Ramesh Singh Summary: External Sector in India- 3 | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Forex Management and Impossible Trinity |

|
| Trade Facilitation |

|
| Trade Logistics |

|
| India's Trade |

|
| India as Pharmacy of the World |

|
| The Quad |

|
| Trade Settlement in INR |

|
| Way Forward |

|
Introduction
India's external sector is a key driver of economic dynamics, encompassing international trade, foreign exchange reserves, and strategic alliances. Understanding this sector sheds light on India's economic resilience, diplomatic engagements, and global positioning. Explore the nuances of trade relations, geopolitical considerations, and policy interventions for insights into India's external economic interactions.
Forex Management and Impossible Trinity
The remarkable surge in forex reserves by early 2021 was primarily driven by a substantial current account surplus, propelled by reduced imports rather than increased exports. This surplus was further bolstered by substantial foreign direct investment (FDI) and foreign portfolio investment (FPI), resulting in a significant Balance of Payments (BoP) surplus. In economic terms, the current account balance mirrors the equilibrium between savings and investment.
- A surplus in the current account signifies higher national savings compared to investment. Accumulation of forex reserves, indicating investments in foreign bonds and securities, implies a deployment of funds outside India. Although essential for domestic investments, this surplus also provides room for heightened investment expenditures. Confronted with a substantial BoP surplus, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) faced the dilemma of either absorbing the surplus by acquiring it from the forex market, leading to increased forex reserves, or allowing the rupee to appreciate.
- In the face of inflation primarily attributed to supply-side disruptions, the RBI opted to intervene in the forex market, accumulate reserves, and prevent a one-sided appreciation of the rupee. This strategy complemented an expansionary monetary policy, characterized by a reduction in the repo rate. However, the RBI had the delicate task of managing headline inflation effectively while stimulating economic growth.
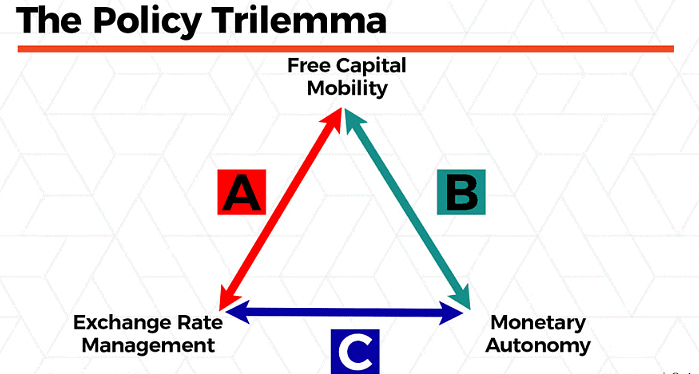
- According to the Economic Survey 2020-21, the accumulation of forex reserves resulted in the concurrent release of rupees into the system. This facilitated the government's higher borrowings, given the lower inflation. Nevertheless, when headline inflation exceeded the policy band (4-6%), the RBI encountered the classic challenge known as the Impossible Trinity or the Mundell-Fleming trilemma. This involves maintaining an open capital account, a stable exchange rate, and independently conducting monetary policy.
- Emphasizing the importance of robust export earnings for sustainable external sector management, the government is dedicated to enhancing exports through trade facilitation measures. This includes reducing transaction costs and time, ultimately boosting export competitiveness.
Trade Facilitation
With the objective of minimizing trade barriers arising from inefficient and burdensome regulatory administrative procedures, the Trade Facilitation Agreement (TFA) was enacted at the WTO in February 2017. Subsequently, the formation of a National Committee on Trade Facilitation (NCTF) took place in August 2016, with the Cabinet Secretary leading the initiative. A National Trade Facilitation Action Plan (NTFAP) for 2017-2020, outlining specific activities to alleviate trade bottlenecks, was devised.
- For the period 2020-2023, a new NTFAP is currently in preparation, aiming to introduce additional reforms to strengthen facilitation efforts and transform the cross-border clearance ecosystem. The emphasis is on efficiency, transparency, risk-based approaches, coordination, seamlessness, and technology-driven solutions.
- India has actively taken strides in implementing Trade Facilitation Agreement under the guidance of the NCTF. Several commitments notified by the WTO, initially due by 2022, have already been implemented by 2021. Key accomplishments include the establishment of a Single Window (Article 10) and the introduction of Risk Management for Clearance of Goods (Article 7.4).
- Transparency notifications, covering information on import and export procedures, enquiry points, and single windows, were executed in April 2019. Additionally, various regulatory relaxations were extended during the COVID-19 pandemic to facilitate trade. These measures include 24x7 clearance, dedicated single window, delayed filing of import declarations, waiver of late filing fees, and acceptance of undertakings instead of bonds.
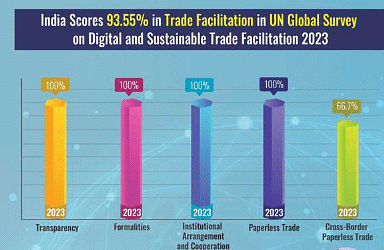
- These initiatives underscore India's commitment to transparent and open trade. Positioned at the forefront, India continues to take initiatives to maximize predictability and automation in trade, as reflected in the consistent improvement on the United Nations' Global Survey on Digital and Sustainable Trade.
Trade Logistics
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic has emphasized the necessity for a resilient logistics sector capable of responding to emergencies and disruptions in the supply chain. Despite facing functional challenges such as fragmented ownership, limited consolidation in operations, sub-optimal modal share favoring road transport, absence of a unified ministry and agencies, and inconsistent policies and regulations, India has shown remarkable progress in the logistics sector, as indicated by leading global indices.
- India scored 70.3% in the 2021 Global Survey on Digital and Sustainable Trade Facilitation by the UNESCAR, marking a significant improvement from 78.5% in 2019.
- The UNESCAD survey highlights India as the best-performing country compared to South and South-West Asia (64.1%) and the Asia-Pacific region (65.9%).
The National Logistics Policy was introduced to develop a modern, efficient, and resilient logistics services sector, seamlessly integrating multiple modes of transportation and inventory management to provide reliable, cost-effective, green, safe, and equitable logistics solutions.

