Weekly Current Affairs (1st to 7th February 2024) | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
Union Cabinet Approves Extension of Subsidised Sugar Scheme and Other Schemes
Subsidised Sugar Scheme
- Union Cabinet has extended the Subsidised Sugar Scheme, which aims to provide sugar at subsidized rates to Antyodaya Anna Yojana (AAY) families, until 31st March 2026. This scheme is designed to improve the health of the poorest citizens by supplementing their diet with sugar. The Central Government provides a subsidy of Rs.18.50 per kg per month of sugar to AAY families in participating States.
- The extension of this scheme is will provide benefits exceeding Rs.1850 crore during the period of the 15th Finance Commission (2020-21 to 2025-26). In addition to this scheme, the Government of India also offers free ration under the Pradhan Mantri Garib Kalyan Anna Yojana (PM-GKAY) and sells essential food items like ‘Bharat Atta,’ ‘Bharat Dal,’ ‘Bharat Rice‘, tomatoes, and onions at affordable prices.
Rebate Scheme for Apparel/Garment Exports
- The Cabinet has approved the continuation of the Scheme for Rebate of State and Central Taxes and Levies (RoSCTL) for export of apparel and garments until 31st March 2026.
- The extension of this scheme is expected to provide a stable policy environment for long-term trade planning, particularly in the textiles sector. Textile products not covered under the RoSCTL can avail benefits under the Remission of Duties and Taxes on Exported Products (RoDTEP).
Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund
- The Animal Husbandry Infrastructure Development Fund (AIHDF) has also been extended for another three years, up to 2025-26. The AIHDF aims to encourage investments in dairy processing, product diversification, meat processing, animal feed plants, and breed multiplication farms.
- The Government of India will provide a 3% interest subvention for 8 years with a two-year moratorium for loans up to 90% from scheduled banks and other financial institutions.
New Technique by RRI Enhances Imaging of Cold Atoms
Flaws Plague Existing Imaging Methods
- Currently, magneto-optical traps paired with laser cooling techniques allow the closest-ever study of elements like sodium, potassium, and rubidium atoms cooled to extreme temperatures. However, fluorescence, absorption, and phase-contrast imaging methods traditionally used to detect atom behaviors have some major image flaws.
- Particularly, the interference fringes (unwanted dark-bright patterns) overlay the true images. This limits image quality and hinders precise calculations of critical measures like atom number, temperature, and real-time dynamics.
New Technique and 50% Fringe Reduction
- Leveraging eigen-face recognition techniques and optimizing with specialized masking, RRI’s new algorithm-based solution minimized interfering fringes in ultracold atom images by 50%. The clarity empowers more accurate temperature uncertainty calculations as well.
Importance of Optical Density Parameter
- The technology centers on accurately determining each image’s Optical Density. This parameter comes from logarithmically subtracting two image frames.
- One frame captures the cold atom cloud itself. The second documents background probe light levels.
- Ideally, identical fringe patterns in both frames cancel each other out through subtraction. But real-world images never align so perfectly. Removal of mismatched fringes enables proper Optical Density values.
Major Applications in Quantum Research
- With cold atom absorption imaging widely deployed across quantum mechanics labs, the fringe reduction technique has enormous potential. RRI scientists successfully applied the algorithm to absorption imaging of rubidium atoms at cryogenic temperatures.
Key areas benefiting include:
- Calculating ultracold atom cloud density profiles
- Measuring temperatures via atom cloud time-of-flight analysis
- Enabling quantum gas microscopy techniques
- In-situ testing of trapped atom behaviors
- Absorption imaging’s unique sensitivity, especially for small atom numbers, means expanded utility studying elusive quantum-state phenomena through enhanced image clarity.
Future Refinements Underway
- While a 50% image improvement demonstrates real progress, RRI researchers believe further refinement of the innovative algorithm method possible. Integrating advanced machine learning alongside the proven eigen-face recognition approach seeks to build on the current fringe reduction gains.
About RRI
- The Raman Research Institute is a renowned scientific research institute in Bengaluru. It was founded in 1948 by Nobel Laureate Sir C.V. Raman and his associates. RRI focuses on research in physics, astronomy and mathematics.
- Its specializations include spectroscopy, nonlinear dynamics and chaos, quantum technologies, and astronomy using multi-wave bands from radio to X-ray. It is currently collaborating with ISRO to develop XPoSAT, India’s first polarimetry mission.
