UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Commerce & Accountancy Optional Notes for UPSC > Mechanistic and Organic Structures
Mechanistic and Organic Structures | Commerce & Accountancy Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Mechanistic and Organic Organizational Structures
- The contingency approach to organizational design tailors organizational structure to the sources of uncertainty facing an organization.
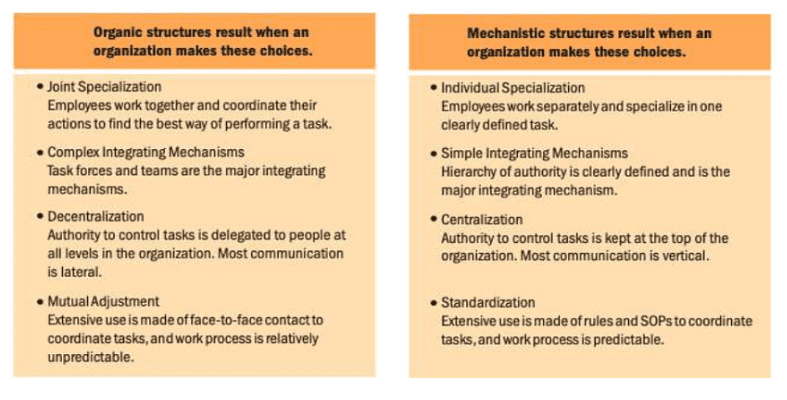
- In a landmark study conducted in 20 British firms during the 1960s, Tom Burns and G.M.Stalker identified two types of organisations— mechanistic and organic. They observed that the mechanistic organisation was characterised by: rules, procedures, a clear hierarchy of authority, centralised decision making, and the control of incoming and outgoing communications from the top and a tendency for information to be provided on a need to know basis.
- By contrast, the organic organisation was characterised by: low formalisation, rules and regulations were not written or if written down were ignored, and open and widely used communication patterns which incorporate horizontal, diagonal as well as vertical channels. Burns and Stalker’s research work stressed the belief that the organisation could change its structure in relation to its environment.
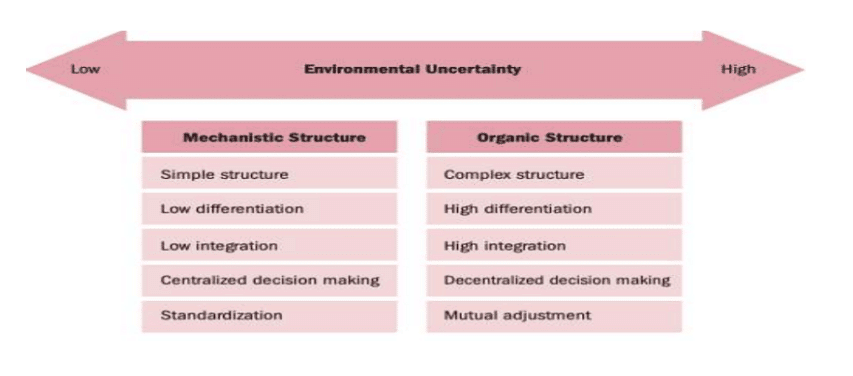
- Thus, in a rapidly changing environment, an organisation tends to change to organic form from the mechanistic form in order to remain competitive. The mechanistic form of organisation structure is adopted when there is relative stability in the environment.
- According to Stephen P. Robbins, these forms of organisation structures represent two extremes of a continuum. While the mechanistic model is generally synonymous with bureaucracy, the organic model looks more like the boundaryless organisation.
- The relation of one form to the other is elastic. As such, an organisation may oscillate from one end (mechanistic) to the other (organic) depending upon the nature of the environment and other factors like the overall strategy of the organisation, organisation size, and technology.
Question for Mechanistic and Organic StructuresTry yourself: Which type of organizational structure is characterized by rules, procedures, a clear hierarchy of authority, and centralized decision making?View Solution
The document Mechanistic and Organic Structures | Commerce & Accountancy Optional Notes for UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Commerce & Accountancy Optional Notes for UPSC.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
196 videos|219 docs
|
FAQs on Mechanistic and Organic Structures - Commerce & Accountancy Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is the difference between mechanistic and organic organizational structures? |  |
Ans. Mechanistic and organic organizational structures are two different approaches to organizing and managing a company. In a mechanistic structure, the organization is highly hierarchical, with clear lines of authority and rigid job descriptions. Decision-making is centralized, and there is a focus on efficiency and control. On the other hand, an organic structure is more flexible and decentralized. Decision-making is distributed throughout the organization, and there is an emphasis on innovation and adaptability.
| 2. What are the advantages of a mechanistic organizational structure? |  |
Ans. A mechanistic organizational structure offers several advantages. Firstly, it provides clear roles and responsibilities, reducing confusion and improving efficiency. Secondly, it allows for centralized decision-making, ensuring consistency and uniformity in the organization's operations. Lastly, it facilitates a high level of control and coordination, making it easier to manage large-scale operations.
| 3. What are the advantages of an organic organizational structure? |  |
Ans. An organic organizational structure has its own set of advantages. Firstly, it encourages innovation and creativity by allowing for decentralized decision-making and empowering employees. This leads to quicker adaptation to changes in the external environment. Secondly, it fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility among employees, which can improve their motivation and job satisfaction. Lastly, it promotes flexibility and agility, enabling the organization to respond rapidly to market demands.
| 4. How can an organization determine which structure is most suitable for them? |  |
Ans. Determining the most suitable organizational structure depends on various factors. One approach is to consider the organization's size and complexity. Mechanistic structures are more suitable for large organizations with standardized processes, while organic structures are better for small or entrepreneurial organizations. Additionally, the organization's industry and external environment should be taken into account. Stable and predictable industries may benefit from mechanistic structures, while dynamic and uncertain environments may require organic structures.
| 5. Can an organization have a combination of mechanistic and organic structures? |  |
Ans. Yes, an organization can have a combination of mechanistic and organic structures, known as a hybrid structure. This allows the organization to benefit from the advantages of both approaches. For example, the organization may have a centralized decision-making process for certain functions that require control and efficiency, while allowing for decentralized decision-making in other areas that require creativity and adaptability. The specific combination of mechanistic and organic elements can be tailored to the organization's unique needs and circumstances.
Related Searches
















