JEE Advanced Previous Year Questions (2018 - 2024): Work, Energy and Power | Physics for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
2024
No Question in JEE Advanced Exam from Chapter Work, Energy and Power in Year 2024 !
2023
Q1: One mole of an ideal gas undergoes two different cyclic processes I and II, as shown in the P-V diagrams below. In cycle I, processes a, b, c and d are isobaric, isothermal, isobaric and isochoric, respectively. In cycle II, processes a', b', c' and d' are isothermal, isochoric, isobaric and isochoric, respectively. The total work done during cycle I is W₁ and that during cycle II is W₂. The ratio W₁/W₂ is ______.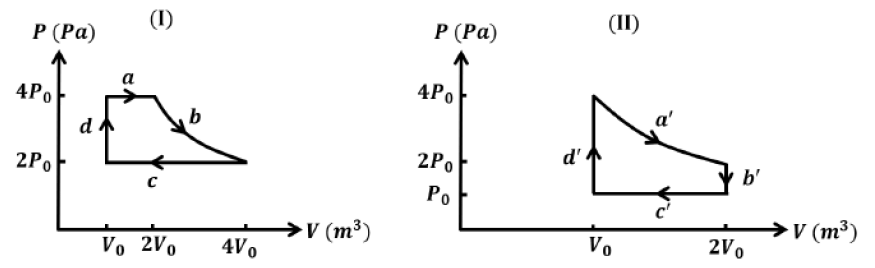
Ans: (2)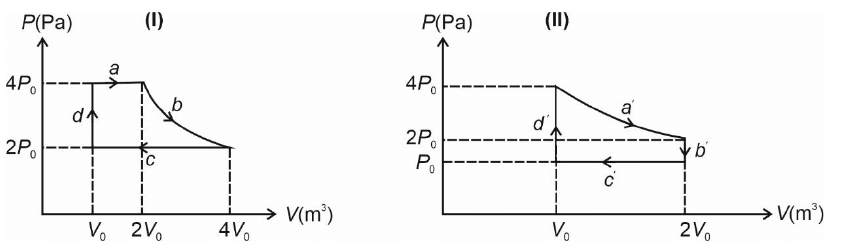 WI = Wa + Wb + Wc + Wd
WI = Wa + Wb + Wc + Wd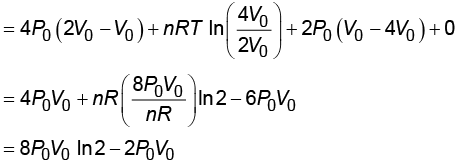
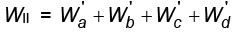
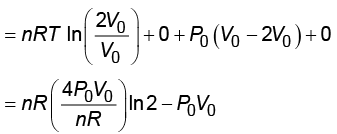
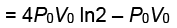
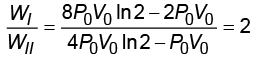
2022
Q1: The minimum kinetic energy needed by an alpha particle to cause the nuclear reaction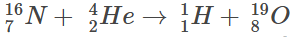 in a laboratory frame is n (in MeV). Assume that
in a laboratory frame is n (in MeV). Assume that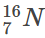 is at rest in the laboratory frame.
is at rest in the laboratory frame.
The masses of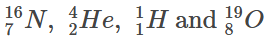 can be taken to be 16.006 u, 4.003 u, 1.008 u and 19.003 u, respectively, where 1 u = 930 MeVc–2. The value of n is _______.
can be taken to be 16.006 u, 4.003 u, 1.008 u and 19.003 u, respectively, where 1 u = 930 MeVc–2. The value of n is _______.
Ans: (2.33)
Q = (mN + mHe – mH – mO) × c2
= (16.006 + 4.003 – 1.008 – 19.003) × 930 MeV
= – 1.86 MeV
= 1.86 MeV energy absorbed.
And,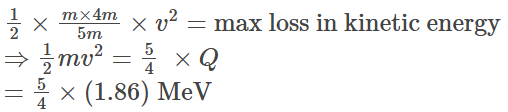 = 2.325MeV
= 2.325MeV
∴ n = 2.33
Q2: In the given P–V diagram, a monoatomic gas (γ = 5/3) is first compressed adiabatically from state A state B. Then it expands isothermally from state B to state C. [Given :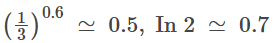 ]
]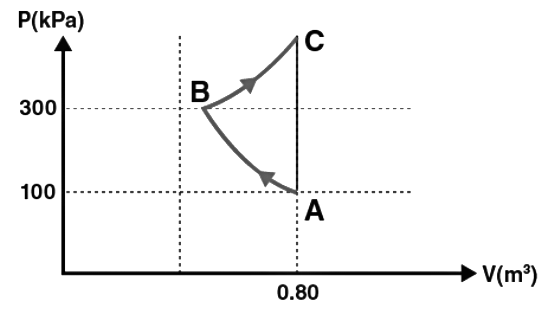 Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
Which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?
