Sculpture & Pottery- 4"
Other Schools of Temple Architecture
Nayaka School
- Flourished under Nayaka rulers (16th-18th centuries AD), also known as Madurai school.
- Architecturally similar to Dravidian style but larger in scope with Islamic influence.
Unique Features
- Presence of Prakarams or huge corridors.
- Gopurams under Nayaka rulers were some of the largest.
- Intricate carvings in the temple structure. Example: Meenakshi Temple.
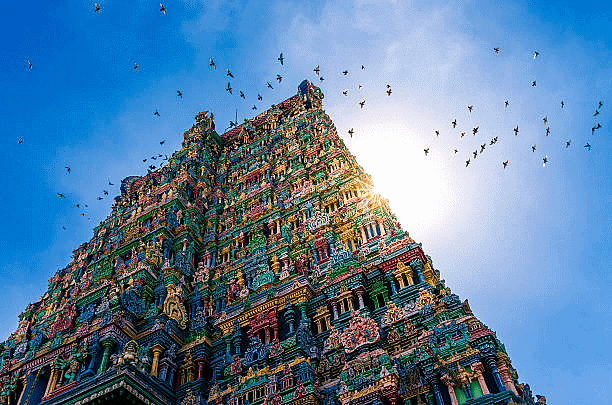 Meenakshi Temple
Meenakshi Temple
Vesara School (Karnataka School)
- Conceptualized under later Chalukya rulers (mid-7th century AD).
- Hybridized style combining Nagara and Dravidian features.
- Features:
- Emphasis on vimana and mandapa.
- Open ambulatory passageway.
- Intricate carvings on pillars, doorways, and ceilings.
- Prominent Dynasties:
- Chalukyas of Badami and Kalyani.
- Rashtrakutas (e.g., Kailasha Temple in Ellora).
- Hoysala Dynasty (e.g., temples at Halebidu and Belur).
 Kailasha
Kailasha
Vijayanagara School
- Rulers of Vijayanagara Empire (1336-1565 AD) were great patrons of art and architecture.
- Combined features of Chola, Hoysala, Pandya, Chalukya styles with Indo-Islamic influence.
- Features:
- Highly decorated walls with carvings and geometrical patterns.
- Gopurams on all sides, monolithic rock pillars.
- Introduction of secular buildings inside temple premises. Examples: Vittalaswami Temple, Lotus Mahal, Virupaksha Temple at Hampi.
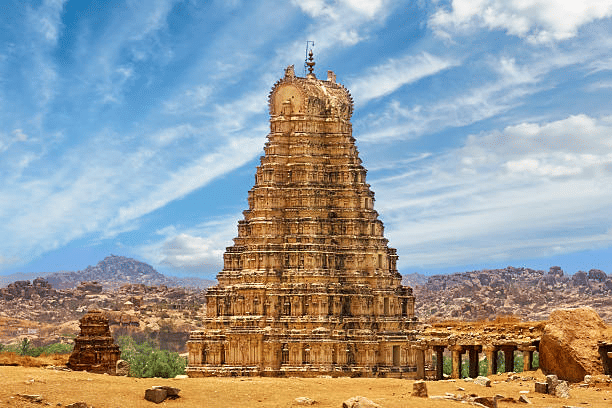 Virupaksha
Virupaksha
Hoysala Art
Distinct style under Hoysala rulers (1050-1300 AD) in Karnataka.
- Features:
- Multiple shrines around a central pillared hall.
- Stellate plan: Shrines in the shape of an intricately designed star.
- Use of soft soapstone, emphasis on intricate sculptures.
- Zigzag pattern on walls and stairs. Examples: Hoysaleswara Temple at Halebidu, Chennakesava Temple at Belur, Somanathapura.
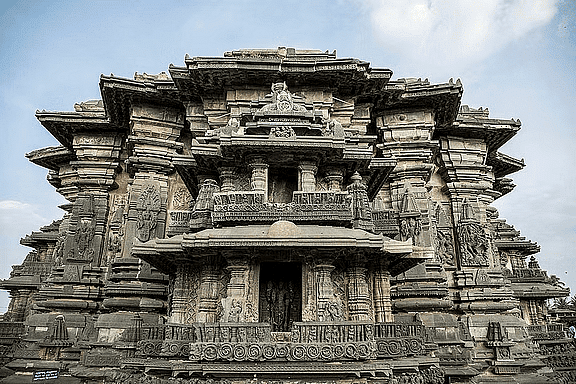 Chennakesava
Chennakesava
Pala and Sena Schools of Architecture
- Developed in Bengal region between 8th and 12th century AD under Pala and Sena dynasties.