Recent process reforms undertaken by the government include:
- Reduction in waiting time for inter-state border crossing due to Goods and Services Tax (GST).
- Revision of axle load norms for heavy vehicles, leading to improved carrying capacity.
- Introduction of paperless EXIM trade processes through E-Sanchit and "Turant Customs" by the Central Board of Indirect Taxes and Customs.
- Installation of scanners at major ports and the implementation of Port Community System at important ports.
- Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tagging of all EXIM containers for tracking and tracing.
- Mandatory electronic toll collection system (FASTag) to reduce time loss at toll plazas.
Infrastructure initiatives at various stages of implementation include:
- Bharatmala Pariyojana, an umbrella program for the highways sector, envisioning the construction of over 80,000 km of roads, highways, and bridges with an investment of around US $107 billion.
- Sagarmala, focusing on port modernization, new port development, port connectivity enhancement, port-linked industrialization, coastal community development, and coastal shipping.
- Multi-Modal Logistics Parks acting as hubs for freight movement and providing modern warehousing space and value-added services.
- The Pradhan Mantri Gati Shakti National Master Plan expected to catalyze growth.
- Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFCs) aiming to reduce transportation costs and increase freight speed, with around 70% of freight expected to shift to rail, freeing up capacity on Indian Railways.
- Trade Infrastructure for Export Scheme (TIES) targeting the creation of appropriate infrastructure for export growth.
Digital and technological initiatives under development include:
- Logistics Planning and Performance Monitoring Tool for real-time monitoring of operations and asset utilization.
- Logistics Platform (LogiX) with various solutions such as Indian Customs EDI Gateway, Single Window interface for Trade (SWIFT), Port Community System (PCS), Freight Operations Information System (FOIS), and National Vehicle Tracking Portal (VAHAN).
- Digital solutions for truck visibility, positioning, and tracking; logistics account number (LAN); digital green corridor; and digital port decongestion and container management system.
Currently employing over 12 million workers, the logistics sector in India involves transportation, warehousing, storage, supply chain, courier, and express services. To enhance the skills of this workforce, a curriculum on logistics and supply chain is being developed for classes 9 and 10 at the school level. It will be introduced in Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs) and polytechnics under the Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) and Deen Dayal Upadhyay Grameen Kaushal Yojana (DDU-GKY) skill missions.
India's Trade
Foreign trade has played a crucial role in enhancing India's external sector resilience. Over time, its contribution to trade as a percentage of GDP has evolved, with a range of 12-15% in the 1980s, 16-25% in the 1990s, and 25-50% in the 2000s. Despite facing adversities such as a pandemic-induced supply chain disruption, geopolitical crises, and monetary tightening, particularly in the USA, India's trade exhibited mixed performance during 2022-24 (April-December).

