UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Economics Optional for UPSC > International Trade Dynamics: Terms of Trade, Offer Curve, and Strategic Trade Theories
International Trade Dynamics: Terms of Trade, Offer Curve, and Strategic Trade Theories | Economics Optional for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Terms of Trade and Offer Curve |

|
| Product Cycle Theory of International Trade |

|
| Strategic Trade Theories |

|
| Trade as an Engine of Growth |

|
| Theories of Underdevelopment In An Open Economy |

|
Terms of Trade and Offer Curve
- The ‘terms of trade’ is the international price ratio. It is the ratio of the price of exports to the price of imports.
- In the case of two trading countries, because one country’s imports are another’s exports, the terms of trade of one country are just the inverse of the terms of trade of the other country.
- The domestic equivalent of the terms of trade for a private individual is the price of the things sold by the individual divided by the cost of the things bought. The terms of trade for a private individual is the nominal real wage divided by the price index or the cost of living.
- The Offer curve is also called the reciprocal demand curve of a country. The curve shows the number of imports and exports that a country is willing to buy and sell on the world market at all the possible relative prices.
- In other words, it shows the country’s willingness to trade at various possible terms of trade. It is a combination of the demand for imports and the supply of exports.
- Considering the two countries to be X and Y, one should look at the following graph:
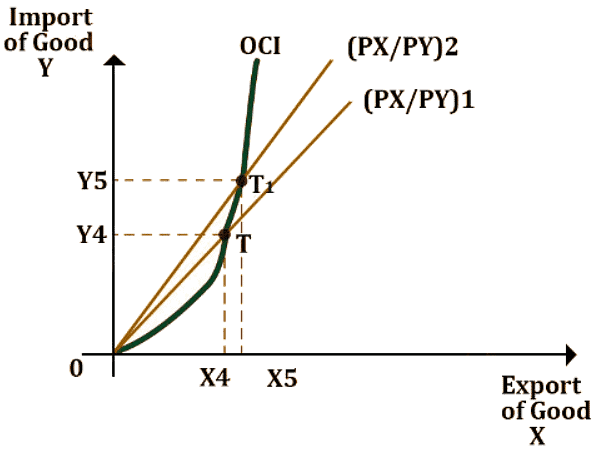
- At point T, the export quantity of Good X equals the import quantity of Good Y. The price ratio can be regarded as terms of trade. The figure represents a steeper price line which means that the country ll will respond by increasing the quantity of Good X that is to be exported.
- With this, Country ll’s curve is as follows:
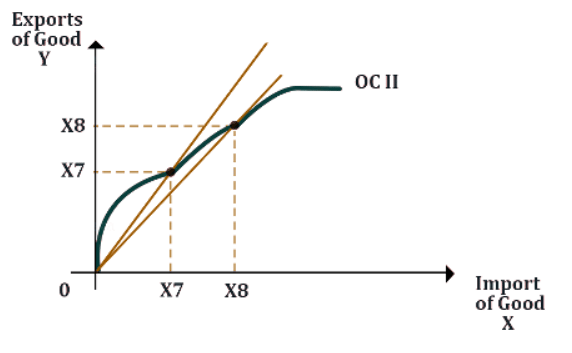
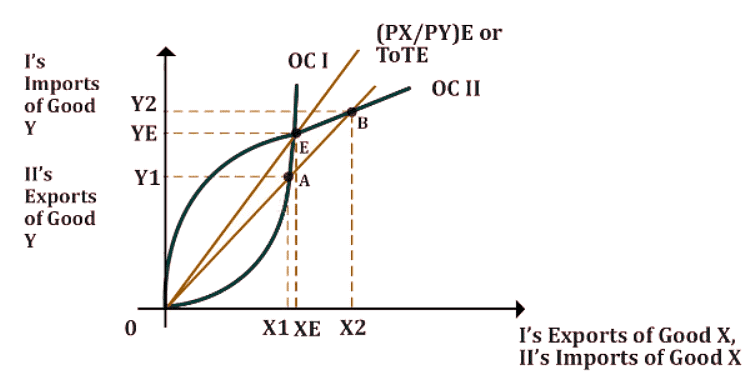
- Bringing together the equilibrium of both countries, the new graph comes out to be:
Question for International Trade Dynamics: Terms of Trade, Offer Curve, and Strategic Trade TheoriesTry yourself: What does the terms of trade represent?View Solution
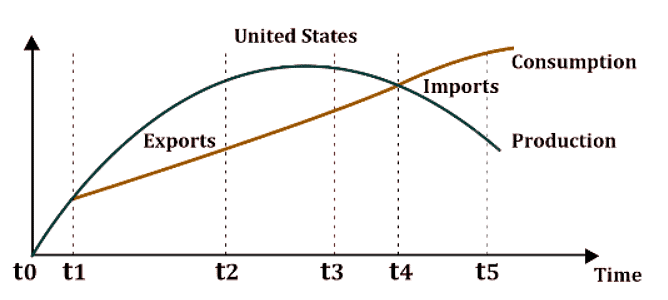
Product Cycle Theory of International Trade
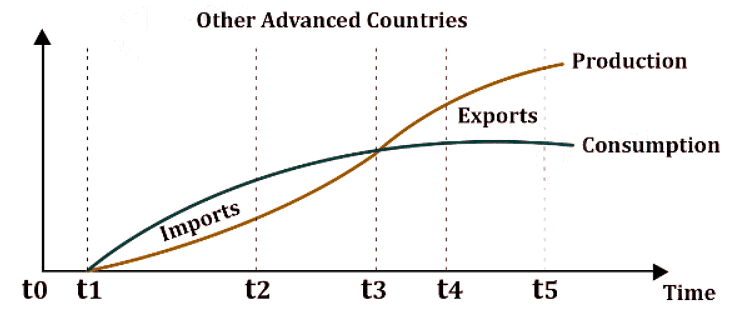
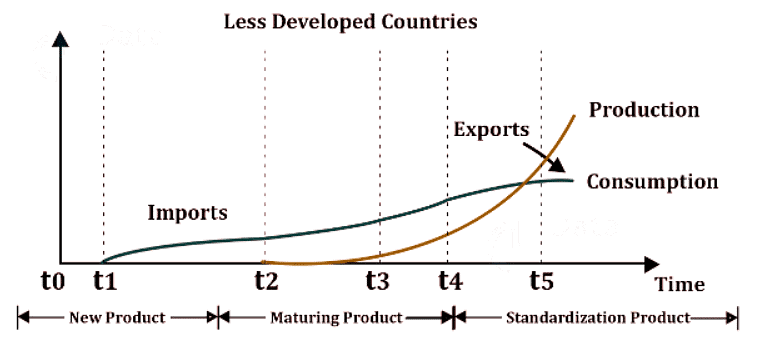
Strategic Trade Theories
- The Strategic Trade Theory or the Strategic Trade Policy talks about the policies that are adopted by various countries. These policies affect the outcome of strategic interactions between firms in an international oligopoly or an industry that is dominated by a small number of firms.
- The term ‘strategic’ here refers to the interactions between the firms. This theory believes that trade policies can raise the level of domestic welfare in a particular state by shifting profits from foreign to domestic firms. It emphasizes the significance of trade agreements that restrict the interventions.