Assam Public Examination (Measures for Prevention of Unfair Means in Recruitment) Bill, 2024
- The draft legislation aims to curb cheating and malpractices during exams in the state through strict penalties.
Purpose of the Bill
- The primary objective of the bill is to provide effective measures to prevent and curb offences related to leakage of question papers and use of unfair means in public examinations for recruitment to any state government post.
- This includes posts in autonomous bodies, authorities, boards, and corporations.
Definition of “Unfair Means”
- The bill defines “unfair means” as cheating by using unauthorized help in a public examination, leaking or attempting to leak a question paper, procuring or attempting to procure a question paper in an unauthorized manner, selling or solving a paper in an unauthorized manner, and directly or indirectly assisting an examinee in an unauthorized manner.
- It also includes conducting an examination or printing a question paper or blank answer scripts somewhere other than designated areas.
Key Features
- Special Courts: The bill proposes that the state government, in consultation with the Chief Justice of the Guwahati High Court, can designate and notify special courts not below the rank of an Additional District and Sessions Judge.
- 10-Year Jail Term: The bill introduces a provision for a 10-year prison sentence for offenses like leaking question papers or helping candidates use unfair means. This aims to act as a strong deterrent against exam malpractices.
- ₹10 Lakh Penalty: The draft law also stipulates a hefty fine of ₹10 lakh for those involved in distributing question papers without authorization or enabling cheating. The financial penalty further discourages such activities.
- More provisions: The bill further proposes that an examinee convicted under this law will be barred from writing any public exam for two years. In cases involving organized crime, the court can order the attachment of the offender’s property to recover any wrongful gains. If an institution or Limited Liability Partnership is found guilty of an offence under the law, it will be required to pay all the costs of the examination and will be banned permanently.
- Ban on Possessing Questions Illegitimately: The proposed law clearly prohibits candidates from possessing question papers without proper permission. This plugs a key loophole enabling cheating.
- Deterring Various Malpractices: Beyond leaking questions, the legislation addresses other common malpractices during exams like copying and external assistance to candidates. Stringent actions against all such activities will help reinforce exam integrity.
Significance
- In the past five years, Assam has witnessed two major recruitment scandals. The first occurred in 2020, when a recruitment exam for 597 sub-inspector posts had to be cancelled due to a paper leak. Senior and retired IPS officers were among those arrested.
- The second scandal emerged in 2021, over two years after the exams had been conducted, when the government announced the cancellation of the 2019 exams for various posts in the Assam Power Distribution Company Limited due to widespread irregularities.
- The bill signifies the Assam government’s firm commitment to eradicate cheating and unfair means in exams. It aims to overhaul the examination system and selection processes. However, effective on-ground enforcement and speedy trials will be key to the success of this law. Administrative and judicial delays could blunt its impact. Supporting awareness drives should accompany strict policing.
Opposition Suggestions
Opposition parties have argued for measures like housing exam centers in CCTV surveillance networks. This could complement laws enhancing surveillance and identifying violations.
Uttarakhand Uniform Civil Code Bill
- The proposed bill aims to regulate and govern laws related to marriage, divorce, successions, and live-in relationships. The bill specifically prohibits bigamy and polygamy, practices that involve marrying multiple people simultaneously or while still legally married to another person. The UCC Bill also outlines five specific conditions for the solemnisation of marriages in the state.
Key Features
- Bans on Polygamy and Child Marriage: The draft UCC includes a complete ban on practices like polygamy and child marriage across religions.
- Standardized Marriage Age: The code sets 18 years as the uniform marriageable age for all girls, enabling them to pursue higher education before marriage. Couples who fail to register their marriages would be ineligible for government facilities to encourage legal documentation.
- Uniform Divorce Laws: The UCC envisages standardized divorce laws such as halala and iddat. This eliminates differential treatments depending on religious affiliations.
- Equal Adoption and Property Rights: The draft grants equal adoption rights to all citizens irrespective of gender or faith. It also confers equal property inheritance rights for both sons and daughters and adopted and biological children. In case of death, the spouse, children and parents will have equal rights over the property.
- Mandatory Registration of Marriages and Live-In Relationships: Another significant proposal requires mandatory registration of all marriages to ensure legal accountability. Live-in relationships would also need to be registered under the new laws.
