Seafloor Spreading | Geology Optional for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Evidence of Sea Floor Spreading |

|
| Driving Mechanism of Sea Floor Spreading |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Introduction
Sea floor spreading, proposed in 1961 by Naval Reserve Rear Admiral Robert S. Dietz and Professor Harry H. Hess of Princeton University in 1962, was a groundbreaking hypothesis aimed at explaining the phenomenon of continental drift. This concept has since become a cornerstone of plate tectonics theory, representing a significant advancement in our understanding of the Earth's geological processes.
Principle of Sea Floor Spreading
- Harry Hess explained the principle of sea floor spreading using the example of the Atlantic Ocean. According to this concept, the drift between the North America and Europe continents occurred gradually through the widening of the Atlantic Ocean. As the ocean floor spreads apart, continental margins move, resulting in the drifting of continents. Hess calculated that South America and Africa had moved approximately 2500 km apart over 250 million years, at a rate of 10 mm/year.
Mechanism and Mid-Oceanic Ridges (MORs)
- The growth of the ocean floor necessitates the continuous formation of new crustal material. This process is believed to be driven by volcanic activity occurring along underwater ridges known as Mid-Oceanic Ridges (MORs). Lava continuously pours out from the Earth's interior along these ridges, adding new crustal material to both sides.
Evidence of Sea Floor Spreading
- Age of Rocks
Samples obtained directly from drilling the ocean floor were isotopically dated, revealing that the youngest rocks are found along MORs, while older rocks occur towards the continental margins. This symmetrical pattern of rock age distribution supports the concept of sea floor spreading. - Anomalous High Values of Heat
Active volcanic islands are often associated with the crests of Mid-Atlantic ridges. The frequent occurrence of earthquakes and the absence of sediments at ridge crests provide further evidence for sea floor spreading. Anomalous high values of heat in these regions indicate the emplacement of hot mantle-derived material near the ridge crests. - Drilling and Dredging
Direct observations, drilling, and dredging activities have provided substantial evidence for sea floor spreading. No materials older than approximately 180 million years have been recorded from the deep ocean floor, supporting the hypothesis. - Magnetic Anomalies
Palaeomagnetic surveys and observations of magnetic anomalies in ocean floor rocks offer compelling evidence for sea floor spreading. These anomalies result from variations in the Earth's magnetic field due to differences in the chemistry or magnetism of the rocks. Mapping these variations helps detect underlying geological structures. - Consideration of Earth's Surface Area
While Hess's idea of sea floor spreading aligns with modern data, the concept raises questions about the Earth's surface area. If the sea is expanding without any destruction or consumption of continental or oceanic material, the Earth's surface area would theoretically increase significantly over time. However, since the Earth's surface area remains relatively constant, there must be other geological processes at play to maintain this equilibrium.
Driving Mechanism of Sea Floor Spreading
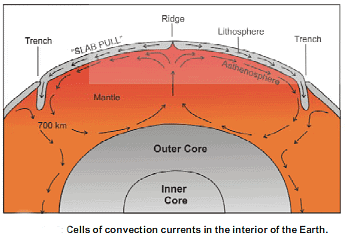
Understanding the mechanisms behind sea floor spreading is crucial for comprehending the dynamics of plate tectonics and the geological evolution of the Earth's crust. Arthur Holmes proposed one of the earliest theories regarding the driving forces behind sea floor spreading, which later contributed to the development of the plate tectonic concept.
- Arthur Holmes' Convection Current Theory
Arthur Holmes hypothesized that convection currents within the Earth's interior could be the primary driving mechanism for sea floor spreading. He suggested that continuous heat generation from radioactive elements within the Earth's interior leads to the formation of convection currents. This process can be likened to the heating of liquids, where heating a beaker containing water with potassium permanganate crystals results in rising and falling convection currents. - Limitations of Holmes' Theory
However, Holmes' theory faced criticism as the heat produced by radioactive minerals was deemed insufficient to cause the motion observed in convection currents. Despite this limitation, Holmes' concept laid the groundwork for further exploration into the role of convection currents in geological processes. - Plate Tectonic Concept
The plate tectonic concept builds upon Holmes' idea of convection currents but offers a refined understanding of the process. According to this concept, convection currents circulate within the mantle, ascending from the deep mantle to the upper mantle before moving horizontally and descending back into the deep mantle. These currents exert significant force on the lithospheric plates, causing them to move over the asthenosphere. - Role of Convection Currents in Plate Movement
Convection currents play a crucial role in driving the movement of lithospheric plates. Where convection currents move in opposite directions, adjacent lithospheric plates are pushed apart. This divergence results in the development of fractures at mid-oceanic ridges (MORs), which are immediately filled with lava from submarine volcanism. - Continuous Formation of New Crust
As convection currents remain in motion, new crust is continuously formed at mid-oceanic ridges due to the upwelling of lava from the mantle. This process of crust formation and spreading leads to sea floor spreading, gradually widening the ocean floor over time.
 Conclusion
Conclusion
While Arthur Holmes' initial theory of convection currents driving sea floor spreading had its limitations, it laid the foundation for the more comprehensive plate tectonic concept. Understanding the role of convection currents in plate movement has been instrumental in elucidating the mechanisms behind sea floor spreading and other geological phenomena.
|
64 videos|135 docs
|
FAQs on Seafloor Spreading - Geology Optional for UPSC
| 1. What is seafloor spreading? |  |
| 2. What evidence supports the theory of seafloor spreading? |  |
| 3. What drives the mechanism of seafloor spreading? |  |
| 4. How does seafloor spreading contribute to the theory of plate tectonics? |  |
| 5. What role does seafloor spreading play in the geological evolution of the Earth? |  |















