Shankar IAS Summary: Aquatic Ecosystem- 2 | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
Government Measures to Protect Mangrove Forest and Coral Reefs
The government seeks to protect, sustain, and augment mangroves and coral reefs in the country through a combination of regulatory and promotional measures.
Under regulatory measures, the Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) Notification (2011) and the Island Protection Zone (IPZ) Notification 2011 govern development activities along the sea coast and tidal-influenced water bodies.
Mangroves and coral reef areas are categorized as ecologically sensitive areas (CRZ-1), where no new constructions are permitted, except for specific projects related to the Department of Atomic Energy, pipelines, conveying systems (including transmission lines), installation of weather radar for cyclone monitoring by the Indian Meteorological Department, and construction of trans-harbour sea links, without affecting the tidal flow of water.
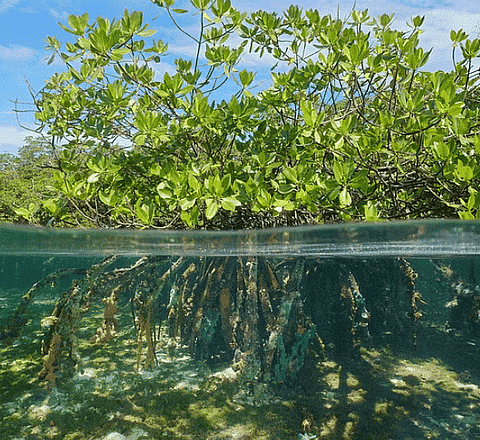
 Mangrove Forest
Mangrove Forest
To enforce and implement the CRZ and IPZ Notifications, the Ministry of Environment and Forests has constituted the National and State/UT level Coastal Zone Management Authorities.
The Ministry of Environment & Forests also provides financial assistance to Coastal States/Union Territories, upon request, under its Centrally Sponsored Scheme for the conservation and management of mangroves and coral reefs.
Additionally, coral reefs are included in Schedule 1 of the Wild Life Protection Act, 1972, affording them the highest degree of protection.
Further, Protected Areas, including 4 National Parks, 96 Sanctuaries, and 3 Marine Biosphere Reserves, have been created nationwide under the provisions of the Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972, aimed at conserving marine life, including coral reefs.
The Wildlife Crime Control Bureau has also been established to strengthen the enforcement of laws, control poaching, and combat illegal trade in wildlife and its products.
Coastal Regulation Zone
The CRZ notification, initially issued in 1991, aims to protect the coastal zone and regulate development activities.
Amendments to the CRZ notification occurred in 20n and 2018, reflecting evolving considerations for coastal zone management.
CRZ encompasses four zones, each serving specific purposes:
 Coral Reefs
Coral Reefs
CRZ-1
It pertains to ecologically sensitive areas with geomorphological features playing a primary role in maintaining the coast's integrity.
Specific features include:
- Mangroves, with a required buffer area of 50 meters if the mangrove area exceeds 1000 square meters.
- Corals, coral reefs, and associated biodiversity.
- Sand dunes.
- Biologically active mudflats.
- Areas covered by National parks, marine parks, sanctuaries, reserve forests, wildlife habitats, and other protected areas under the provisions of the Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972, the Forest (Conservation) Act, 1980, or Environment (Protection) Act, 1986, including Biosphere Reserves.
- Salt marshes.
- Turtle nesting grounds.
- Horseshoe crab habitats.
- Seagrass beds.
- Nesting grounds of birds.
- Areas or structures of archaeological importance and heritage site
CRZ-II
- It Refers to areas developed up to or close to the shoreline.
- Includes regions within municipal limits.
CRZ-III
- Encompasses relatively undisturbed areas.
- Includes rural and urban areas not falling under Category I or II.
- Encompasses regions that are not substantially developed.
 Marine Park
Marine Park
CRZ-IV
- Pertains to the aquatic area from the low tide line up to territorial limits.
- Includes the area of tidal-influenced water bodies.
Significant provisions in the Coastal Regulation Zone Notification, 2011 include:
The entire water area, comprising 12 nautical miles in the sea and the entire water area of a tidal water body (creek, river, estuary), falls under the regulation of the Notification.
Introducing the hazard line to safeguard the livelihood and property of local communities, including coastal infrastructure. The hazard line will be demarcated by the offices of the Survey of India.
