Role and Importance of Materials Management | Management Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
Material management within an organization encompasses several fundamental objectives:
- Acquiring materials at the lowest feasible price while ensuring that quality and continuity of supply are not compromised.
- Minimizing inventory levels without impeding the timely availability of materials, thereby freeing up working capital for other organizational needs.
Ultimately, the essence of any material management system lies in reducing procurement, storage, and handling costs without compromising quality or material availability.
- Material management procedures are strategically integrated into an organization, holding varied significance for different stakeholders. While some emphasize purchasing, others prioritize inventory control. Effective material management often intertwines with quality management and assurance, leading to reduced material rejection rates and overall production costs. Quality control throughout the procurement-to-distribution process significantly impacts productivity and corporate reputation.
- A robust logistics system is crucial for ensuring a continuous flow of materials into the production pipeline, potentially minimizing the reliance on extensive material management practices. However, the effectiveness of this continuum and its alignment with quality control processes within an organization warrant scrutiny.
- Material management thus emerges as a critical strategic concern within organizational operations, warranting further exploration in subsequent sections.
Objectives and Advantages of Material Management in an Organization
Material management in an organization serves several primary and secondary objectives. The core objectives include:
- Efficient and cost-effective procurement of materials.
- Proper storage practices to minimize wastage and delays.
- Ensuring timely availability of materials.
A well-functioning material management system maintains comprehensive records, preferably using computer-based tools. Additionally, it serves several secondary objectives related to its functions:
- Identifying new or improved sources of supply.
- Establishing and nurturing vendor relationships.
- Standardizing product quality.
- Conducting value analysis of inventory to manage costs.
- Facilitating smooth material and information flow across different sections of the management system.
Material management aligns with the broader organizational objectives of maximizing profit, sustaining growth, satisfying customers and staff. It achieves this by:
- Maintaining a consistent flow of materials to ensure continuity of supply.
- Employing scientific techniques and electronic tools to reduce material and handling costs.
- Minimizing working capital holdups through effective inventory control.
- Releasing working capital by optimizing inventory control.
- Providing high-quality materials at competitive prices.
- Cultivating better relationships with customers and suppliers.
Integrated Material Management: Why?
The material management process encompasses various functions such as planning, purchasing, receiving, stores, inventory control, and disposal of scrap and surplus. Integration of these functions is essential because:
- Operating these functions independently may lead to suboptimal outcomes.
- Similar to assembling computer hardware, where component compatibility is crucial, integration ensures alignment of functions to avoid conflicts and optimize outcomes.
Advantages of Material Management:
Organizations implementing integrated material management enjoy several advantages, including:
- Improved accountability across departments.
- Enhanced coordination due to centralized material management authority.
- Timely supply of high-quality materials, leading to improved organizational performance.
- Informed decision-making through the use of information systems.
- Indirect benefits include the development of ethical and moral standards within the organization, although empirical studies on this aspect are lacking.
Scope of Materials Management
However, it's important to outline the scope of materials management after discussing its role extensively.
Although the scope of a material management system is vast, yet we can define the following functions as its scope functions.
Material Planning and Control: One crucial aspect defining the scope of materials management is material planning and control. This function is guided by the organization's sales forecast and production plans. Activities within this function include:
- Estimating material requirements
- Developing the organization's materials budget
- Determining inventory levels needed
- Scheduling vendor orders to ensure material availability
- Monitoring production against sales to maintain control.
Purchasing: Purchasing is another significant function within materials management, involving the following activities:
- Identifying and selecting potential suppliers
- Finalizing purchase terms and conditions
- Placing purchase orders, possibly staggered based on inventory control needs
- Managing purchase orders until materials are delivered
- Authorizing payment for received goods
- Evaluating supplier performance and rating them.
Stores and Inventory Control: This function focuses on the physical control of materials and includes the following activities:
- Minimizing material losses due to obsolescence and mishandling, ensuring timely disposal and efficient handling.
- Maintaining accurate store records and organizing material storage.
- Conducting physical stock verification and reconciliation.
- Implementing inventory setting and control measures, such as ABC analysis, determining economical ordering quantities, identifying safety stock levels, and analyzing lead times.
Roles of materials management in an organization
Materials Management is a system that tries to ensure the following for an organization:
- Availability of products desired by customers should be ensured, with a focus on optimizing cost of manufacture. Quality and cost considerations fall under the purview of the Production Manager, but material management plays a supportive role by ensuring timely delivery of quality materials.
- Additionally, material management can provide valuable input for advising on sales pricing by maintaining comprehensive records. For instance, determining the cost of materials used in a product can aid in setting appropriate pricing strategies.
- The material flow process, depicted in Figure, demonstrates how customer demand initiates a series of material and information flows. Material management is essential throughout this lifecycle, generating strategic insights from the wealth of information generated during these flows.