- As per the Economic Survey 2022-24, the merchandise exports were at USD 528 billion, compared to USD 650 billion a year ago. Non-petroleum and non-gems & jewellery exports were at USD 205 billion, a decrease from USD 230 billion a year ago. Petroleum, oil, and lubricants (POL) exports constituted about 21.1% of the total, reaching approximately USD 140 billion.
- Merchandise imports were at USD 317 billion, an increase from USD 318 billion a year ago. Among the imported commodities, gold and silver recorded a growth of 330%, while edible oils grew by 110%. The overall merchandise trade deficit stood at USD 218 billion, compared to USD 130 billion two years ago.
- Top export destinations in April-December 2022 were the USA, followed by the UAE and the Netherlands. The share of South Asia in India's total exports increased from 1.2% in 2018-19 to 2.0% in 2022-23. The shares of Brazil and Saudi Arabia also witnessed growth from 1.2% to 2.8% and 1.7% to 2.3%, respectively.
- For import sources, China, UAE, USA, Russia, and Saudi Arabia jointly contributed to 50% of India's total imports. However, China's share increased to 13.8% from 13.3% a year ago, while the USA's share decreased to 6.9% from 7.2% in April-November 2022.
India as Pharmacy of the World
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic presented both an opportunity and a challenge for India to emerge as the pharmacy of the world — showcasing vulnerabilities and potential alike. The global pharmaceutical market is projected to surpass USD 1.5 trillion by 2023. In this context, the Indian pharma industry, currently valued at USD 41 billion, is anticipated to reach USD 65 billion by 2024 and around USD 120-130 billion by 2030. Noteworthy aspects of India's pharma industry include:
- Third-largest globally in terms of volume (after China and Italy) and fourth-largest in terms of value.
- Global export share nearly doubled to 2.6% in 2019 from 1.6% in 2010, securing the 11th position globally.
- Emergence as a global hub for generic medicines, in addition to serving as a raw material base and having a skilled workforce.
- Largest number of US-FDA compliant pharma plants (over 262, including APIs) outside of the United States.
- High Trade Specialization Coefficient (TSC) close to 1, indicating robust export competitiveness.
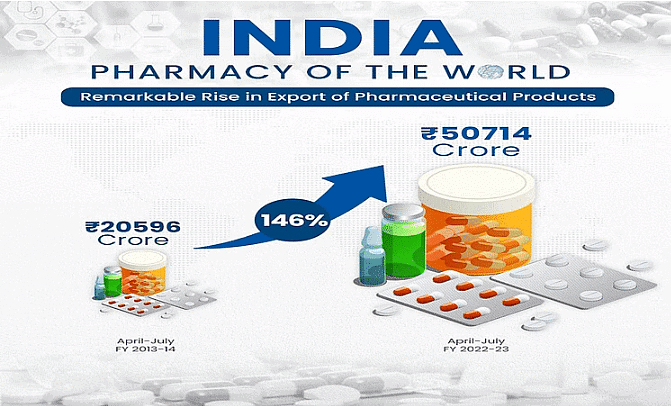
During 2020-21 (April-October), India's pharma exports reached USD 11.1 billion, growing impressively by 18.0%, contributing to 7.3% of total exports and making it the third-largest exported commodity. Commitment to supplying COVID-19 vaccines to other countries has positioned India as a manufacturing epicenter. Indian pharma companies gained nearly 45% of all new Abbreviated New Drug Application (ANDA) approvals in the first nine months of 2020-21, showcasing export potential.
However, challenges exist, including excessive dependence on China for sourcing Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (APIs) and Key Starting Materials (KSMs), and disproportionate reliance on the United States for pharma exports. Government initiatives such as the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme and the promotion of parks for bulk drugs and medical devices aim to address these challenges.
To solidify its position as the pharmacy of the world, the industry needs a comprehensive development strategy involving:
- Broadening the market base and product categories, exploring opportunities in newer classes like biosimilars, gene therapy, and expanding into traditionally underpenetrated markets.
- Restructuring the regulatory framework and enhancing capacities at the National Institute of Pharmaceutical Education and Research (NIPER).
- Increasing R&D expenditure to move up the value chain from generics to Novel Chemical Entities (NCEs).
The Quad
The global economic landscape holds significant implications for India, with several factors influencing its trade, currency, and overall economic health. Key considerations include:
- Impact of Protectionist Policies: The rise of protectionist policies, especially in the United States and China, poses challenges for global trade, affecting India's exports and economic growth.
- China's Economic Shift: Changes in China's economic policies, particularly its ability to successfully rebalance its economy, will have repercussions on global trade, with potential positive or negative spillover effects on India.
- India's Trade Dynamics: India's trade in goods and services becomes crucial, and the growth of services exports will test global capacity for globalization in services. The restrictions imposed by developed countries on labor mobility and outsourcing will play a significant role in shaping this scenario.
- Comparison with China's Trade Patterns: Comparisons with China's trade patterns highlight potential differences. India's tendency to run a current account deficit, coupled with a more balanced export-import profile, may contribute to a more equitable distribution of jobs and economic benefits.
- Political Implications: The political backlash against globalization, particularly in advanced economies, may impact India differently. India needs to carefully navigate these changing dynamics and monitor the evolving global economic scenario.
In essence, India's economic outlook is intertwined with global developments, and staying abreast of changing dynamics is imperative for informed decision-making.
Trade Settlement in INR
As of mid-2022, India initiated efforts to boost trade transactions in Indian rupee (INR), aiming to cater to the growing interest in INR as an international currency. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) established a policy framework, involving the invoicing of exports and imports in INR at market-determined exchange rates with partner countries. Settlement occurs through special Rupee Vostro accounts held with authorized dealer banks in India.
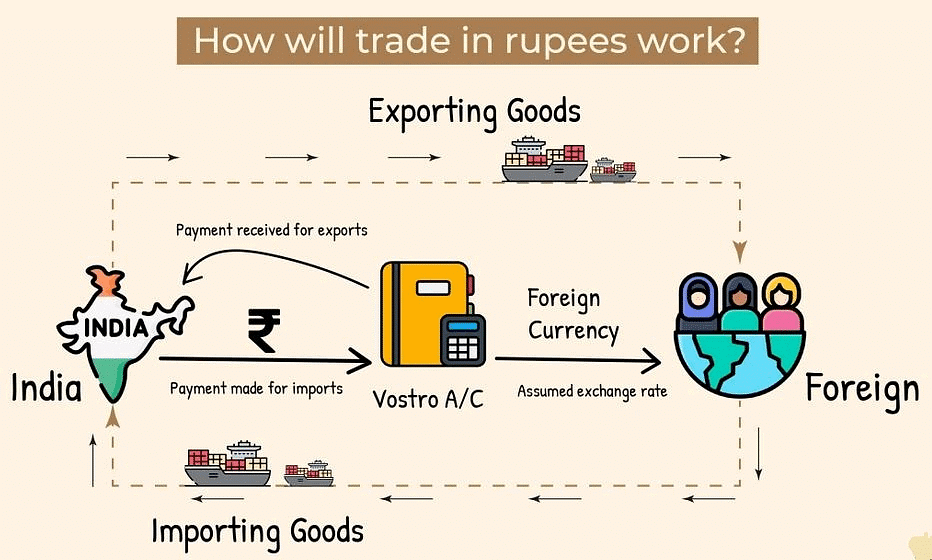
This arrangement offers various advantages for India's trading activities:
- Indian importers make payments in INR, credited to the Special Vostro account of the correspondent bank in the partner country.
- Indian exporters receive payments for exports in INR from the designated Special Vostro account of the correspondent bank in the partner country.
This settlement framework gains significance due to the aggressive policy rate hikes by the US Federal Reserve, leading to the US dollar strengthening and causing currency depreciation in emerging market economies, including INR. The Economic Survey 2022-23 identifies potential benefits for trading partners, particularly India, such as:
- Reducing the need for foreign exchange, especially the US dollar, to settle trade deficits.
- Mitigating currency risk for Indian businesses.
- Decreasing reliance on holding forex reserves and foreign currency.