(A) The magnitude of the total work done in the process A → B → C is 144 kJ.
(B) The magnitude of the work done in the process B → C is 84 kJ.
(C) The magnitude of the work done in the process A → B is 60 kJ.
(D) The magnitude of the work done in the process C → A is zero.
Ans: (B, C, D)
Pvγ = c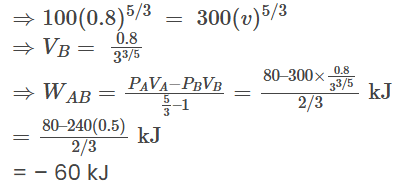 ⇒ (C) is correct
⇒ (C) is correct
C → A is isochoric ⇒ (D) is correct
BC : WBC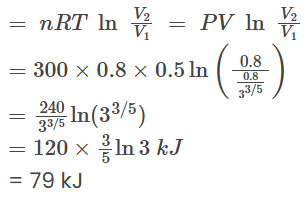 ⇒ (A) & (B) are not correct.
⇒ (A) & (B) are not correct.
2021
Q1: A special metal S conducts electricity without any resistance. A closed wire loop, made of S, does not allow any change in flux through itself by inducing a suitable current to generate a compensating flux. The induced current in the loop cannot decay due to its zero resistance. This current gives rise to a magnetic moment which in turn repels the source of magnetic field or flux. Consider such a loop, of radius a, with its centre at the origin. A magnetic dipole of moment m is brought along the axis of this loop from infinity to a point at distance r (>> a) from the centre of the loop with its north pole always facing the loop, as shown in the figure below.
The magnitude of the magnetic field of a dipole m, at a point on its axis at distance r, is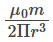
, where μ0 is the permeability of free space. The magnitude of the force between two magnetic dipoles with moments, m1 and m2, separated by a distance r on the common axis, with their north poles facing each other, is km1m2/r4, where k is a constant of appropriate dimensions. The direction of this force is along the line joining the two dipoles.
The work done in bringing the dipole from infinity to a distance r from the centre of the loop by the given process is proportional to?
(a) m/r5
(b) m2 /r5
(c) m2 /r6
(d) m2 /r7
Ans: (c)
Magnetic flux due to dipole through ring =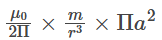
for net magnetic flux through the loop to be zero.
Magnetic flux due to dipole = Magnetic flux due to induced current
⇒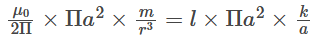 , where k is proportionality constant.
, where k is proportionality constant.
⇒ l∝ m/r3
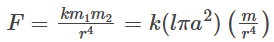 F = C(m2/r7) where C is a constant obtained by substituting the value of I
F = C(m2/r7) where C is a constant obtained by substituting the value of I
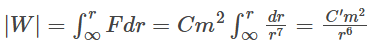 where C′ is a constant
where C′ is a constant
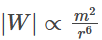
2020
Q1: A student skates up a ramp that makes an angle 30∘ with the horizontal. He/she starts (as shown in the figure) at the bottom of the ramp with speed v0 and wants to turn around over a semicircular path xyz of radius R during which he/she reaches a maximum height h (at point y) from the ground as shown in the figure. Assume that the energy loss is negligible and the force required for this turn at the highest point is provided by his/her weight only. Then (g is the acceleration due to gravity)
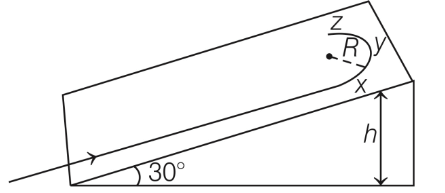
(a) 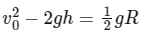
(b) 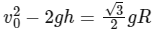
(c) the centripetal force required at points x and z is zero
(d) the centripetal force required is maximum at points x and z [JEE Advanced 2020 Paper 2]
Ans: (a) & (d)
Apply energy conservation,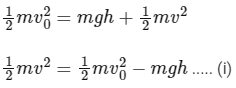
At top point y, the centripetal force provided by the component of mg,
mg sinθ = centripetal force = mv2 / R
mv2 / R = mg sinθ
Putting this value in Eq. (i), we get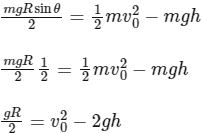
At point x and a of circular path, the points are at same height but less than h. So the velocity is more than point y.
