Spectrum Summary: The NDA Years (1998–2004) | History for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Introduction
The National Democratic Alliance (NDA) was in government for two terms: first from March 1998 to October 1999 and then from October 1999 to May 2004.
National Democratic Alliance NDA Government: First Stint (March 1998-October 1999)
- After the 1998 elections, the BJP formed the National Democratic Alliance (NDA) with various regional parties.
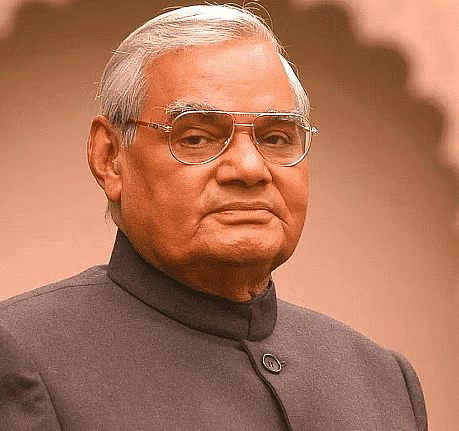
- Atal Bihari Vajpayee from the BJP became the leader of the NDA and was sworn in as prime minister in March 1998 for the second time.
- The NDA successfully demonstrated its majority in the Lok Sabha.
- The government's duration was extended until April 1999 when the AIADMK withdrew from the NDA.
- A key no-confidence motion on April 17, 1999, resulted in the government's defeat by a single vote, mainly due to Giridhar Gamang's decision.
- Despite serving as the chief minister of Orissa, Gamang's position as an MP was crucial in the government's loss.
- With no suitable alternative from the Opposition to form a new government, President K.R. Narayanan dissolved the Lok Sabha.
- New elections were held in September–October 1999, during which Vajpayee remained as caretaker prime minister until a new government was formed.
- Meanwhile, Sharad Pawar and other leaders left the Congress due to disagreements when the party elected Sonia Gandhi as its leader.
- The brief period of Vajpayee's government saw several significant events.

Pokhran II: Operation Shakti
- In May 1998 , India conducted a series of five nuclear explosions at the Pokhran Test Range, located in the Thar Desert of Rajasthan. This operation was part of Operation Shakti and marked a significant moment in India’s nuclear history.
- The tests included the underground explosion of various types of nuclear devices: a regular fission device, a fusion device, and a sub-kiloton device. These tests aimed to demonstrate and verify India’s nuclear capabilities and advancements in nuclear technology.
- Following the successful tests, Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee held a press conference to officially declare India a full-fledged nuclear state . This declaration highlighted India’s position as a responsible nuclear power and its commitment to maintaining strategic stability.
- Key figures in the success of Operation Shakti included A.P.J. Abdul Kalam , who played a crucial role in the planning and execution of the tests and later became the President of India, and R. Chidambaram , the Director of the Department of Atomic Energy, who oversaw the scientific and technical aspects of the operation.
May 11 is celebrated as National Technology Day to honor the nuclear tests conducted on this day in 1998 .
- The tests were carried out in secret, catching the US and the world by surprise. This led to a significant downturn in US-India relations .
- In reaction to the tests, the US implemented the Glenn Amendment for the first time, imposing new sanctions on India.
- In response to India’s nuclear tests, Pakistan conducted its own nuclear tests, known as Chagai I and II , later in May 1998 .
- In June 1998 , the UN Security Council passed a resolution condemning both India and Pakistan for their nuclear tests.
The Lahore Summit
- In late 1998 and early 1999 , Prime Minister Vajpayee made efforts to establish a peaceful diplomatic relationship with Pakistan .
- A significant step in this direction was the initiation of the Delhi-Lahore bus service in February 1999 .
- Prime Minister Vajpayee personally traveled to Lahore on this new bus service, marking a important moment in India-Pakistan relations.
