Shankar IAS Summary: Protected Area Network- 2 - UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
A Protected Area Network is a vital tool in global conservation efforts. These designated areas are dedicated to preserving biodiversity and natural ecosystems. With a focus on balancing human activities and ecological preservation, these areas serve as sanctuaries for endangered species, promote sustainable land use, and play a crucial role in addressing challenges such as habitat loss, climate change, and biodiversity decline.
Wildlife Protection Act 1972
India holds the distinction of being the first country globally to embed environmental protection in its constitution. On June 5, 1972, international attention turned to environmental issues during the U.N. Conference on Human Environment in Stockholm, marking the inception of World Environment Day.

Constitutional Provisions
Constitutional amendments in 1976 introduced Article 48-A, emphasizing the state's duty to protect and enhance the environment, safeguard forests, and preserve wildlife. Article 51-A (g) highlights citizens' responsibility to nurture the natural environment, including forests, lakes, rivers, and wildlife.
The Wildlife (Protection) Act of 1972
This pivotal legislation, enacted soon after the Stockholm Conference, became a landmark in wildlife legislation. It shifted the jurisdiction from being a state subject to a concurrent subject, and all states, except Jammu and Kashmir, adopted it. The Act lays the foundation for wildlife protection and has undergone amendments to enhance its effectiveness.
Salient Features
-Schedules categorize wildlife for protection based on their risk of survival.
- Expert committees regularly review amendments.
- The 1991 amendment withdrew powers from state governments, making immunization of livestock mandatory near protected areas.
Wildlife Protection Act Amendment 2022
The recent amendment introduces significant changes: - Adds a new schedule for CITES-listed species. Establishes a Standing Committee with delegated powers. - Modifies Section 43 to allow elephants' use for religious purposes. - Grants Central Government authority for managing and regulating invasive alien species. - Increases penalties, with the maximum fine reaching Rs. 1 lakh.
Did you know?
Sri Venkateshwara Zoological Park in Tirupati, Andhra Pradesh, stands as the largest zoo in India.
Export of Prohibited Goods
The export of prohibited items is strictly forbidden, and normal export licenses won't be granted for goods falling under this category.

Prohibited Items in Flora and Fauna Category
- All wild animals, animal articles, and their products and derivatives, excluding those with granted ownership certificates and those required for education, scientific research, and management under the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- Export of beef from cows, oxen, and calves, including beef in the form of offal, is not allowed.
- Export of buffalo meat (both male and female), whether fresh, chilled, or frozen, is prohibited.
- Prohibition extends to peacock tail feathers and related handicrafts.
- Shavings and manufactured articles made from shed antlers of Chital and Sambhar are on the prohibited list.
- Seashells fall under the prohibited category.
- Export of wood and wood products, including fuel wood and wood charcoal, is not permitted.
- Sandalwood in any form is prohibited for export, except for finished handicraft products, machine-finished sandalwood products, and sandalwood oil.
- Red Sanders wood and its value-added products are prohibited for export.
- Mechanical, chemical, and semi-chemical wood pulp fall under the prohibited category.
World Network of Biosphere Reserves (WNBR)
International Coordination and Admission
- Admission to International Network:
- Biosphere Reserves (BRs) seek entry into the International Network through UNESCO's Man and Biosphere (MAB) Programme's International Coordinating Council (ICC).
- Admission is contingent upon the participating country fulfilling prescribed criteria.
- Sovereignty and Voluntary Participation:
- BRs, once part of the World Network, maintain their sovereignty within the respective country or state of location.
- Participation in the World Network is entirely voluntary.
- Delisting Criteria:
- Delisting from the international Network is a rare occurrence.
- It occurs only in cases of violations related to conservation and sustainable development obligations.
- The decision involves consultation with the concerned government.
MAB Programme and World Network Creation
- Establishment of World Network:
- A significant milestone of the MAB programme was the establishment of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves in 1977.