So required centripetal force = mv2 / r is more.
2019
Q1: A particle is moved along a path AB-BC-CD-DE-EF-FA, as shown in figure, in presence of a force
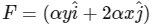 N, where x and y are in meter and α = −1 Nm-1. The work done on the particle by this force F will be ............... Joule. [JEE Advanced 2019 Paper 1]
N, where x and y are in meter and α = −1 Nm-1. The work done on the particle by this force F will be ............... Joule. [JEE Advanced 2019 Paper 1]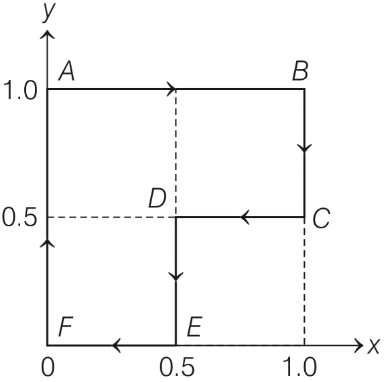
Ans:0.75
d = F.dr
d = αydx + 2αxdy
A → B, y = 1, dy = 0
then, 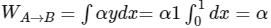
B → C, x = 1, dx = 0
then, 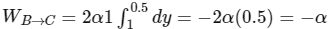
C → D, y = 0.5, dy = 0
then, 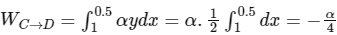
D → E, x = 0.5, dx = 0
then, 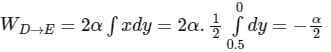
E → F, y = 0, dy = 0 then WEF = 0
F → A, x = 0, dx = 0 then WF→A = 0
∴ 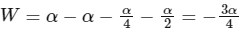
Given, α = −1
⇒ 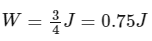
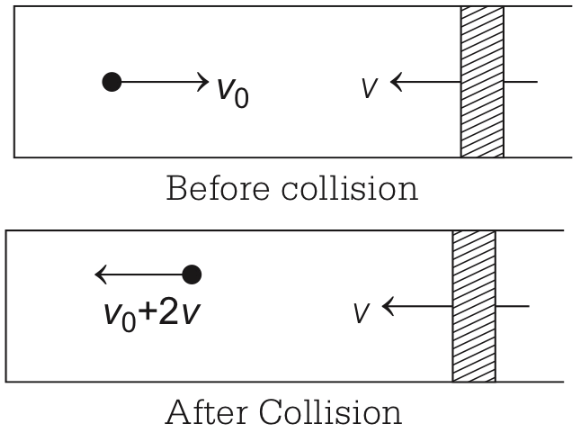
Q2: A small particle of mass m moving inside a heavy, hollow and straight tube along the tube axis undergoes elastic collision at two ends. The tube has no friction and it is closed at one end by a flat surface while the other end is fitted with a heavy movable flat piston as shown in figure.
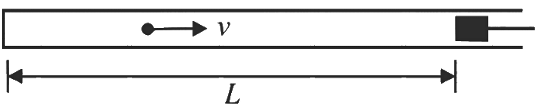
When the distance of the piston from closed end is L = L0, the particle speed is v = v0. The piston is moved inward at a very low speed V such that 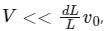 where dL is the infinitesimal displacement of the piston. Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
where dL is the infinitesimal displacement of the piston. Which of the following statement(s) is/are correct?
(a) After each collision with the piston, the particle speed increases by 2V.
(b) If the piston moved inward by dL, the particle speed increases 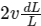 .
.
(c) The particle's kinetic energy increases by a factor of 4 when the piston is moved inward from L0to 1/2 L0.