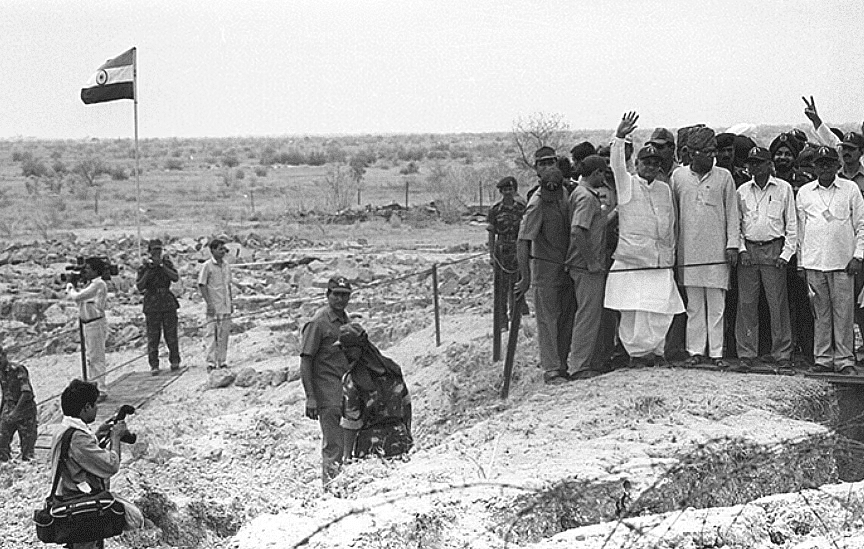

Lahore Declaration
- In February 1999, during a summit in Lahore, Indian Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee and Pakistani Prime Minister Nawaz Sharif signed the Lahore Declaration .
- This agreement demonstrated a mutual commitment to several key principles, including:
- Encouraging meaningful dialogue between India and Pakistan.
- Enhancing trade relations for mutual benefit.
- Cultivating a friendly atmosphere.
- Avoiding interference in each other's internal matters.
- Taking immediate steps to reduce the risk of accidental or unauthorized use of nuclear weapons .
- The leaders also condemned terrorism in all its forms and expressed their determination to combat it, along with a commitment to protecting all human rights and fundamental freedoms.
Kargil Conflict
- The events following the Lahore Declaration had a significant impact on Indo-Pak relations, particularly evident in the Kargil conflict .
- Just three months after the Lahore summit, armed militants and Pakistani soldiers infiltrated Kashmir , taking control of strategic locations such as hilltops and unmanned border posts.
- This operation was orchestrated by the Pakistani military under General Pervez Musharraf , without the knowledge of the civilian prime minister, and focused on the Kargil district.
- The Indian Army became aware of the infiltration in May 1999 through reports from local shepherds.
- In response, a coordinated effort by the Indian Army and Air Force, named 'Safed Sagar' , was launched to counter the infiltration, with strict orders not to cross the Line of Control .
Captain Vikram Batra
Operation Vijay
- Operation Vijay was successful, with Indian forces recapturing crucial peaks, including Tiger Hill in the Drass sector.
- These peaks were vital because they overlooked the Srinagar-Leh highway, an important all-weather road link between Srinagar and Leh.
- In June 1999, Pakistani Prime Minister Nawaz Sharif sought U.S. intervention, but President Bill Clinton declined to mediate until Pakistani troops withdrew from the Line of Control.
- Following this, Nawaz Sharif ordered the suspension of the Pakistani military operation.
- The war concluded on July 26, 1999, with India emerging victorious in Kargil.
- The Kargil victory boosted Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee's image as a decisive and sensible leader, evoking patriotic sentiments among the public.

NDA: Second Stint (October 1999-May 2004)
The memory of the Kargil war was fresh in people's minds as the country approached the 1999 elections. There was great public support for the NDA , especially for the prime minister. The election results gave the NDA, led by the BJP , a majority, with backing from new allies like the Janata Dal (United) and the DMK .
On October 13, 1999 , Atal Bihari Vajpayee was sworn in as prime minister for the third time.
Economic and Social Steps
- The NDA government built upon the economic reforms started by the Narasimha Rao government.
- There was a strong focus on infrastructure development, particularly in telecom and highways , including the National Highways Development Project and the Golden Quadrilateral .
- The launch of the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana focused on improving rural connectivity by providing all-weather roads.
- The government actively supported the services sector , especially the software industry .
- A new telecom policy was introduced, and state monopolies like VSNL were privatised.
- Fiscal changes, such as duty-free imports , were made to boost economic growth.
- The Disinvestment Commission was upgraded to a ministry.