Special dispensation was provided to Greater Mumbai, Kerala, Goa, and Critically Coastal Vulnerable Areas like the Sunderban, considering environmental and social issues.
Addressing erosion concerns along coastal areas caused by man-made interventions. The shoreline will be mapped using up-to-date satellite images, and classified as 'high eroding,' 'medium eroding,' and 'low or stable stretches.' No foreshore development will be permissible in high-eroding areas.
To accommodate the increasing housing demands for fishing communities and other traditional coastal communities, the No Development Zone, typically 200 meters from the High Tide Line, is being reduced to 100 meters.
Activities Permitted and Restricted in CRZ
A. CRZ-1
- Permitted activities under 20n Notification include:
- No new construction is allowed, except for specific projects (e.g., Department of Atomic Energy, pipelines, conveying systems, weather radar, trans-harbour sea links).
- Permitted activities between the Low Tide Line and High Tide Line include natural gas exploration, construction of essential facilities, salt harvesting, and more.
 Coastal Ecosystem
Coastal Ecosystem
B. CRZ-II
- Buildings are permissible on the landward side of existing roads, authorized structures, or hazardous lines.
- Permissible activities include desalination plants and storage of non-hazardous cargo.
C. CRZ-III
- Provisions changed with CRZ 2018 notification.
D. CRZ-IV
- No restriction on traditional fishing; comprehensive sewage treatment plan required; no dumping of untreated waste.
CRZ Notification, 2018
Dr. Shailesh Nayak Committee (Secretary, Ministry of Earth Sciences) was constituted in June 2014 to examine issues and concerns of Coastal States/UTs and stakeholders for recommending changes in CRZ Notification, 2011.
The government states that CRZ Notification, 2018, will meet aspirations of Coastal communities, ensure the welfare of the poor, and create opportunities for affordable housing and tourism.
Designed to balance economic growth promotion with coastal region conservation principles.
 Dr. Shailesh Nayak
Dr. Shailesh Nayak Salient Features:
Allowing ISI in CRZ areas:
- In CRZ-II (Urban) areas, Floor Space Index (FSI) or Floor Area Ratio (FAR) is de-frozen to permit ISI for construction projects based on prevailing norms.
Densely populated rural areas development:
- CRZ-III (Rural) areas are categorized into CRZ-III A (higher population density) and CRZ-III B (lower population density).
- NDZ was reduced to 50 meters for CRZ-III A areas and remains 200 meters for CRZ-III B areas.
Promotion of tourism infrastructure:
- Temporary tourism facilities are allowed on beaches and in NDZ of CRZ-III areas.
- A minimum distance of 10 meters from the High Tide Line (HTL) for setting up such facilities.
Streamlined CRZ clearances:
- CRZ clearances are streamlined; projects in CRZ-I and IV to be dealt with by the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change.
Island NDZ stipulation:
- NDZ of 20 meters is stipulated for all islands close to the mainland coast and backwater islands.
Ecologically Sensitive Areas importance:
- Specific guidelines for conservation and management plans were drawn up for all Ecologically Sensitive Areas.
Pollution abatement focus:
- Pollution abatement addressed; treatment facilities permitted activities in the CRZ-II area with necessary safeguards.
Defence and strategic projects dispensation:
- Defence and strategic projects accorded necessary dispensation.
Coastal Ecosystems
Coastal Ocean Monitoring and Prediction System (COMAPS)
- COMAPS implemented since 1991, assesses coastal waters' health, manages pollution-related issues.
- Program restructured in 2000-2001 for pollution monitoring, liaison, regulation, legislation, and consultancy services.
Land-Ocean Interactions in the Coastal Zone (LOICZ)
- Launched in 1995, investigates global change effects on the coastal zone.
- Aims for integrated management of coastal environments.
Integrated Coastal and Marine Area Management (ICMAM)
- Launched in 1998, aims at integrated management of coastal and marine areas.
- Model plans for specific regions like Chennai, Goa, and the Gulf of Kutch were prepared.
 Gulf of Kutch
Gulf of Kutch
Institutions for Coastal Management
- National Coastal Zone Management Authority (NCZMA) and State Coastal Zone Management Authority (SCZMA) were established.