(d) The rate at which the particle strikes the piston is v/L. [JEE Advanced 2019 Paper 2]
Ans:(a) & (c)
Change in speed = (2v + v0 − v0) = 2vIn every collision it acquires 2v, 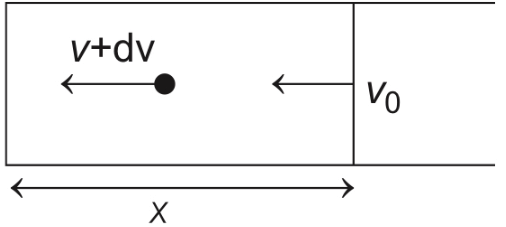
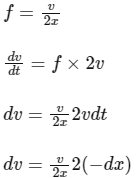
Integration on both sides limits v0 to v, we get
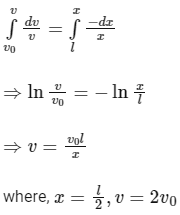
So, 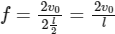
∴ 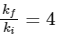
2018
Q1: A spring-block system is resting on a frictionless floor as shown in the figure. The spring constant is 2.0Nm−1and the mass of the block is 2.0kg.Ignore the mass of the spring. Initially the spring is an unstretched condition. Another block of mass 1.0kgmoving with a speed of 2.0ms−1collides elastically with the first block. The collision is such that the 2.0kgblock does not hit the wall. The distance, in metres, between the two blocks when the spring returns to its unstretched position for the first time after the collision is __________. [JEE Advanced 2018 Paper]
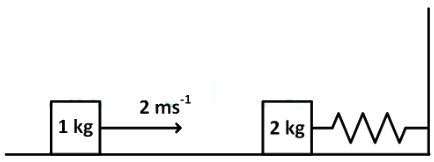 Ans: 2.09
Ans: 2.09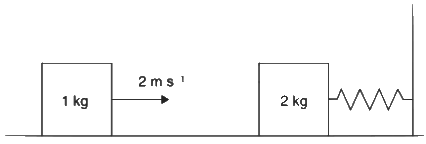
After collision the 2.0 kg block will perform simple harmonic oscillation with time period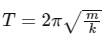
Given m = 2.0 kg and k = 2.0 N m−1, we have
T = 2π
Thus, the block returns to its original position in time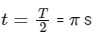
That is, t = 3.14 s
Now, if v1 and v2 are velocities of 1.0 kg block and 2.0 kg block, respectively, before collision; v'1 and v'2 are velocities of 1.0 kg block and 2.0 block, respectively, after collision. So, by conservation of momentum
m1v1 + m2v2 = m1v'1 + m2v'2
Here, m1 = 1.0 kg, v1 is initial speed of 1.0 kg block = 2.0 m s−1, m2 = 2.0 kg, v2 is initial speed of 2.0 kg block = 0.0 m s−1, v'1 is final speed of 1.0 kg block after collision and v'2 is final speed of 2.0 kg block after collision. Then, 1.0 kg × 2.0 m/s + 2.0 kg × 0 m/s = 1.0 v'1 + 2.0 v'2
v'1 + 2v'2 = 2 ..... (1)
Also, using definition of coefficient of restitution
v'2 − v'1 = ε(v1 − v2)
Since collision is elastic, So ε = 1
⇒ v'2 − v'1 = v1 − v2
⇒ v'2 − v'1 = 2 − 0
⇒ v'2 − v'1 = 2 ...... (2)
From Eqs. (1) and (2), we get
v′2 = 43 m s−1 and v'1 =−23 m s−1
Therefore, distance between the blocks is given as
s = v′1× t = −2 / 3 × 3.14
= 2.09 m
Q2: In the List-Ibelow, four different paths of a particle are given as functions of time. In these functions, αand βare positive constants of appropriate dimensions and α ≠ βIn each case, the force acting on the particle is either zero or conservative. In List-II, five physical quantities of the particle are mentioned 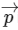 is the linear momentum,
is the linear momentum, 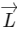 is the angular momentum about the origin, Kis the kinetic energy, Uis the potential energy and Eis the total energy. Match each path in List-Iwith those quantities in List-II, which are conserved for that path. [JEE Advanced 2018 Paper 2]
is the angular momentum about the origin, Kis the kinetic energy, Uis the potential energy and Eis the total energy. Match each path in List-Iwith those quantities in List-II, which are conserved for that path. [JEE Advanced 2018 Paper 2]
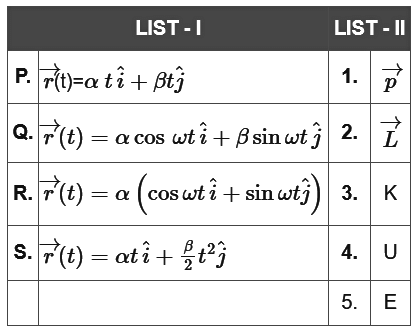
(a) P → 1, 2, 3, 4, 5; Q → 2, 5; R → 2, 3, 4, 5; S → 5
(b) P → 1, 2, 3, 4, 5; Q → 3, 5; R → 2, 3, 4, 5; S → 2, 5
(c) P → 2, 3, 4; Q → 5, 5; R → 1, 2, 4; S → 2, 5
(d) P → 1, 2, 3, 4, 5; Q → 2, 5; R → 2, 3, 4, 5; S → 2, 5
Ans:(a)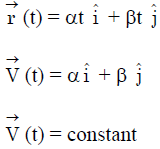
a = 0
F = 0
P = conserved ,
K = conserved
L = conserved ,
U = conserved
E = conserved
P → 1, 2, 3, 4, 5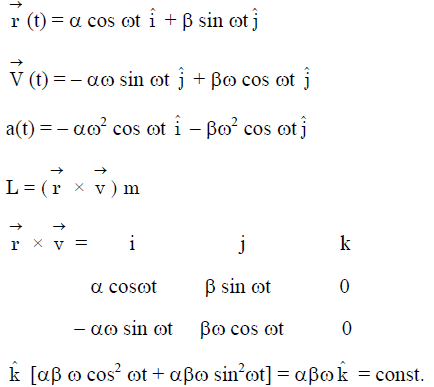
L = conserved τ of the force about origin is zero its mean this force is always passed through origin so it is central & conservative E = conserved.