- Opening the economy attracted foreign companies to invest in Indian markets, particularly from Europe and the US .
- The Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act of 2003 aimed at instilling financial discipline, reducing fiscal deficits, and improving public fund management.
- The Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan , launched in 2000-2001 , aimed for universal elementary education.
- The Constitution 86th Amendment Act, 2002 , included the right to education in the Fundamental Rights of the Constitution.
Terrorist Trouble and Relations with Pakistan
- In December 1999 , Pakistani terrorists hijacked Indian Airlines flight IC 814 from Nepal, taking it to Taliban-controlled Afghanistan. The government agreed to the terrorists' demands, which led to the release of individuals, including Maulana Masood Azhar , in exchange for the passengers' freedom.
- This incident worsened relations between India and Pakistan.
- In July 2001 , Prime Minister Vajpayee tried to improve relations by inviting Pakistan's President Pervez Musharraf for talks in Delhi and Agra, but no agreement was reached as Musharraf insisted on discussing the Kashmir issue.
- The attack on the Parliament House in December 2001 by terrorist groups Lashkar-e-Taiba and Jaish-e-Mohammed further strained relations.
- In response to these attacks, the government passed the Prevention of Terrorism Act (POTA) .
Relations with the US
- India strengthened its relationship with the United States , highlighted by a visit from President Clinton .
- Efforts were made to improve trade relations and cooperation on strategic matters.
Kashmir Elections
- In September 2002 , elections were held in Kashmir, with the Election Commission ensuring fair and free elections.
- Despite calls from militants to boycott the elections, people voted actively, resulting in the National Conference losing power.
- The Congress-Peoples Party alliance won the elections.
The Downside
- In 2001 , Defence Minister George Fernandes resigned due to the Barak Missile Deal scandal and issues concerning the supply of coffins for Kargil soldiers.
- An inquiry suggested that the government could have prevented the Kargil incursion.
- BJP chief Bangaru Laxman faced controversy after allegedly accepting a bribe in a media sting operation.
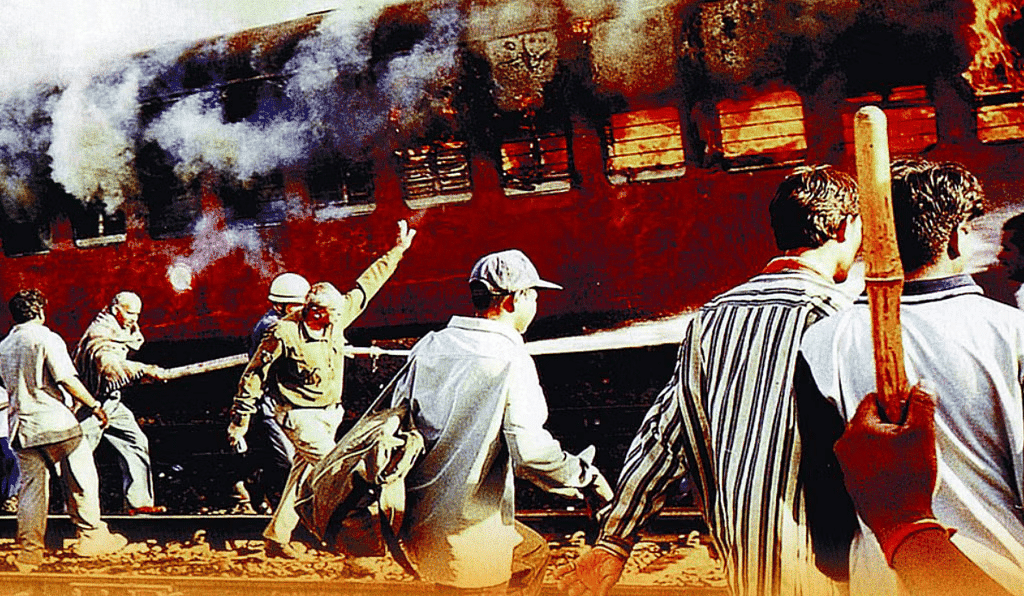
- The Sabarmati Express caught fire in February 2002 in Godhra , Gujarat, leading to the deaths of many pilgrims returning from Ayodhya .
- It was believed that a Muslim mob set fire to the train, causing severe communal riots in Ahmedabad and Vadodara .