- Delegated powers under Section 5 of the Environmental (Protection) Act, 1986.
Integrated Coastal Zone Management (ICZM)
- ICZM concept was introduced in 1992, and adopted globally for coastal zone management.
- MoEF & CC launched ICZM activities in India through the Society of Integrated Coastal Management (SICOM).
Society of Integrated Coastal Management (SICOM)
- Established 2010, the nodal agency for ICZM practices.
- Technical Secretariat to NCZMA for regulatory provisions and CRZ classification.
- Involved in Pilot Blue Flag Programme for world-class beaches.
'Blue Flag' Certification
- The 'Blue Flag' certification, a voluntary accolade, is bestowed upon beaches, marinas, and sustainable boating tourism operators, serving as an eco-label.
- Recognized globally, the certification is granted by the non-profit "Foundation for Environment Education in Denmark," with adherence to 33 stringent criteria.
- Initiated in 1985, the Blue Flag program expanded beyond Europe in 2001, advocating sustainable development in freshwater and marine areas, emphasizing water quality, environmental management, environmental education, and safety as its core criteria.
 Blue Flag
Blue Flag
- Awarded annually to beaches and marinas in Foundation for Environment Education (FEE) member countries.
- Currently, 47 countries actively participate in the program, with 1,573 beaches, marinas, and boats holding this prestigious certification.
- Owners/operators of certified entities are granted the privilege to proudly display the Blue Flag, signifying their commitment to environmental excellence.
Blue Flag Certified Beaches in India
- Notable Blue Flag certified beaches in India include Kappad, Shivrajpur, Ghoghla, Kasarkod, Padubidri, Rushikonda, Golden, Radhanagar, Kovalam, Eden, Minicoy Thundi, and Kadmat.
Permitted Activities in CRZ of Beaches, Including Islands
- Within the Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ), approved activities, such as portable toilet blocks, solar power plants, seating benches, and more, are permitted. These adhere to a minimum distance of 10 meters from the High Tide Line.
Exemption from Prior Clearance
- These sanctioned activities, essential for Blue Flag Certification, are exempt from prior clearance under CRZ, Island Protection Zone, and Island Coastal Regulation Zone Notifications.
Island Protection Zone Notification, 2011
Approximately 500 islands in Andaman & Nicobar and 30 in Lakshadweep.
Diverse biodiversity hotspots, with Andaman & Nicobar having 85% forest coverage.
Geographical constraints lead to overlapping Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) regulations.
The necessity for a separate Island Protection Zone (IPZ) Notification.
Aims to manage the entire island, excluding four islands in Andaman & Nicobar.
 Andaman & Nicobar Island
Andaman & Nicobar Island
Objectives of IPZ Notification:
- Ensure livelihood security for fishing communities, tribals, and local inhabitants.
- Conserve and protect coastal stretches.
- Promote sustainable development based on scientific principles.
- Consider risks of natural hazards and potential sea-level rise due to global warming.
Ganga Action Plan
Launched on January 14, 1986, the Ganga Action Plan's primary goal was pollution abatement, aiming to enhance water quality. Strategies included intercepting, diverting, and treating domestic sewage, as well as managing toxic and industrial chemical wastes from identified heavily polluting units entering the river.
In response to assessing the effectiveness of the Ganga Action Plan, the government introduced the "Mission Clean Ganga" on December 31, 2009. The mission's objective was to ensure that by 2020, no municipal sewage or industrial waste would be discharged into the river without treatment. The allocated budget for this comprehensive initiative was around Rs.15,000 crore.
 River Ganga
River Ganga
To oversee and facilitate these efforts, the government established the National Ganga River Basin Authority (NGRBA), chaired by the Prime Minister. The NGRBA aimed to ensure effective pollution abatement and conservation of the Ganga River by adopting a river basin approach for comprehensive planning and management.
Namami Ganga Program
- The Namami Gange initiative, part of the Integrated Ganga Conservation Mission, aims to allocate Rs. 2,037 crores for the conservation and enhancement of the Ganga.
- An additional Rs. 100 crores is earmarked for Ghats and Riverfront development in key locations like Kedarnath, Haridwar, Kanpur, Varanasi, Allahabad, Patna, and Delhi for the current financial year.
- Namami Gange consolidates existing efforts and formulates a robust action plan for the future.