Conditions for Solemnisation of Marriages
Under section 4 of the UCC Bill, five conditions are laid out for the valid solemnisation of a marriage between a man and a woman. These conditions include:
- Neither party should have a living spouse at the time of the marriage.
- Neither party should be incapable of giving valid consent due to mental unsoundness, suffering from a mental disorder rendering them unfit for marriage, or subject to recurrent attacks of insanity.
- The man should have completed 21 years of age and the woman 18 years of age.
- The parties should not be within the degrees of prohibited relationship unless their custom or usage permits such a marriage. However, these customs and usages should not be against public policy and morality.
- The marriage should not be prohibited under any existing law.
Religious Beliefs, Practices, and Ceremonies
- The UCC Bill also allows for the solemnisation of marriages according to various religious beliefs, practices, customary rites, and ceremonies. These include but are not limited to “Saptapadi”, “Ashirvad”, “Nikah”, “Holy Union”, “Anand Kara” under The Anand Marriage Act 1909, The Special Marriage Act, 1954, and Arya Marriage Validation Act, 1937.
Exemptions in the UCC Bill
- Despite its broad scope, the UCC Bill does not apply to certain groups. Members of any Scheduled Tribes as defined in clause (25) of Article 366 read with Article 142 of the Constitution of India are exempted.
- Additionally, persons and groups of persons whose customary rights are protected under Part XXI of the Constitution of India are also not subject to the provisions of the UCC Bill.
TOI-715b: NASA Discovers Potential Life-Sustaining ‘Super-Earth’
Characteristics of Planet TOI-715b
- The planet TOI-715 b resides within the star’s “conservative habitable zone,” meaning liquid water could potentially exist on its surface given the right atmospheric conditions.
- While several factors must align for surface water, including a suitable atmosphere, the conservative habitable zone makes conditions ripe for further investigation. NASA notes the planet could be slightly larger than Earth and may be a “water world,” making its atmosphere more prominent.
Properties of Parent Star
- The super-Earth orbits a red dwarf star, which is smaller and cooler than our Sun. Red dwarfs are known to host small, rocky worlds in very close orbits compared to planets around Sun-like stars.
- But due to cooler temperatures, these tight orbits can remain safely in the habitable zone. More transits also occur due to tight orbits, enabling better detection and study of planets.
Follow-up Plans to Study Viability
- NASA plans further scrutiny of TOI-715 b by the James Webb Space Telescope, which will characterize the planet based on additional properties.
- Much depends on the planet’s mass, whether it has an atmosphere, and any water content. These factors impact both habitability and the ability to study its atmosphere from Earth-based telescopes if present.
Earth Like Planets
- While Earth is the only known place harboring life, estimates of habitable zones and discoveries of thousands of exoplanets suggest there may be many more habitable places in the Universe. Based on Kepler data, there could be 40 billion Earth-sized planets in habitable zones of Milky Way stars, including 11 billion orbiting Sun-like stars.
- The nearest such potentially habitable exoplanet may be just 12 light-years away. As of 2024, more than 60 potentially habitable exoplanets have been confirmed, though more await discovery.
About Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS)
- Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) is a NASA mission designed to search for exoplanets or planets around other stars. The mission was launched in 2018 and has made significant progress so far. Its mission objective is to discover new planets that periodically block part of the light from their host stars, events called transits.
- TESS has identified over 5,000 candidate exoplanets, 173 of which have been confirmed. TESS has found a number of rare exoplanet discoveries earlie like TOI 700 d, a potentially habitable Earth-sized world; AU Mic b, a nearby Neptune-sized planet; and LTT 9779b, a planet slightly bigger than Neptune with two suns.
PETA Challenges Traditional Buffalo, Bulbul Fights in Assam
Bulbul fighting in Hajo temple
- Another tradition involves bulbul fighting at the Hayagriva Madhava Temple in Hajo, about 30km from Guwahati. Rearing and training bulbuls for fighting during Magh Bihu is considered a religious practice by the temple authorities.
- The fights are held with lamps lit and offerings made to Lord Vishnu. The tradition is claimed to have origins dating back to the rule of the Ahom kings in Assam.
Ban after Supreme Court ruling in 2014
These events were discontinued after the Supreme Court ruling in 2014 that prohibited the use of bulls and other animals for entertainment like jallikattu and bullock cart racing. Following this, the Animal Welfare Board of India (AWBI) directed the Assam government to ban animal fights during Bihu. The state government passed orders prohibiting buffalo and bulbul fights in 2015, though some defiant events continued. The Hajo temple authorities also challenged the ban in court.