- The riots were seen as a pogrom, with violence directed at Muslims. Narendra Modi , the Chief Minister of Gujarat at the time, faced harsh criticism for not controlling the violence.
- Prime Minister Vajpayee condemned the events and reportedly considered asking Modi to resign, although internal party dynamics stopped him from doing so.
Significance of NDA
- The NDA government achieved the notable milestone of completing nearly its entire term, which was a first for a non-Congress government.
- Prime Minister Vajpayee effectively navigated the challenges of coalition politics, managing a multi-party alliance successfully.
- The NDA's term completion showcased a credible alternative to Congress , essential for a strong democracy.
- The government introduced significant programmes during its tenure, and its commitment to further liberalising the economy proved beneficial for India.
2004 General Elections
- The government opted for early polls, leading to the dissolution of the Lok Sabha in February .
- Voting occurred in April-May 2004 .
- With the slogan 'India Shining' and recent assembly election victories in Rajasthan , Madhya Pradesh , and Chhattisgarh , the government felt confident.
- However, the public's sentiment differed from the government's optimism, and the focus on economic issues may not have pleased BJP supporters on ideological grounds.
- The outcome resulted in the NDA's loss, with Congress , led by Sonia Gandhi , emerging as the single largest party.
Terrorist Issues and Relations with Pakistan
- In December 1999, terrorists from Pakistan hijacked Indian Airlines flight IC 814, taking it from Nepal to Afghanistan, which was under Taliban rule.
- The Indian government agreed to the terrorists' demands, resulting in the release of certain individuals, including Maulana Masood Azhar , in exchange for the passengers' safety.
- This incident significantly worsened the relationship between India and Pakistan .
Efforts to Improve Relations
- In July 2001, Prime Minister Vajpayee extended an invitation to Pakistan’s President Pervez Musharraf for a summit and peace talks in Delhi and Agra.
- However, no significant progress was made as Musharraf focused on the Kashmir issue.
- The situation further deteriorated after the December 2001 attack on the Parliament House in Delhi by Lashkar-e-Taiba and Jaish-e-Mohammed terrorists.
- In response to these attacks and other terrorist incidents, the Indian government successfully passed the Prevention of Terrorism Act (POTA) .
Relations with the United States
- During this period, India strengthened its ties with the United States , highlighted by a visit from President Bill Clinton .
- Efforts were made to enhance trade relations and foster cooperation on strategic issues between the two countries.
Kashmir Elections
- In September 2002, elections were held in Kashmir , overseen by the Election Commission to ensure their fairness and integrity.
- Despite calls from militants to boycott the elections, there was enthusiastic participation from the people.
- As a result, the National Conference lost power, and the Congress-Peoples Party alliance emerged victorious.
The Negative Aspects
- In 2001, Defence Minister George Fernandes resigned due to the Barak Missile Deal scandal and issues concerning the supply of coffins for Kargil soldiers.
- An inquiry commission suggested that the government could have potentially prevented the Kargil incursion with better intelligence and preparedness.
- The BJP party chief Bangaru Laxman faced controversy after allegedly accepting a bribe, captured in an early media sting operation.
- In February 2002, the Sabarmati Express caught fire in Godhra , Gujarat, resulting in the deaths of several pilgrims and kar sevaks returning from Ayodhya.
- It was widely believed that a Muslim mob set fire to the compartments, triggering communal riots with extreme violence, primarily in Ahmedabad and Vadodara .
- The riots, considered a pogrom, involved targeted violence against Muslims.
- Narendra Modi , the Chief Minister of Gujarat at the time, faced severe criticism for allegedly failing to control the situation.
- Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee officially condemned the events, and there were speculations that he considered asking Modi to resign.
Importance of NDA
- The NDA government achieved the notable accomplishment of completing nearly its entire term, a first for a non-Congress government in India.
- Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee exhibited skill in navigating the complexities of coalition politics, effectively managing a multi-party alliance.
- The successful completion of the NDA's term signified the emergence of a credible alternative to the Congress party at the national level, crucial for a functioning democracy.
- The government introduced several notable programs and initiatives during its tenure, contributing to India’s development.
- The commitment to further liberalize the economy under the NDA proved advantageous for India's economic growth and development.
