Measures of Economic Development and Social Welfare | NABARD Grade A & Grade B Preparation - Bank Exams PDF Download
Introduction
- The nation’s economic development and social welfare are also considered to measure the nation’s prosperity. Economic development is a concept and an activity in general to assess the core competencies of a nation and it’s innovation, and use the of available resources.
- This process improves the political, economic, and social well being of the people. When we discuss economic development we often discuss terms like modernization, industrialization, and so on. Many times you confuse industrial development with economic development.
Measures of Economic Development and Social Welfare

Economic development is just policy with aims at improving the social well-being as well as economic conditions of the nation.
While economic growth is a result of rising in GDP as well as market productivity. There are various needs we need to consider while measuring economic development. Here, below we will explain these factors in detail.
- Rise in real per capita income
- Quality of life and expectancy
- Real gross national product
- Human development index
- Gender-related development index
- Poverty index
Rise in Real per Capita Income
- One of the factors that measure the economic development of a nation is the rise in real per capita income.
- There’s a perception that whenever the income of individual increases than it’s real income increases.
- And when this happens the person is happy and prosperous. But there are some limitations to this.
- These limitations through per capita income do not determine whether the rise is due to equal distribution or unequal distribution.
- Same is the case with the quality of goods and services being provided and consumed. Further, the quality of public goods also affects economic welfare.
Quality of Life and Expectancy
- When the basic facilities like water, electricity, and housing are available to anyone that the quality of life is considered as good in that nation.
- Here the measuring factor is the needs of the people. These needs are basic needs like access to health, sanitation, education, nutrition, etc.
- For this, the main factor is the infant mortality rate. This is the death rate of a child who is less than a year old. While life expectancy is the average life of the population that lives.
Real Gross National Product
- As mentioned above, GNP, as well as GDP, are the measuring factors for economic development of a nation. Increase in both of these ensures that the larger availability of the good and services in that country. If this supports the standard of living of the people than it increases the economic conditions of the nation.
- But there are some limitations to this as well. Like the increase in the size of GDP does not directly means the more availability of services and goods.
- Whenever the GDP is calculated for the current prices, there may be an increase due to price rise. This does not mean the availability of goods and services have increased.
Human Development Index
- It includes several factors like long and healthy living, the welfare of the people, etc. This index also includes the standard of living of people, literacy rate, and purchasing power parity in terms of real income.
- The Human Development Index (HDI) was developed by two economists – Prof. Mehbub Al Haque of Pakistan and Prof. Amartya Sen of India in 1990.
- Since 1993, HDI has been used by the United Nations Development Programme (UNDP) each year to calculate the Human Development Index (HDI) and publish it as a report which is known as Human Development Report (HDR).
- The HDI was created to emphasize that people and their capabilities should be the ultimate criteria for assessing the development of a country, not economic growth alone.
HDI Indicators
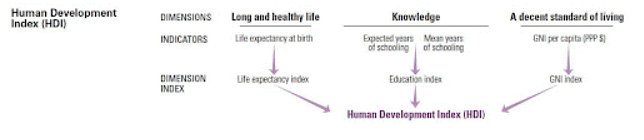
- The HDI captures there dimensions which are long and healthy life, knowledge/Education and a decent standard of living.
- The health dimension is assessed by life expectancy at birth, the education dimension is measured by means of years of schooling for adults aged 25 years and more, and expected years of schooling for children of school entering age. The standard of living dimension is measured by gross national income per capita.
- The above mentioned dimensions are measured by the following indicators:
- Life Expectancy Index: Calculated from Life expectancy at birth.
- Education Index: Calculated from Mean years of schooling and Expected years of schooling
- Income Index: Calculated from GNI per capita (PPP USD).
Categories of Human Development
- Human development is defined as the process of expansion of human capabilities, a widening of choices, a fulfillment of human rights, an enhancement of freedom and opportunities and improving their well-being.
- According to the United Nations, there are three essential choices for people which are: leading a long and healthy life; acquiring knowledge; and having access to the resources needed for a decent standard of living.
- Countries fall into four broad human development categories based on HDI index: Low human development, Medium human development, High Human Development and Very High Human Development.

What are the consequences and implications?
- The HDI is used to capture the attention of policy-makers, the media and nongovernmental organizations, and to change the focus from the usual economic statistics to human outcomes. It was created to re-emphasize that people and their capabilities should be the ultimate criteria for assessing the development of a country, not economic growth.
- The HDI is also used to question national policy choices and to determine how two countries with the same level of income per person can have widely different human development outcomes. For example, two countries may have similar incomes per person, but have drastically differing life expectancy and literacy levels, such that one of the countries has a much higher HDI than the other. These contrasts stimulate debate on government policies concerning health and education to determine why what can be achieved in one country is beyond the reach of the other.
- The HDI is also used to highlight differences within countries, between provinces or states, and across genders, ethnicities and other socioeconomic groupings. Highlighting internal disparities along these lines has raised the national debate in many countries.
Note: HDI Rank of India 2023: This score is a remarkable improvement compared to the South Asian region’s average value of 0.508 and is close to the world average of 0.465, and India ranks 132 out of 191 countries.
Gender-related development index
- This is popularly known as GDI. This is used to measure gender inequalities by measuring three basic dimensions of human development. They are education, health, and economic resources.
- They measure education by calculating expectancy years for schooling for males and females. While health measures the male and female life expectancy during the time of birth.
- While economic resources are the command over them is measured by income earned by males as well as females. This index is useful to show the inequality between male and female in the above-mentioned dimensions.
Poverty Index
- The poverty index which is otherwise called multidimensional poverty index aka MPI helps in identifying various factors. These various factors are health, the standard of living, and education.
- For this index, the microdata which is available from surveys is used. This data is collected on the basis of deprivation of toilet, water, cooking fuel, assets, etc. Based on the availability of these factors each person is termed as poor and nonpoor.
- The indicators are decided on this basis. For education, they consider two factors, school attainment, and school attendance. School attainment is to determine when no member of the family has attended at least 6 years of schooling.
- While school attendance is determined when the child is of the school age is not attending the school. Similarly, for health, the factors are child mortality and health.
- While for the standard of living the factors are drinking water, electricity, sanitation, and cooking fuel.
|
847 videos|1297 docs|420 tests
|
FAQs on Measures of Economic Development and Social Welfare - NABARD Grade A & Grade B Preparation - Bank Exams
| 1. What are some measures of economic development and social welfare? |  |
| 2. How does the rise in real per capita income contribute to economic development and social welfare? |  |
| 3. What is the Human Development Index (HDI) and how does it measure a country's development level? |  |
| 4. How does the Gender-related Development Index (GDI) measure gender equality in a country? |  |
| 5. How does the Poverty Index assess poverty and income inequality within a country? |  |
















