the capitalist sector slows down, capital may move out of the country as the economy is an open one. This may in turn lead to balance of payments problems and the problem of stability of rate of exchange.
Critical Review of the Lewis’s Model
Some of the objections against Lewis’s model are as follows:
- The assumption that disguised unemployment exists in the agriculture sector has not been accepted by many economists. Schultz, Viner, Heberler and Hopper are a few of such economists. According to them, the production in the subsistence sector will be affected when labour is withdrawn from it.
- Lewis ignored the cost involved in training the unskilled worker transferred from the subsistence sector. Even if it is obtained at a constant wage rate, so for as its transfer from the subsistence sector is concerned, the supply curve may slope upwards so far as the capitalist, sector is concerned if the cost of training rises as more and more labour is transferred.
- When labour is transferred from the subsistence sector share of agricultural output falling to each one left in the agricultural sector will go a rising. This means the institutional wage will go on rising with every transfer and so will be the wages paid in the capitalist sector.
- The model assumes that, besides labour, there is unlimited supply of entrepreneurs in the capitalist sector. This is not true in the case of many of the underdeveloped countries.
- It is wrong to assume that a capitalist will always re-invest their profits. They to can indulge in un-productive pursuits. They can use their profits for speculative purposes.
- It is also wrong to assume that landlords always squander away their savings. The role of landlords of Japan in industrialisation of the country is well known.
- The model assumes that there already exists a market for the industrial products in the country. This is wrong. People of an underdeveloped country may not be able to purchase the products perturbed by the expanding capitalist sector. Foreign markets, too, may not be available to the capitalist sector in the beginning.
- Inflation is not liquidating, as has been assumed by Lewis, Experience of various, countries shows that if once prices start rising, it, becomes difficult to control them.
- It is not easy to transfer labour from the subsistence Sector to the capitalist sector by offering them an incentive of a little higher wage.
- Mobility of labour is very low. Many factors like family affection, difference in language, caste, religion etc. affect it adversely.
- Every underdeveloped country does not have surplus labour in the subsistence sector. As such, the model does not apply to countries which are sparsely populated.
The only positive point in the model is its ‘general’ emphasis on the role of saving in economic development and on the potential that overpopulated countries have in developing themselves with the help of surplus labour.
|
846 videos|1297 docs|420 tests
|
FAQs on Lewis Model of Economic Development - NABARD Grade A & Grade B Preparation - Bank Exams
| 1. What is the Lewis Model of Economic Development? |  |
| 2. What are the assumptions of the Lewis Model? |  |
| 3. How does the Lewis Model work? |  |
| 4. What is the role of bank credit in the Lewis Model? |  |
| 5. What are the criticisms of the Lewis Model? |  |