2004 General Elections
- The NDA government opted for early elections, leading to the dissolution of the Lok Sabha in February 2004.
- Elections were conducted in April-May 2004.
- The government, buoyed by its slogan 'India Shining' and successes in assembly elections in Rajasthan , Madhya Pradesh , and Chhattisgarh , was optimistic about its prospects.
- However, the ground sentiment differed from the government’s expectations.
- The campaign’s focus on economic issues may have disappointed supporters who backed the BJP on ideological grounds.
- Ultimately, the NDA lost, with the Congress party , led by Sonia Gandhi , emerging as the single largest party in the Lok Sabha.
Government Actions in Response to Terrorism
- The government met the terrorists' demands, resulting in the release of specific individuals, including Maulana Masood Azhar , in exchange for the passengers' freedom.
Attempts to Improve Relations
- In July 2001 , Prime Minister Vajpayee made an effort to improve relations by inviting Pakistan’s President Pervez Musharraf to Delhi and Agra for a summit and peace discussions.
- However, no progress was made as Musharraf insisted on addressing the Kashmir issue.
- In December 2001 , the attack on the Parliament House in Delhi by Lashkar-e-Taiba and Jaish-e-Mohammed terrorists further deteriorated Indo-Pakistani relations.
- In response to this attack and other terrorist incidents, the government successfully enacted the Prevention of Terrorism Act ( POTA ).

Elections in Kashmir and Other Significant Events
In September 2002, elections were held in Kashmir under the supervision of the Election Commission , which ensured that the process was fair and free. Despite militant groups urging a boycott, the public participated enthusiastically, leading to the National Conference losing power. The Congress and People's Party formed the winning alliance.
Important Events Leading Up to the Elections
- In 2001, Defence Minister George Fernandes resigned amidst the Barak Missile Deal scandal and controversies regarding the supply of coffins for Kargil soldiers.
In February 2002, a tragic incident occurred when the Sabarmati Express caught fire in Godhra , Gujarat , resulting in the deaths of several pilgrims and kar sevaks returning from Ayodhya .

Document Review
Riots in Gujarat
- There was a strong belief that a Muslim mob was responsible for setting fire to the train compartments, which triggered communal riots marked by severe violence, mainly in Ahmedabad and Vadodara .
- During this chaotic period, Narendra Modi , the Chief Minister of Gujarat, faced intense criticism for his alleged inability to control the situation.
- Prime Minister Vajpayee publicly condemned the violent events, and it is widely thought that he considered the possibility of asking Modi to resign. However, due to the internal dynamics of the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), he refrained from taking such action.
NDA Government's Term
- The National Democratic Alliance (NDA) government made history by completing its full term, marking the first time a non-Congress government achieved this feat.
- Prime Minister Vajpayee showcased his skill in handling the intricacies of coalition politics , successfully managing a diverse multi-party alliance.
- The NDA's ability to complete its term signified the emergence of a credible alternative to the Congress party at the national level, which is vital for the functioning of a genuine democracy.
- Throughout its tenure, the government introduced several significant programs and remained committed to further liberalising the economy, a move that proved advantageous for India under the NDA.

Election Outcomes and Changes in Government
- The government declared early elections, resulting in the dissolution of the Lok Sabha in February.
- Elections were held in April-May 2004.
- With the slogan 'India Shining' and wins in state elections in Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, and Chhattisgarh, the government felt optimistic.
- However, public sentiment differed from this optimism.
- The emphasis on economic issues may have disappointed BJP supporters who prioritized ideological concerns.
- As a result, the NDA faced a loss, impacting governance and policy direction.
- The Congress party, led by Sonia Gandhi , emerged as the single largest party.
|
216 videos|853 docs|219 tests
|
FAQs on Spectrum Summary: The NDA Years (1998–2004) - History for UPSC CSE
| 1. What were the two stints of the NDA government and when did they take place? |  |
| 2. What happened in the 2004 General Elections? |  |
| 3. How long did the NDA government serve in total during the years 1998-2004? |  |
| 4. Can you provide a brief overview of the NDA government's achievements during their time in power? |  |
| 5. What were the major challenges faced by the NDA government during their tenure? |  |
