Revival after amended law in 2021
In May 2021, the Supreme Court approved amendments made by some states to allow jallikattu and similar events, overturning its 2014 judgment. Subsequently, the Assam government approved framing of standard operating procedures (SOPs) for regulated conduct of buffalo and bulbul fights without cruelty. The SOPs restricted fights to traditional venues, prohibited use of drugs or weapons, and mandated care for animals’ well-being. With this, the events resumed in 2022 after a gap of several years.
Recent Context: PETA challenges in High Court
Animal rights group PETA India has now filed petitions in the Gauhati High Court seeking a complete ban on buffalo and bulbul fighting events. PETA claims its investigations found violations of animal cruelty laws and the government’s own SOPs at recent events. It alleges animals were abused and forced to fight despite injuries. The court has admitted the petitions and ordered action against any event violating the SOPs.
What is deadly Fungus Candida Auris, that is Rapidly Spreading in US?
What is Candida auris?
- Candida auris (C. auris) is a fungal pathogen that can cause serious infections in the bloodstream and other parts of the body. It’s considered a serious global health threat. C. auris is often resistant to antifungal medications, making it difficult to treat. In some cases, multiple antifungal medications at high doses may be needed to treat the infection. C. auris is spread in health care facilities through contact with contaminated surfaces or equipment, or from physical contact with a person who has C. auris.
- It can live on surfaces for several weeks. C. auris mostly affects patients with severe underlying medical conditions and requiring complex medical care. Patients with invasive medical devices such as breathing tubes, feeding tubes, catheters in a vein, or urinary catheters tend to be at increased risk. More than 1 in 3 patients with invasive C. auris infection die, thus it has very high fertility rate.
- It often infects people who have weakened immune systems. The fungal infection is resistant to several common antifungal medications, making it difficult to treat.
Symptoms and Risk Factors
- The symptoms of Candida auris infection depend on where in the body the infection occurs. Bloodstream infections can cause fever and chills. Infections in wounds may cause redness, pain and drainage. Symptoms are similar to other types of fungal infections.
- People at highest risk include those who are hospitalized, especially patients who have feeding tubes, breathing tubes or catheters. Candida auris can spread easily in healthcare facilities and colonize the skin without making people sick. Colonized individuals can still transmit the fungus to others.
Recent U.S. Cases
- Following the first confirmed case in Washington state in January, 2024, three more infections were reported recently. Prior to these cases, 2,377 Candida auris infections were reported in the U.S. in 2022 compared to just 53 in 2016.
- The Centers for Disease Control (CDC) and World Health Organization now consider it an urgent threat.
Prevention and Control
- To prevent the spread of Candida auris, hospitals isolate infected patients in private rooms and use gowns, gloves and disinfectants. Frequent hand washing with soap and water or alcohol-based sanitizers before and after contact with patients is critical.
- Cleaning hospital rooms with disinfectants that work against Clostridioides difficile (C. diff) is recommended after patients with Candida auris are discharged. Caregivers and visitors should clean hands before entering and leaving patient rooms.
Treatment and Outcomes
- Since Candida auris is often resistant to antifungal medications, treatment can be challenging. Testing is needed to determine which drugs may be effective.
- About 1 in 3 patients die within a month of infection. Outcomes depend on the patient’s overall health and underlying medical conditions.
Global Spread
- First discovered in Japan in 2009, Candida auris has now spread to over 40 countries around the world. Infections have continued rising steeply in recent years.
- Its ability to spread in healthcare settings and persist on surfaces make it difficult to control. Improved infection prevention measures are critical to curb transmission.
What is the ‘Widow Year’ in China?