- A significant milestone of the MAB programme was the establishment of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves in 1977.
- World Network Composition:
- The World Network comprises 610 biosphere reserves.
- These reserves are distributed across 117 countries.
- Additionally, there are 12 transboundary sites within the network.
- Platform for International Cooperation:
- The World Network serves as a platform for international cooperation in biodiversity conservation.
- It facilitates knowledge-sharing and experience exchange among participating countries.
Biodiversity Hotspots
Concept and Criteria
The biodiversity hotspot concept, introduced by Norman Myers in 1988, requires a region to meet strict criteria to qualify as a hotspot.
To qualify, a region must have at least 1,500 species of vascular plants (more than 0.5% of the world's total) as endemics and must have lost at least 70% of its original habitat.
Global Significance
- Biodiversity hotspots represent unique ecosystems with extraordinary floral and faunal endemicity, facing challenges in rapidly shrinking environments.
- More than 50% of the world's plant species and 42% of terrestrial vertebrate species are endemic to these 35 biodiversity hotspots.
Hottest Hotspots Factors
- Five factors, including endemic plants, endemic vertebrates, endemic plants/area ratio, endemic vertebrates/area ratio, and remaining primary vegetation, determine the hottest hotspots.
- The eight hottest hotspots globally, considering these factors, are Madagascar, Philippines, Sundaland, Brazil's Atlantic Forest, Caribbean, Indo-Burma, Western Ghats/Sri Lanka, and Eastern Arc and Coastal Forests of Tanzania/Kenya.
Indian Biodiversity Hotspots
- India hosts four biodiversity hotspots: The Himalayas, Indo-Burma, Western Ghats & Sri Lanka, and Sundaland.
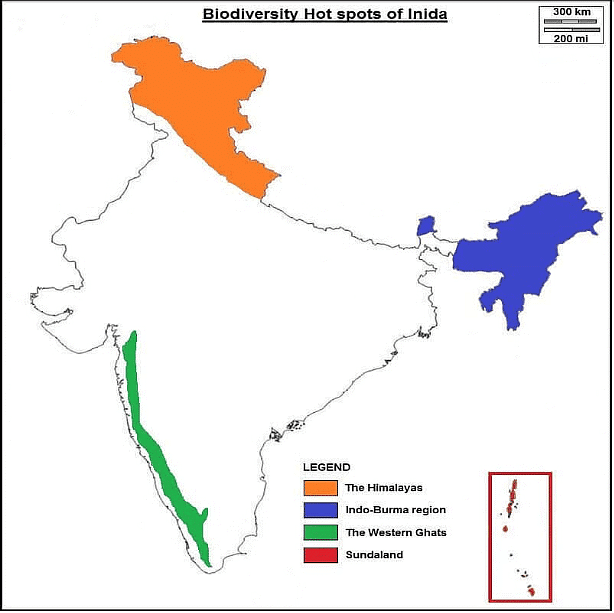
Details of Indian Hotspots
- The Eastern Himalayas Hotspot: - Encompassing Bhutan, northeastern India, and southern, central, and eastern Nepal, this region boasts high altitudinal variation and diverse ecosystems due to the abrupt rise of the Himalayan Mountains.
- Indo-Burma Region: - Spanning Eastern Bangladesh to Malaysia, including North-Eastern India, Myanmar, southern China's Yunnan province, Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam, and Thailand.
- Western Ghats and Sri Lanka: - Covering the southwestern parts of India and highlands of southwestern Sri Lanka, this hotspot exhibits varied vegetation types due to complex geography and rainfall patterns.
Biodiversity Coldspots
Biodiversity coldspots refer to areas with relatively low biological diversity but facing a high rate of habitat loss. While these areas may lack species richness, they hold importance for conservation because they might be the sole habitat for rare species.

Significance
- Extreme physical environments with low or high temperatures, pressures, or unusual chemical composition, housing just a few specially adapted species, are considered coldspots worthy of conservation. These areas showcase unique biological and physical characteristics, making them biologically and physically intriguing.
Marine Mega Fauna Stranding Guidelines
Objective and Coordination
- The purpose of the 'Marine Mega Fauna Stranding Guidelines' is to enhance coordination among different governments and civil societies involved in responding to marine strandings, conducting research, managing data, and fostering inter-sectoral collaboration for the conservation of marine animals.
Key Initiatives
- The guidelines focus on creating a comprehensive database on cetacean sightings and strandings across the country.
- They aim to establish a national stranding center and appoint district/local coordinators in areas with high stranding and bycatch cases.

Role of Marine Wildlife Stranding Network
- The primary functions of a marine wildlife stranding network include providing information, rescuing/rehabilitating stranded animals, collecting biological data, and, if possible, determining the cause of death.
Constituents of a Basic Marine Stranding Network
- A basic marine stranding network comprises first responders, forest guards, divisional forest officers, government veterinary officials, and marine police.
- First responders play a crucial role in ensuring the comfort of live individuals and preventing dead ones from being washed back into the sea. They also assist scientists, veterinarians, and departments in data collection or rescue-release operations.
Tagging for Live Strandings
- In instances of live strandings, where animals can be released into the sea, they will be tagged for identification purposes.
Long-Term Conservation Focus
- The overarching goal of these guidelines is to contribute to the long-term conservation of marine species and their habitats.
FAQs on Shankar IAS Summary: Protected Area Network- 2 - UPSC
| 1. What is the Wildlife Protection Act 1972? |  |
| 2. What is the purpose of the Export of Prohibited Goods? |  |
| 3. What is the World Network of Biosphere Reserves (WNBR)? |  |
| 4. What are Biodiversity Hotspots? |  |
| 5. What are Marine Mega Fauna Stranding Guidelines? |  |






