- Reducing vulnerability to external shocks.
- Promoting INR as an international currency.
For a currency to be considered international, it must increasingly be used for trade settlement. As per the BIS Triennial Central Bank Survey 2022, the US dollar dominates global forex turnover at 88%, with the INR accounting for 1.6%. If the INR turnover reaches 4%, equivalent to the share of non-US, non-Euro currencies, it could be recognized as an international currency.
Way Forward
The ongoing impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the external sectors of various countries has been varied. While there was a contraction in exports and imports globally, Advanced Economies (AEs) experienced more significant contractions compared to Emerging Market and Developing Economies (EMDEs), particularly in East Asian economies. To ensure a sustainable external sector, India's future concerns and related policy actions should focus on the following:
- Trade partners have been pressuring India for custom cuts. The government should continue defending the current custom regime to safeguard trade interests.
- The practice of an 'inverted duty' structure, where custom duties are higher on intermediate goods than finished goods, has been detrimental to India's trade interests. Addressing this issue is crucial, especially for sectors where the import elasticity of exports is greater than 1.
- Enhancing the supply chain of the economy and integrating it with the global value chain will boost India's export competitiveness. Previous free trade agreements were not fully beneficial due to disruptions in the value chain.
- Reducing delays in clearances at ports and airports is essential for speeding up shipment movement. While some steps have been taken, more efforts are required in this regard.
- Ensuring Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) have healthy access to loans and streamlining the GST regime for them is crucial.
- Creating a conducive macroeconomic environment for trade by signing suitable trade agreements and avoiding arbitrary taxes, restrictions, and tariffs is important.
- Implementing effective labor reforms and enhancing workforce skills will provide India with a competitive edge in exports.
- The disruption of global manufacturing value chains due to the pandemic offers a significant opportunity for India to become a key node in the chain. The government's plan focusing on trade facilitation, ease of exporting, and regulatory reforms is vital for tapping into this opportunity.
- Despite competition from South Asian countries in certain export competitive products, India, with its advantages of a younger working population and economies of scale, can meet global demand cost-effectively.
- Global growth directly influences India's exports, and while the growth rate has decreased, market share gains become crucial. Governments can open markets through Free Trade Agreements (FTAs), but private sector participation is essential to leverage this advantage.
|
108 videos|425 docs|128 tests
|
FAQs on Ramesh Singh Summary: External Sector in India- 3 - Indian Economy for UPSC CSE
| 1. What is the concept of Forex Management and its relevance in international trade? |  |
| 2. What is the Impossible Trinity and how does it affect Forex Management? |  |
| 3. What are trade facilitation and trade logistics? |  |
| 4. How does India contribute as the Pharmacy of the World? |  |















