UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Polity for UPSC CSE > Recent Amendments in Indian Constitution
Recent Amendments in Indian Constitution | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE PDF Download

Context
In September 2023, the Constitution (106th Amendment) Act, 2023, was passed by Parliament to grant one-third reservation to women in the Lok Sabha, State Assemblies, and the NCT of Delhi.
Historical Background of Women’s Reservation
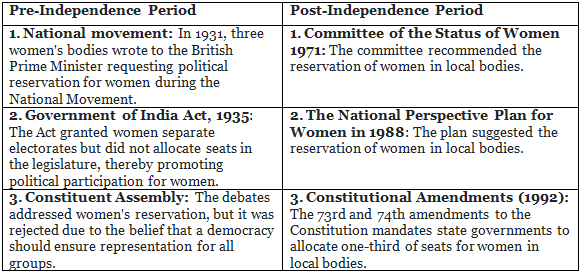
Background of the bill
The Constitution has been amended several times to allocate seats for women in Parliament and state legislative assemblies.
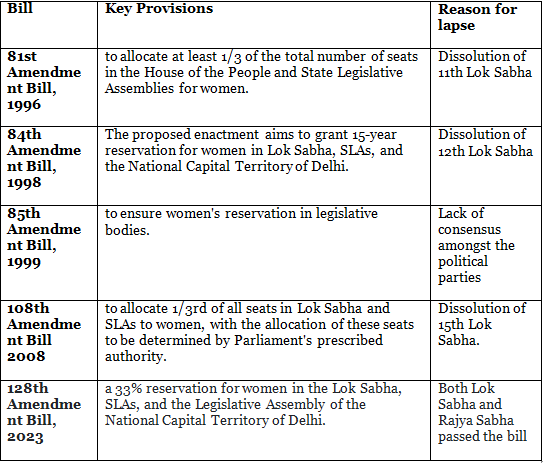
Key changes between 2008 and 2023 Bills
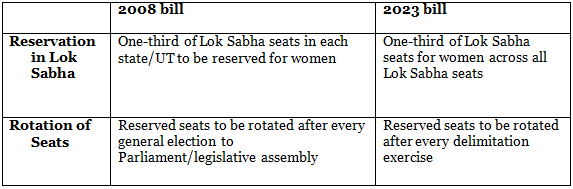
Key Features of the 2023 Act
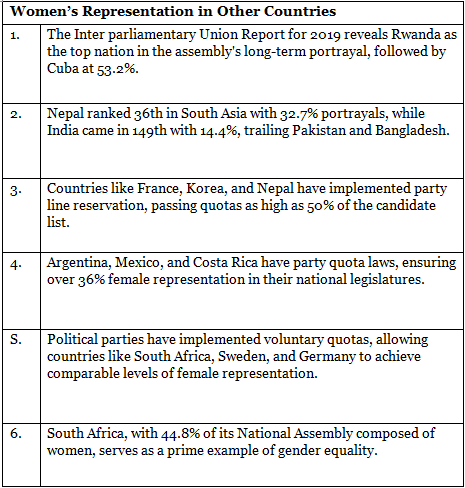
Status of Women Representation in India
- India ranks 48th out of 146 in the Global Gender Gap Report 2022 for Political Empowerment, including women's representation in Parliament and Ministerial positions.
- Currently, only 14.4% of the Indian Parliament’s members are women, the highest number so far.
- 3The 2019 Lok Sabha election saw nearly equal representation of women and men in voting, marking a significant milestone in India's political journey towards gender equality.
Reservation for Women in Lower House (Lok Sabha)
- The Bill introduced Article 330A to the constitution, incorporating provisions from Article 330, which grants seats to SCs/STs in the Lok Sabha.
- The Bill allows for the rotation of reserved seats for women to different states or Union Territories.
- The Bill aims to allocate one-third of the seats reserved for SCs/STs to women on a rotational basis.
Reservation for Women in State Legislative Assemblies
- The Bill introduces Article 332A, which mandates the reservation of seats for women in every state Legislative Assembly.
- One-third of the seats reserved for SCs and STs should be allocated to women.
- One-third of the seats allocated to women in direct elections to the Legislative Assemblies will also be reserved for them.
Reservation for Women in NCT of Delhi (New clause in 239AA):
- The bill added a new clause Article 239AA(2)(b) that stipulates Reservation of 1/3rd seats for women in the Legislative Assembly of the National Capital Territory (NCT) of Delhi.
- Article 239AA of the constitution grants special status to the Union Territory of Delhi as the national capital in terms of administrative and legislative functioning.
Commencement of Reservation (New article - 334A):
- The Bill incorporated Article 334 of the constitution, which mandates parliament to review reservation provisions after 70 years of laws' existence.
- The provisions of this act will take effect after delimitation and the first census taken after the commencement of this act.
- The bill introduced a 15-year sunset clause for the review of reservation provisions for women by parliament.
- Parliament can legally extend the reservation for women.
Rotation of Seats
- The Parliament may by law determine the periodic rotation of seats reserved for women after each subsequent delimitation.
- This act's provisions will not impact the representation in legislative assemblies and the Lok Sabha until their dissolution.