- Palas were primarily Buddhist rulers, while Senas were Hindus, reflecting both influences.
Monuments under Pala Rulers
- Universities: Nalanda, Jagaddala, Odantapuri, Vikramshila.
- Somapura Mahavihara in Bangladesh.
 Nalanda
Nalanda
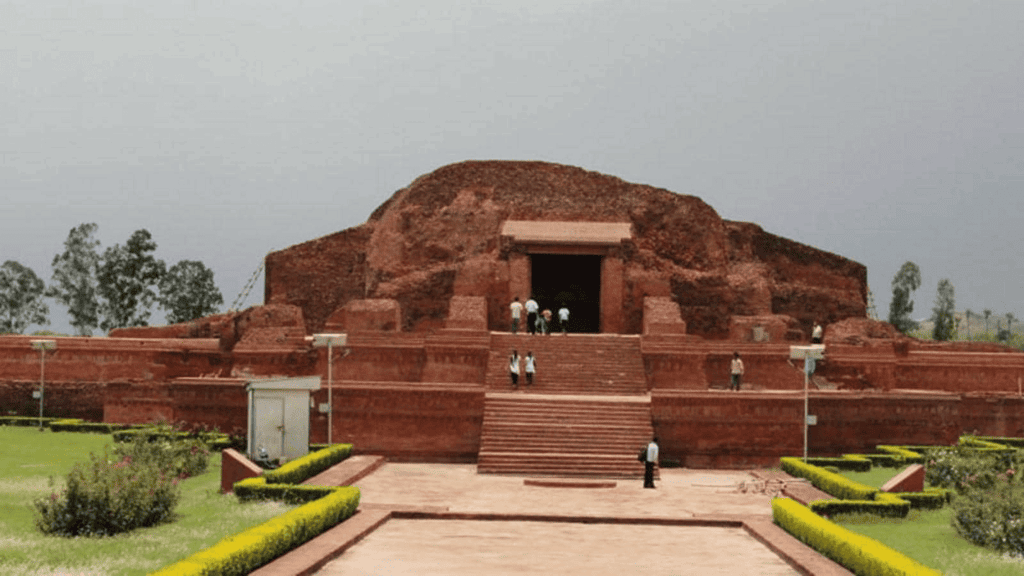 Vikramshila
Vikramshila
Monuments under Sena Rulers
- Dhakeshwari Temple in Bangladesh.
Features of Sena Rulers' Architecture
- Curved or sloping 'Bangla roof,' adopted by Mughal architects later.
- Burnt bricks and terracotta bricks as the principal building material.
- Tall, curving shikhara crowned by a large amalaka, similar to the Odisha School.
- Use of both stone and metal for sculptures with a highly lustrous finish. Examples: Siddhesvara Mahadeva Temple in Barakar, temples around Bishnupur (WB).
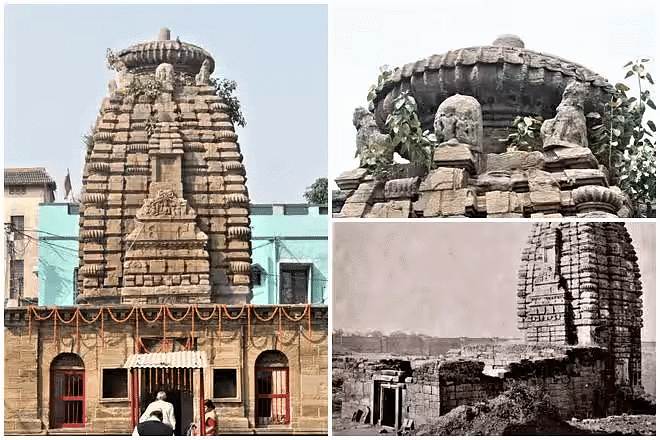 Mahadeva Temple
Mahadeva Temple
Vishnu Forms Commonly Found in Temples
- Sheshashayana - Vishnu reclining on Ananta (sheshanaga).
- Nara-Narayan - discussion between human soul and eternal divine.