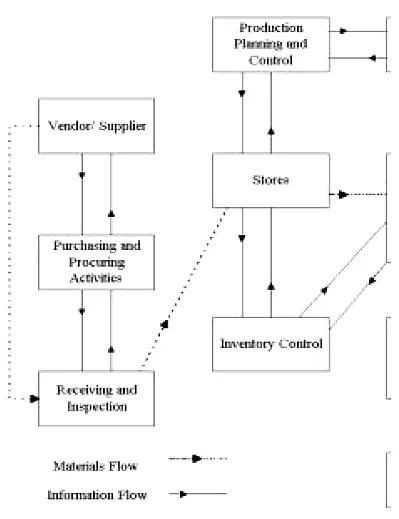
- To further delineate the strategic role of material management, it's essential to examine its internal interfaces in greater detail. While the indirect benefits of material management have been linked to external interfaces, internal interfaces play a crucial role in enhancing organizational efficiency.
Internal interfaces and the role of Material Management
- Market Forecasting: A significant role played by material management involves forecasting future demands. For instance, consider a scenario where a university like IGNOU is producing study materials for its students. Material management must anticipate the demand for study materials across various programs based on historical usage patterns, enrollment trends, and responses to new programs. However, it's essential to note that forecasting is inherently an estimation process.
- Production: Material management ensures seamless production processes. Using the university example again, printing operations require continuous availability of printing paper and art card paper for covers. Any shortage in these materials disrupts the printing process. Additionally, forecasting demand aids in calculating material requirements accurately, although predicting sales in production organizations poses significant challenges.
- Finance: Material management is intricately linked with cost reduction and effective budgeting. Procurement of paper for printing study materials must be timely to avoid financial delays. For example, paper procurement should ideally occur several months before printing to ensure smooth production without financial holdups.
- Inventory Control: A key strategic function of material management is minimizing organizational inventory levels to reduce costs. Production schedules must align with material procurement and supply to prevent disruptions. In the university scenario, procuring materials in advance ensures seamless printing operations.
- Inspection or Quality Control: While material management isn't directly responsible for product quality, it indirectly influences it. Proper handling and storage of materials, such as paper, purchased in advance, prevent quality deterioration. This aspect also intersects with inventory control practices.
- Material Handling, Traffic, and Physical Distribution Logistics: Material management ensures efficient handling and distribution of materials. For instance, locating paper stores near printing presses and distribution units close to main post offices streamlines operations for the university's study material distribution process.
The material flow process is depicted in Figure. It's essential to note that while Figure 2.1 illustrates how materials are flowing, the flow of information is equally crucial.
Activities within the materials management system impact various aspects:
- Purchasing and procurement activities involve gathering details on past vendor performance and quality, aiding in vendor selection. Orders can be strategically distributed over time if necessary.
- Receiving and inspection processes are critical quality control steps where information regarding quality is documented.
- Production planning and sales information directly influence materials management processes.
- Therefore, materials management can be regarded as a social technology requiring specialized expertise, directly affecting an organization's cost effectiveness. It can be defined in terms of coordinating planning, sourcing, moving, storing, and controlling materials optimally to deliver predetermined services to customers at minimal cost. However, determining which department should oversee the coordination of materials management functions remains a question.
In recent times, materials management is not confined to any specific department but rather is system-oriented. It considers functional interdependence across various activities, enhancing material utility as they progress through each stage of the production process until the final product. Consequently, centralized databases or enterprise resource planning (ERP) packages are increasingly viewed as suitable mechanisms for controlling material management processes.
Functional Role of Materials Management
Materials management plays a crucial role in various organizational functions. Here's a summary of its key roles:
Decision Making on Procurement:
- Deciding whether to procure materials or not based on past supply performance, quality standards, and capacity constraints.
Materials Forecasting:
- Predicting material requirements by considering factors such as long-term need, supplier stability, technological advancements, and price trends.
Materials Planning and Budgeting:
- Implementing control measures for effective planning and budgeting, facilitated by materials management practices.
Selection of Information Sources:
- Identifying potential suppliers and market research sources for gathering information on price trends, market conditions, and technological advancements, utilizing materials management data.
Creative Purchasing:
- Leveraging materials management information for innovative purchasing strategies, especially in uncertain situations, to optimize capital allocation.
Price Forecasting:
- Implementing a robust price forecasting system based on materials management data and market research to achieve advantageous outcomes.
Store Management and Inventory Control:
- Overseeing store operations with precision, including receiving, storage, minimizing obsolescence, inventory verification, timely delivery, proper presentation, and handling of scrap materials, facilitated by materials management practices.
FAQs on Role and Importance of Materials Management - Management Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What is integrated material management and why is it important? |  |
| 2. What are the roles of materials management in an organization? |  |
| 3. How does materials management contribute to internal interfaces within an organization? |  |
| 4. What is the functional role of materials management? |  |
| 5. What is the role and importance of materials management in UPSC? |  |





