Q → 2, 5
Q3: A particle of mass m is initially at rest at the origin. It is subjected to a force and starts moving along the x-axis. Its kinetic energy K changes with time as dK / dt = γt, where γ is a positive constant of appropriate dimensions. Which of a positive constant of appropriate dimensions. Which of the following statement is (are) true? [JEE Advanced 2018 Paper 2]
(a) The force applied on the particle is constant
(b) The speed of the particle is proportional to time
(c) The distance of the particle from the origin increases linearly with time
(d) The force is conservative
Ans: (a), (b) & (d)
Given, a particle at rest is subjected to force. Motion of particle is along x-axis.
Change in kinetic energy is given as
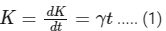
where γ is positive constant.
We know that kinetic energy is given by
K = 1/2mv2...... (2)
Now, differentiate Eq. (2), we get
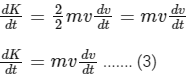
From Eqs. (1) and (3), we get
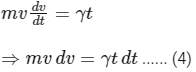
Integrating Eq. (4), we get
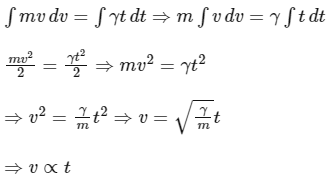
Since, γ and m are constant so the speed of particle is proportional to time therefore option (B) is true.
Also, 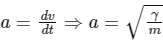 = constant
= constant
F = ma = constant
So, option (A) is true.
Also, v = dr/dt
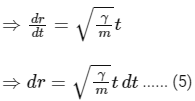
Integrating Eq. (5), we get
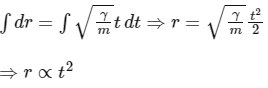
So, the distance of the particle from the origin increases at t2 so option (C) is false.
A force is conservative if work done by the force in any closed loop is zero (i.e., work done is independent of the path). If force is constant (both magnitude and direction) then work done by the force in a closed loop is given by
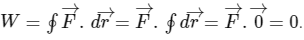
Note that we are able to take 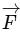 out of integral sign because
out of integral sign because 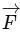 is constant and
is constant and 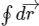 is zero because integration is carried out over a closed loop. The argument 'since force is constant, hence it is conservative' should be understood properly. The kinetic friction force and viscous drag force (when body moves with a terminal speed) are both constant (in magnitude) but are non-conservative. These forces cannot start the particle motion from the rest. The situation given in this problem is similar to a particle dropped from rest under the gravitational force. This force is constant, can initiate the motion given in the problem and is conservative.
is zero because integration is carried out over a closed loop. The argument 'since force is constant, hence it is conservative' should be understood properly. The kinetic friction force and viscous drag force (when body moves with a terminal speed) are both constant (in magnitude) but are non-conservative. These forces cannot start the particle motion from the rest. The situation given in this problem is similar to a particle dropped from rest under the gravitational force. This force is constant, can initiate the motion given in the problem and is conservative.
|
297 videos|953 docs|172 tests
|
FAQs on JEE Advanced Previous Year Questions (2018 - 2024): Work, Energy and Power - Physics for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What are the key concepts of Work, Energy, and Power that are frequently tested in JEE Advanced? |  |
| 2. How can I effectively prepare for Work, Energy, and Power questions in JEE Advanced? |  |
| 3. Are there any important formulas related to Work, Energy, and Power that I should memorize for JEE Advanced? |  |
| 4. What types of numerical problems can I expect in the Work, Energy, and Power section of JEE Advanced? |  |
| 5. How important are previous year JEE Advanced questions in mastering Work, Energy, and Power? |  |





