- Gajendramoksha - story of achieving moksha, symbolized by Vishnu's suppression of an elephant-shaped asura.
Provincial Schools of Architecture
Indo-Islamic Influence on Local Architectural Styles- Bengal, Bijapur, Jaunpur, and Mandu became important seats of architectural development.
Bengal School (1203-1573 AD)
- Characterized by the use of bricks and black basalts.
- Mosques continued the use of sloping 'Bangla roofs.'
- Examples: Qadam Rasul Mosque, Adina Mosque.
 Qadam Rasul Mosque
Qadam Rasul Mosque
Jaunpur School (1394-1479 AD)
- Also known as Sharqi style, patronized by the Sharqi rulers.
- Unique feature: Bold and forceful characters painted on huge screens in prayer hall.
- Example: Atala Mosque, Jaunpur.
Malwa School (1405-1569 AD)
- Prominent in Dhar and Mandu.
- Use of different colored stones and marbles, large windows, stylized arches and pillars.
- Environmental adaptation features like well-ventilated buildings, airy pavilions, 'baulis' for water storage.
- Examples: Rani Roopmati Pavilion, Jahaz Mahal, Ashrafi Mahal.
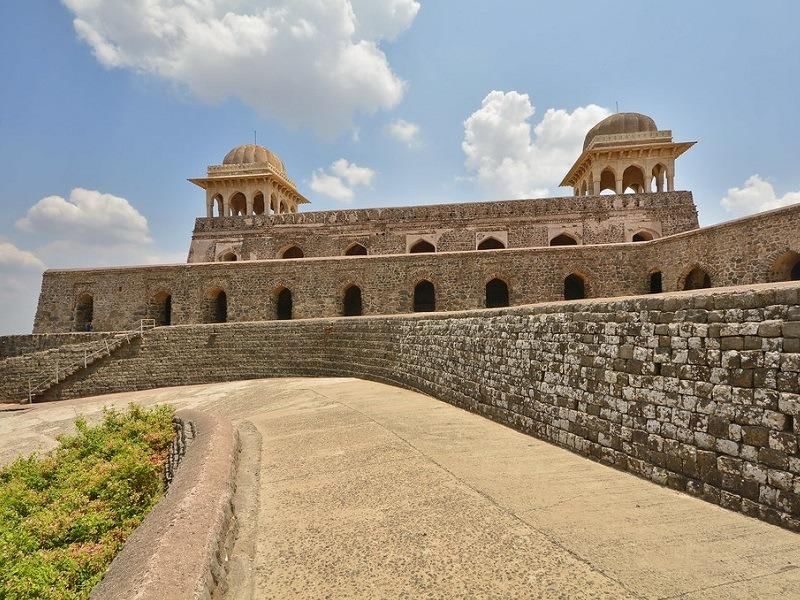 Rani Roopmati Pavilion
Rani Roopmati Pavilion
Bijapur School (1490-1656 AD)
- Developed under Adil Shah, characterized by three-arched facade, bulbous dome, unique ceilings.
- Use of iron clamps, strong plaster for support, rich carvings on walls.
- Example: Gol Gumbaj (mausoleum of Adil Shah) in Bijapur.
Humayun
- Foundation of Dinpanah, introduction of Persian style.
- Humayun's Tomb commissioned in 1558, UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Sher Shah
- Qila-i-Kuhna mosque in Delhi, Rohtas Fort in Pakistan, Sher Shah Suri Masjid in Patna.
- Transition from Lodi style to Mughal style.
- Construction of Sadak-e-Azam (Grand Trunk Road).
Akbar
- Interest in art and architecture, use of red sandstone, introduction of 'Pudor arch.'
- Construction of Agra Fort, Fatehpur Sikri.
Fatehpur Sikri (Continued)
- Buland Darwaza, Salim Chishti's tomb, Panch Mahal, Ibadat Khana, Hiran Minar.
- Blend of Hindu and Persian styles, Charbagh style gardens.
