UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Economics Optional for UPSC > Intellectual Property Rights - 2
Intellectual Property Rights - 2 | Economics Optional for UPSC PDF Download
Trade Marks
- The Trade Marks Registry was established in India in 1940 and presently it administers the Trade Marks Act, 1999 and the rules made thereunder. It acts as a resource and information Centre and is a facilitator in matters relating to trademarks in the country.
- The objective of the Trade Marks Act, 1999 is to register trademarks applied for in the country and to provide for better protection of trademark for goods and services and also to prevent fraudulent use of the mark.
- The main function of the Registry is to register trademarks which qualify for registration as per provisions of the Trade Marks Act and Rules, and to maintain the Register of trademarks.
- After accession to the Madrid Protocol, a treaty under the Madrid System for international registration of trademarks, the Trade Marks Registry also functions as an office of origin in respect of applications made by Indian entrepreneurs for international registration of their trademarks and as an office of the designated Contracting party in respect of international registrations in which India has been designated for protection of the relevant trademarks.
- The Head Office of the Trade Marks Registry is at Mumbai and branch offices are at Ahmedabad, Chennai, Delhi and Kolkata. For the purposes functions related to international applications and registrations under the Madrid Protocol, an International Registration wing is set up in the Head Office of the Trade Marks Registry at Mumbai.
- Apart from the above, the Registry has to discharge various other functions like offering preliminary advice as to registrability; causing a search to be made for issue a certificate under Section 45(1) of the Copyright Act, 1957 to the effect that no trademark identical with or deceptively similar to such artist work as sought to be registered as a copyright has been registered as a trademark; providing public information and guidance to the public on the subject; providing information to various government agencies including Police, Central Excise personnel, Public Grievance Redressal, maintenance of top class IP library, the production of annual statistical report, production of official Trade Marks Journal in electronic form and submit an Annual Report to Parliament.
- The Controller General of Patents, Designs and Trade Marks heads the TRADE MARKS Registry offices and functions as the Registrar of TRADE MARKS. He, from time to time, assigns functions of the Registrar to other officers appointed by the Central Government and such officers also function as Registrar in respect of matters assigned to them.
- Presently all the functions of the Trade Marks Registry are performed through an automated Trade Marks System. The Central Server of TMR is at Intellectual Property Office (IPO) Building in Delhi and Disaster Recovery server is at IPO, Mumbai. All branches of the Trade Marks Registry are connected to the main server in Delhi with Virtual Private Network (VPN). All the actions done by the office staffs through the TMS are recorded in the central server on real time basis.
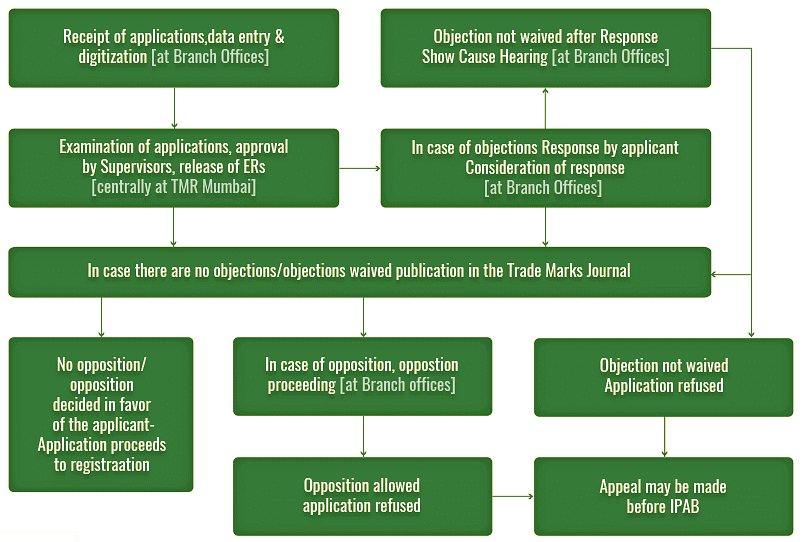
Office actions in processing applications for registration of trademarks
Vision and Mission
- Intellectual Property Rights is an inevitable tool for today’s globalized economy. Fostering innovation is one of the sustainable development goals set by the Government of India. “An India where Intellectual Property stimulates creativity and innovation for the benefit of all” is the vision of our National IPR Policy. Several initiatives have already proven to foster innovation like the Make in India, Start up India, Digital India and Skill India. The Atal Innovation Mission nurtures the innovative energies across the country in schools and universities. Under the IPR policy, the cell for IPR Promotion and Management, CIPAM has been tasked to facilitate creation and commercialization of IP assets in collaboration with the Office of the Controller General of Patents, Designs and Trademarks.
- The filings for IP rights have considerably increased and the Intellectual Property Offices are also getting revamped in terms of capacity building. More Examiners have been recruited and trained in Patents. The Patent Office started functioning as International Searching and Examining Authority since October 2013. It is encouraging to note that more applicants are now choosing IPO for international search. Applicants registered as Start-ups and those who have chosen Indian Patent Office as ISA or IPEA in the corresponding international application can avail of the facility of Expedited Examination. To ensure quality in all our operations, a dedicated Quality Assurance Division has been set up in the Patent Office.
- Manpower augmentationand business process reengineering have proved to substantially increase the output of the Trademarks Registry. Electronic communication has been initiated for Designs for quicker processing. Many of the globally famous products that are part of India’s rich cultural heritage have been registered as Geographical Indications. The Copyrights Office is also brought under the Office of CGPDTM.
- With all efforts in place, it is expected that IPO would leap to even greater heights.
The document Intellectual Property Rights - 2 | Economics Optional for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Economics Optional for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
66 videos|222 docs|73 tests
|
FAQs on Intellectual Property Rights - 2 - Economics Optional for UPSC
| 1. What are trade marks and why are they important? |  |
Ans. Trade marks are distinctive signs used by businesses to identify their products or services and differentiate them from those of their competitors. They can include words, logos, symbols, or even sounds or smells. Trade marks are important because they help consumers recognize and trust specific brands, and they also allow businesses to build and protect their reputation and goodwill in the market.
| 2. How do I register a trade mark? |  |
Ans. To register a trade mark, you need to file an application with the appropriate intellectual property office in your country. The application should include details about the mark, such as its description, representation, and the goods or services it will be associated with. It is essential to conduct a thorough search beforehand to ensure that your intended trade mark is not already registered by someone else. Once the application is filed, it will go through an examination process, and if approved, the trade mark will be registered.
| 3. Can I use the ™ symbol without registering my trade mark? |  |
Ans. Yes, you can use the ™ symbol without registering your trade mark. The ™ symbol indicates that you claim rights to a particular mark, even if it is not registered. However, it is important to note that using the ™ symbol does not provide the same level of protection as a registered trade mark. Registering your trade mark provides stronger legal protection, exclusive rights, and the ability to take legal action against infringement.
| 4. How long does a trade mark registration last? |  |
Ans. The duration of a trade mark registration can vary depending on the country. In general, trade mark registrations are valid for a certain period, typically 10 years, and can be renewed indefinitely as long as the mark continues to be used in commerce. However, it is essential to comply with renewal requirements and pay the necessary fees to maintain the registration.
| 5. What can I do if someone infringes on my trade mark rights? |  |
Ans. If someone infringes on your trade mark rights, you can take legal action to protect your rights and seek remedies. This can include sending a cease and desist letter, filing a lawsuit for trademark infringement, or seeking mediation or arbitration. It is advisable to consult with a qualified intellectual property attorney who can guide you through the process and help you enforce your trade mark rights effectively.
Related Searches





