Different Types of Chinese Years
China has 12 different types of years listed below including their corresponding zodiac signs and elements:
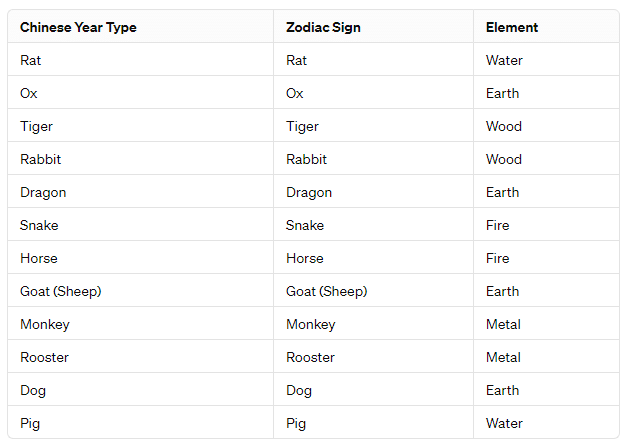
These are the 12 zodiac signs in the Chinese lunar calendar, and they repeat in a cycle of 12 years. Additionally, each year is associated with one of the five elements: Wood, Fire, Earth, Metal, or Water, which also follow a cyclical pattern. The combination of the zodiac sign and element determines the unique characteristics and qualities associated with each year in Chinese astrology.
Origin of the Term ‘Widow Year’
The term “Widow Year” (gua fu nian in Chinese) originates from a misunderstanding of gua nian, meaning “the year lacking Spring Commences.” Spring Commences symbolized a blessed and lucky year in ancient Chinese culture, as it marked the coming of spring and renewal. The absence of Spring Commences was seen as inauspicious. Over time, gua nian transitioned into the term Widow Year.
Associations with Marriage
In Chinese superstition, Spring Commences represents masculine, yang energy. Therefore, a Widow Year without Spring Commences is considered a year lacking yang energy. This gave rise to the belief that women who marry in a Widow Year may face early widowhood or other misfortunes in marriage. The term Widow Year reinforces this belief. However, historical data shows Widow Years do not significantly impact marriage rates.
Other Superstitions
Beyond marriage, Chinese superstitions advise against many major activities during Widow Years. Building houses, starting businesses, erecting tombstones, and other big endeavors are often avoided in Widow Years due to beliefs about bad feng shui. However, these superstitions have lessened in modern times.
Marriage Customs Endure
While many Chinese no longer alter marriage plans due to Widow Year superstitions, traditions for ensuring a lucky marriage remain. Many couples still consult fortune tellers to select auspicious wedding dates. Symbolic decorations, rituals, and other Chinese wedding customs are still widely practiced.
Sphaerotheca varshaabhu: New Burrowing Frog Species Discovered in Karnataka
Urban Adaptation
“Sphaerotheca varshaabhu has adapted to its urban surroundings in surprising ways, displaying behaviours and physical attributes that enable it to navigate the challenges posed by urbanisation. The discovery emphasises the need for continued exploration of urban ecosystems and the preservation of biodiversity in areas heavily impacted by human activities,” the statement read.
Multi-Institutional Collaboration
The new species discovery is an outcome of multi-institutional collaborations like Mount Carmel College, Bengaluru, Zoological Survey of India (ZSI), Western Regional Centre (WRC), Pune, JAIN (Deemed- to- be-University), Bengaluru, Institute of Systematics, Evolution, Biodiversity (ISYEB), National Museum of Natural History, CNRS, Sorbonne University, Paris, France, Centre for Ecological Sciences (CES), Indian Institute of Science, Bengaluru; Laboratory of Animal Behaviour and Conservation, College of Biology and the Environment, Nanjing Forestry University, Jiangsu, China and Genetics Research Laboratory, Department of Zoology, Yuvaraja College, University of Mysore, Mysuru.
Tamilaga Vettri Kazhagam
- Vijay stated that his target is the 2026 state election. He clarified he wouldn’t participate in the upcoming national election. Vijay’s fans, who call him ‘Thalapathy’ (General), celebrated his new career path in the streets and on social media. The ruling DMK and opposition BJP conveyed their best wishes to the actor.
- Vijay had previously launched his fan club in 2009 which participated in 2011 elections. The club also contested local body elections in 2021, winning 115 of 169 seats. This set the stage for Vijay’s entry into politics with TVK in 2024.
Cinema Stars in Tamil Nadu Politics
Tamil Nadu has a long history of cinema stars in politics. MGR, K Karunanidhi and Jayalalithaa ruled state politics for about 50 years. In recent times, several stars tried entering politics but with limited success. Kamal Haasan started the Makkal Needhi Maiam party. Rajinikanth formed the Rajini Makkal Mandram but later abandoned politics due to health issues. Vijayakanth formed the DMDK in 2005 but never attained power. CM Stalin’s son Udaynidhi has been an actor.