- Initiatives at the Ghats and River fronts foster citizen engagement, promoting river-centric urban planning.
- Nirmal Dhara (Sustainable Municipal Sewage Management)
- Prioritizing projects in coordination with the Ministry of Urban Development.
- Providing incentives to states for Ganga Main-stem projects.
- Enforcing uniform standards and mandatory O&M for 10 years.
- Expanding sewerage infrastructure in 118 urban habitations along the Ganga.
 Logo of Namai Ganga Program
Logo of Namai Ganga Program
Nirmal Dhara (Managing Sewage from Rural Areas)
- Implementing the Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation scheme for Ganga Bank Gram Panchayats, ensuring freedom from open defecation by 2022, with a central share of Rs. 1700 crores.
Nirmal Dhara (Managing Industrial Discharge)
- Mandating Zero Liquid Discharge for Industries.
- Implementing rationalized water tariffs for encouraging reuse.
- Introducing real-time water quality monitoring.
Aviral Dhara (Ensuring River Flow):
- Enforcing River Regulatory Zones on Ganga Banks.
- Implementing rational agricultural practices and efficient irrigation methods.
- Restoring and conserving wetlands.
Ecological Rejuvenation: Ensuring conservation of aquatic life and biodiversity.
Tourism and Shipping Promotion: Promoting tourism and shipping rationally and sustainably.
Knowledge Management: Establishing a Ganga Knowledge Centre leading to a Ganga University of River Sciences.
NRI Ganga Fund
- Set up to finance special projects for Ganga conservation.
- Contributions expected from Non-Resident Indians (NRIs).
- Aimed at harnessing enthusiasm and contributions from NRIs.
Clean Ganga Fund (CGF)
- Proposed to increase people's participation in Ganga cleanup efforts.
- Operated through a Trust headed by the Finance Minister.
- Domestic donors eligible for tax benefits similar to "Swachh Bharat Kosh."
- Foreign donors may receive suitable tax exemptions.
- Exploration of setting up daughter funds in other jurisdictions/countries.
- Catalytic in nature, identifying and funding specific projects.
Broad Activities Financed from CGF
- Outlined under "Namami Gange" program.
- Control of non-point pollution from agricultural runoff, human defecation, cattle wallowing, etc.
- Setting up waste treatment and disposal plants along the river around cities.
- Conservation of the biotic diversity of the river.
- Community-based activities to reduce polluting human interface with the river.
- Development of public amenities, including Ghat redevelopment.
- Research and Development, innovative projects, and new technology/processes for cleaning the river.
- Independent oversight through intensive monitoring and real-time reporting.
- Any other activity approved by the Trust.
Recent Measures
- Union Environment Ministry adopts a new strategy for river conservation and rejuvenation.
- The approach considers the entire river basin contributing to a specific river stretch.
- A holistic strategy combining water and environment management for overall river rejuvenation.
Arth Ganga
- Signifies a sustainable development approach linked to economic activities along the Ganga river.
- Zero Budget Natural Farming promoted chemical-free agriculture along a 10-kilometer stretch on both sides.
- Promotion of cow dung as a natural fertilizer through the Gobardhan scheme.
- Monetization and Reutilization of Sludge & Wastewater for agricultural and industrial use.
- Revenue generation for Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) through repurposing treated water.
- Creation of opportunities for livelihood generation by establishing local markets (haats).
- Focus on enhancing public participation and collaboration among various stakeholders.
- Emphasis on bolstering cultural heritage and tourism through activities like boat tourism, adventure sports, and yoga events.
- Promotion of institutional development by empowering local administrations to enhance water governance practices.
|
743 videos|1444 docs|633 tests
|
FAQs on Shankar IAS Summary: Aquatic Ecosystem- 2 - Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests)
| 1. What is the purpose of the Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ) in protecting mangrove forests and coral reefs? |  |
| 2. How does the Island Protection Zone Notification, 2011 contribute to the protection of mangrove forests and coral reefs? |  |
| 3. What is the Ganga Action Plan, and how does it relate to the protection of aquatic ecosystems? |  |
| 4. How does the Namami Ganga Program contribute to the protection of mangrove forests and coral reefs? |  |
| 5. How do coastal ecosystems benefit from the government measures mentioned in the article? |  |
