Trade as an Engine of Growth
A rise in trade can help a nation grow and bloom into a better economy that serves its people and the trade.
Some of the positive effects of the trade on a nation are:
- It hampers employment opportunities in the country.
- Trade helps the industries grow.
- It helps to maintain and enhance relations with the trading countries.
- Marks nation’s presence in the world.
- Hampers the Gross Domestic Product of the nation.
Theories of Underdevelopment In An Open Economy
Though there are several theories of Underdevelopment that have been bought up by different economists, the three major ones are the Classical Marxian Theory, the Neo-Marxian Theory, and the Dependency and the Dualism theory.
a. Classical Marxian Theory
- The theory is implicit in Marx’s study of the laws of motion of the capitalist mode of production in 3 volumes of Capital.
- Marx claimed that the introduction of capitalism in India was a necessary evil. He claims that the prospects for the development of capitalism crucially depend upon the pre-existing modes of production.
- He considers the “Asiatic” mode of production as a “prehistoric” in a sense that it had remained in a state of primordial animation and stagnation till the contact with European capitalism.
b. Neo-Marxian Theory
- The failure of capitalism helped to encourage economic development in the former colonial regions as Marx had envisaged, and gave a rise to the neo-Marxian theories of underdevelopment.
- There is a consensus that the modern capitalist system can be further divided into an advanced “center” or metropolis, and an underdeveloped “periphery”. The causes of underdevelopment become one of the central focuses of analysis.
c. Dependency and Dualism Theory
- Here, Underdevelopment is an externally-induced process that is preserved by a small but influential domestic elite who ally with the international capitalist system.
- Therefore, systemic and path-dependent is the development of underdevelopment. Here, the concept of hegemony acquires a strategic meaning. From the historical perspective, capital accumulation has been governed by the law of ‘uneven development’.
- Critics argued that capital movements tend to increase regional inequality by concentrating on the more developed regions.
Question for International Trade Dynamics: Terms of Trade, Offer Curve, and Strategic Trade TheoriesTry yourself: What is the terms of trade?View Solution
The document International Trade Dynamics: Terms of Trade, Offer Curve, and Strategic Trade Theories | Economics Optional for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Economics Optional for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
66 videos|222 docs|73 tests
|
FAQs on International Trade Dynamics: Terms of Trade, Offer Curve, and Strategic Trade Theories - Economics Optional for UPSC
| 1. What are terms of trade and how do they affect international trade? |  |