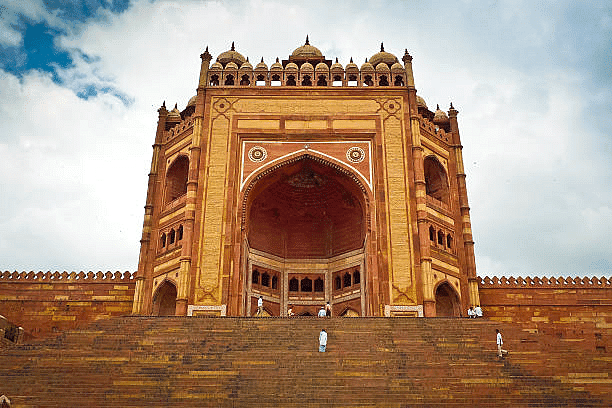 Buland Darwaza
Buland Darwaza
Jahangir
- Focus on paintings and other arts.
- Construction of Akbar's tomb in Sikandra, Moti Masjid at Lahore.
Shah Jahan
- Mughal architecture reaches its climax.
- Principal works: Taj Mahal, Red Fort in Delhi, Jama Masjid in Delhi, Shalimar Bagh in Lahore.
- Construction of Peacock Throne, exquisite metalwork.
- Chief architect: Ustad Ahmad Lahori.
Aurangzeb
- Mughal architecture declines under puritanical rule.
- Construction of Bibi Ka Maqbara in Aurangabad, poor imitation of Taj Mahal.
Rajput Style
- Influenced by Mughal style, focus on imposing palaces and forts.
- Use of hanging balconies (jharokha).
Sikh Style
- Developed in Punjab, influenced by Mughal and Rajput styles.
- Features: Multiple Chhatris, shallow cornices, fluted domes.
- Example: Harmandir Sahib (Golden Temple).
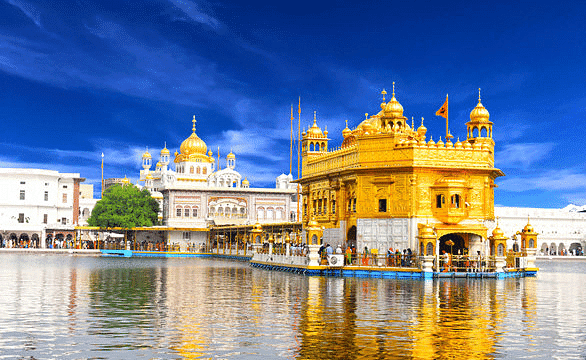 Harmandir Sahib (Golden Temple)
Harmandir Sahib (Golden Temple)
Kashmiri Architecture
- Early medieval Hindu phase and 14th-century onwards Muslim rule.
- Kashmiri temple architecture features trefoil arches, cellular layout, pyramidal roofs.
- Monuments: Martand Sun Temple, Temples at Awantipora, Pandrethan Temple.
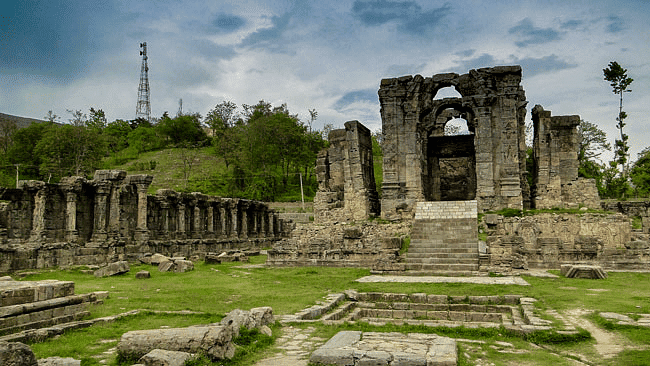 Martand Sun Temple
Martand Sun Temple
Islamic Rule in Kashmir
- Blend of Kashmiri style and Islamic sensibilities.
- Monuments: Jamia Masjid and Aali Masjid in Srinagar, Pari Mahal.
Gardens in Kashmir
- Mughal-inspired Charbagh style gardens with water streams and fountains.
- Examples: Chashme Shahi, Shalimar Bagh, Nishat Bagh, Achabal Gardens.
|
122 videos|653 docs|168 tests
|
FAQs on Sculpture & Pottery- 4"
| 1. What are the Pala and Sena Schools of Architecture? |  |
| 2. What are the Provincial Schools of Architecture in India? |  |
| 3. What are some key features of Indian temple architecture? |  |
| 4. How do the Pala and Sena Schools of Architecture differ from each other? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the different schools of temple architecture in India? |  |






