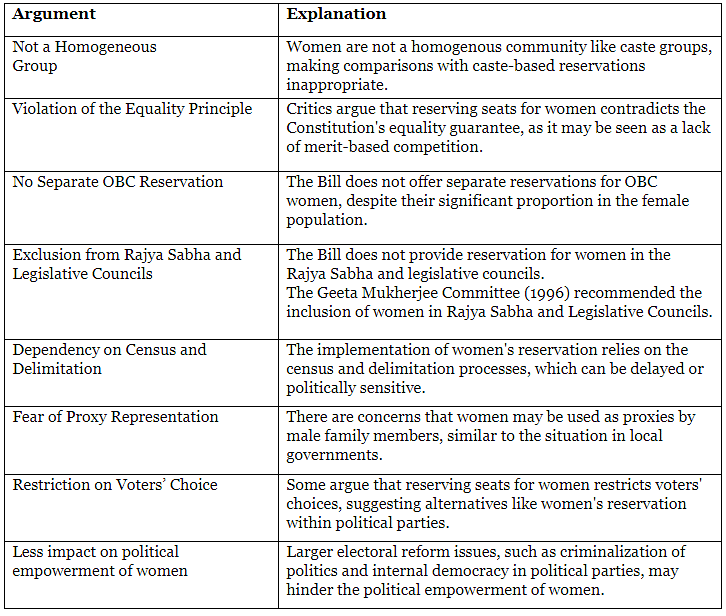
Arguments in favor
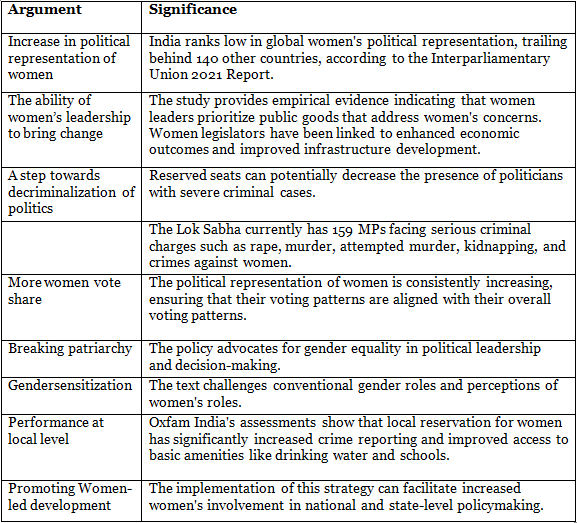
Arguments against the act
Way forward
- Timely implementation: The act's implementation should be ensured through timely conduct and publication of census data and delimitation exercise.
- Capacity building: This involves involving civil society and other institutions in the local training and mentorship of women leaders to ensure their effective mobilization at state and national levels.
- Raise Awareness and Education: To raise awareness about women's rights and the significance of political participation.
- Combat Gender-Based Violence: Implement policies and legal measures to combat gender-based violence and harassment, thereby fostering a safer political environment for women.
- Electoral Reforms: The proposed reforms include the implementation of electoral reforms such as proportional representation and preferential voting to increase the representation of women in the political process.
- Intra-Party Democracy: To institutionalize intra-party democracy and promote more women candidates.
- Strengthen Women’s Self-Help Groups: To encourage women's involvement at the grassroots level to prepare them for higher office positions.
- Support Women’s Agencies: To enhance organizations that promote gender equality and women's empowerment.
- Engage Young Women: To promote girls' involvement in student politics and political debates at colleges and universities.
Recent Developments
- Implementation Delays: As of April 2025, the women's reservation remains unimplemented due to the delay in the 2021 Census, postponed due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The delimitation process, critical for implementing the reservation, is now expected post-2026, affecting election timelines.
- Regional Concerns on Delimitation: Southern states like Tamil Nadu and Kerala have raised concerns about potential loss of representation in the delimitation process, as population-based redistricting may favor northern states like Uttar Pradesh, potentially shifting political power dynamics.
- Digital Personal Data Protection Act (DPDPA): Expected to be fully operational in 2025, the DPDPA aligns with the Supreme Court's recognition of privacy as a fundamental right under Article 21, impacting constitutional interpretations of data rights and governance.
- Digital India Act, 2023: This Act aims to regulate the digital ecosystem, with implications for constitutional rights and governance, particularly in areas like digital access and cybersecurity.
- Judicial Oversight: Since 2023, no significant judicial challenges to the 106th Amendment have been reported, but ongoing discussions about its implementation may lead to future legal scrutiny, relevant for constitutional law studies.
- Capacity Building: Efforts are underway to involve civil society in training women leaders to prepare for the eventual implementation of the reservation, ensuring effective mobilization at state and national levels.
- Awareness and Education: Campaigns to raise awareness about women's political rights continue to gain traction, emphasizing the importance of gender equality in governance.
- Combating Gender-Based Violence: Policies to create a safer political environment for women are being strengthened, addressing harassment and violence as barriers to participation.
- Electoral Reforms: Proposals for proportional representation and preferential voting are being discussed to enhance women's representation beyond the mandated reservation.
Conclusion
The reservation is expected to significantly enhance the nation's development, particularly for women, by tackling the underlying socioeconomic and political disparities.
The document Recent Amendments in Indian Constitution | Indian Polity for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Polity for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
142 videos|780 docs|202 tests
|
Related Searches
