Ans. Terms of trade refer to the ratio at which a country exchanges its exports for imports with another country. It indicates the purchasing power of a country's exports in terms of imports. If a country's terms of trade improve, it means it can import more goods for the same amount of exports. This can lead to increased welfare and economic growth. Conversely, if a country's terms of trade deteriorate, it means it needs to export more to afford the same amount of imports, which can negatively impact its economy.
| 2. What is the offer curve and how does it relate to international trade? |  |
Ans. The offer curve represents the various combinations of goods that a country is willing and able to export at different relative prices of those goods. It shows the relationship between the price ratio of two goods and the quantity of each good that a country will export. The offer curve is upward sloping, indicating that as the relative price of a good increases, the country's willingness to export that good also increases. The offer curve is a crucial tool in understanding a country's export behavior and its position in international trade.
| 3. How does the product cycle theory of international trade explain the pattern of trade between countries? |  |
Ans. The product cycle theory suggests that the pattern of trade between countries is influenced by the life cycle of a product. According to this theory, when a new product is introduced, it is initially produced in the country where it was invented. As the product matures, production shifts to other countries with lower production costs. Eventually, the original innovating country becomes a net importer of the product. This theory explains why certain countries specialize in the production of specific goods at different stages of their life cycle, leading to trade between countries.
| 4. What are strategic trade theories and how do they impact international trade? |  |
Ans. Strategic trade theories argue that governments can play a proactive role in promoting certain industries to gain a competitive advantage in international trade. These theories suggest that strategic government intervention, such as subsidies or trade barriers, can help domestic firms overcome market failures and achieve economies of scale. By supporting specific industries, governments can create a favorable environment for their growth, leading to increased exports and economic prosperity. However, strategic trade policies can also lead to trade disputes and retaliation from other countries.
| 5. How does trade act as an engine of growth for countries? |  |
Ans. Trade plays a crucial role in driving economic growth for countries. By engaging in international trade, countries can specialize in the production of goods and services in which they have a comparative advantage. This allows them to enhance their productivity, efficiency, and innovation. Trade also facilitates the transfer of technology, knowledge, and ideas between countries, promoting economic development. Additionally, trade provides access to larger markets, increases competition, and stimulates investments, which further contribute to economic growth.
Related Searches