Champai Soren Sworn in as Jharkhand Chief Minister
Champai Soren
Mr. Champai Soren will be 12th Chief Minister of Jharkhand. He is from the Jharkhand’s Kolhan region which comprises East Singhbhum, West Singhbhum and Seraikela-Kharsawan districts. In the 81-member Jharkhand Assembly, the majority alliance has 47 MLAs — JMM 29, Congress 17 and RJD 1. The BJP has 26 members and the AJSU Party three. The NCP and CPI (ML) have one lawmaker each, apart from two Independents.
Other Chief Ministers of Jharkhand
- Babulal Marandi (1958-): Jharkhand’s first CM. Served from 2000-2003 after leading BJP to power in the new state’s first election. Had differences with BJP later. Formed his own regional party but did not regain power.
- Arjun Munda (1968- ): Youngest CM from 2003-05. Allied with BJP. Returned for two more brief terms in 2010 and as recently as 2021-2022. Seen as a prominent tribal leader nationally.
- Shibu Soren (1944-): The JMM patriarch. Served three very short stints as CM in 2005-06 and 2008-10. Unable to provide stable governments. But remains the tallest Moolvasi (tribal) face in state politics.
- Madhu Koda (1971- ): Independent MLA who became CM backed by UPA allies from 2006-2008. Forced to resign after massive corruption charges. Spent time in jail. Political career destroyed.
- Hemant Soren (1975-): Inherited JMM from father Shibu Soren. Became youngest CM in 2013.
- Raghubar Das (1955-): BJP’s first non-tribal CM from 2014-2019. Credited with bringing stability, pushing infrastructure and industries. But alienated tribals. Voted out in 2019.
High Risk of Cervical Cancer Among Indian Women
Cause of Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is often caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) infections. HPV is a sexually transmitted infection. If HPV persists in the body for years, it can cause changes in the cervical cells that may lead to cancer. Women with compromised immune systems, such as those with HIV, are at higher risk of cervical cancer.
Need for Cervical Cancer Vaccine
India has over 500 million women aged 15 and above who are at risk of cervical cancer. Vaccination against HPV can help prevent cervical cancer. The National Technical Advisory Group for Immunization (NTAGI) recommended HPV vaccination for girls aged 9-14 under the Universal Immunization Programme in 2022.
Cervical Cancer Vaccines Available in India
Currently, Merck’s HPV vaccine Gardasil and Serum Institute of India’s indigenous vaccine CERVAVAC are available in the Indian market. Gardasil is priced at around Rs. 10,850 per dose while CERVAVAC costs around Rs. 2,000 per dose. In 2023, India rolled out CERVAVAC nationally in partnership with DBT and BIRAC.
Government’s Move to Support HPV Vaccination
In the 2024 budget speech, Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman announced an initiative to promote HPV vaccination for girls aged 9-14 years. The aim is to vaccinate this age group against cervical cancer and save over 125,000 lives annually. The budget signals the government’s intent to strengthen the cervical cancer immunization program across the country.
UP’s Mission to Eradicate Filariasis
What is Filariasis?
Filariasis is a disease caused by parasitic worms transmitted through mosquito bites. It can lead to conditions like swelling of limbs and genitals. The government aims to eliminate this disease from the country by 2027.
Key Details of the MDA Campaign
- Duration and Location: The 15-day campaign will cover 17 districts in UP. These are Amethi, Azamgarh, Ballia, Banda, Barabanki, Bareilly, Hamirpur, Jaunpur, Jalaun, Lucknow, Pilibhit, Shahjahanpur, Prayagraj, Pratapgarh, Sonbhadra, Unnao, and Varanasi. Presently, 51 districts in UP are affected by filariasis. The MDA will expand to cover the rest of the districts from August 10, 2024
- Target Population: Health workers will go door-to-door to administer preventive medication to all residents except children under 2 years, pregnant women and seriously ill people.
Need for Preventive Efforts
The government has asked people to take the medication even without symptoms. This is important because:
- Symptoms can take 5-15 years to show up after infection
- Once infected, the disease is irreversible and only management is possible
- Preventive efforts can safeguard the next generation
Government’s Commitment
The government is training health workers at primary health centers to identify filariasis patients. It is also tracking and recording data of existing patients in the state. By conducting regular MDA drives, the government aims to completely eliminate the disease by the targeted year.
|
164 videos|626 docs|1130 tests
|