JEE Advanced Previous Year Questions (2018 - 2024): Vector Algebra and 3D Geometry | Mathematics (Maths) for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
2024
Q1: Let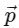 = 2î + ĵ + 3k̂ and q = î - ĵ + k̂. If for some real numbers α, β, and γ, we have
= 2î + ĵ + 3k̂ and q = î - ĵ + k̂. If for some real numbers α, β, and γ, we have 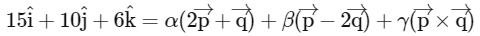 .
.then the value of γ is ______. [JEE Advanced 2024 Paper 2]
Ans: 2
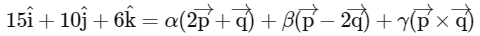
taking dot with 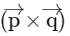
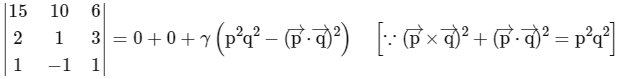
⇒ 52 = 26γ
∴ γ = 2
Q2: Let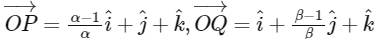 , and
, and 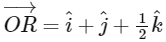 be three vectors, where α, β ∈ ℝ - {0} and O denotes the origin. If
be three vectors, where α, β ∈ ℝ - {0} and O denotes the origin. If 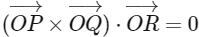 and the point (α, β, 2) lies on the plane 3x + 3y - z + l = 0, then the value of l is ________. [JEE Advanced 2024 Paper 1]
and the point (α, β, 2) lies on the plane 3x + 3y - z + l = 0, then the value of l is ________. [JEE Advanced 2024 Paper 1]
Ans: 5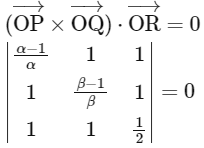
α + β + 1 = 0 ...(i)
Also, (α, β, 2) lies on 3x + 3y - z + l = 0
⇒ 3α + 3β - 2 + l = 0 ⇒ l = 2 - 3(α + β)
Use (1) in it ⇒ l = 5
Q3: Let γ ∈ ℝ be such that the lines L₁ : x+111 = y+212 = z+293 and L₂ : x+163 = y+112 = z+4γ intersect.
Let R₁ be the point of intersection of L₁ and L₂. Let O = (0, 0, 0), and n̂ denote a unit normal vector to the plane containing both the lines L₁ and L₂.
Match each entry in List-I to the correct entry in List-II.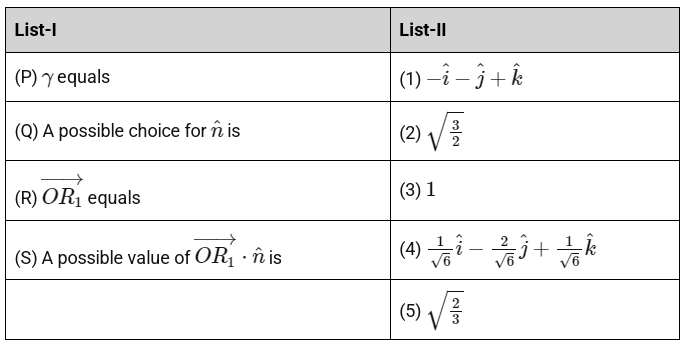
The correct option is:
(a) (P) → (3), (Q) → (4), (R) → (1), (S) → (2)
(b) (P) → (5), (Q) → (4), (R) → (1), (S) → (2)
(c) (P) → (3), (Q) → (4), (R) → (1), (S) → (5)
(d) (P) → (3), (Q) → (1), (R) → (4), (S) → (5) [JEE Advanced 2024 Paper 1]
Ans: (c)
Let γ ∈ ℝ be such that the lines L₁ : x+111 = y+212 = z+293 = a
L₂ : x+163 = y+112 = z+4γ = b
x = a - 11 = 3b - 16 ⇒ a - 3b = -5 .... (1)
y = 2a - 21 = 2b - 11 ⇒ 2a - 2b = 10 .... (2)
z = 3a - 29 = br - 4 ⇒ 3a - by = 25 .... (3)
From (1) & (2)
a = 10, b = 5
Now from (3)
3(10) - 5γ = 25 ∴ γ = 1
R₁ ≡ (-1, -1, 1)
OR₁ = -î - ĵ + k̂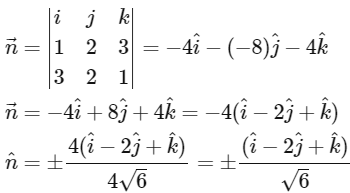
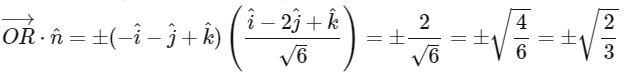
Q4: A straight line drawn from the point P(1,3,2), parallel to the line x - 21 = y - 42 = z - 61, intersects the plane L₁: x-y+3z=6 at the point Q.
Another straight line which passes through Q and is perpendicular to the plane L₁ intersects the plane L₂ : 2x - y + z = -4 at the point R.
Then which of the following statements is (are) TRUE?
(a) The length of the line segment PQ is √6
(b) The coordinates of R are (1,6,3)
(c) The centroid of the triangle PQR is 43, 143, 53
(d) The perimeter of the triangle PQR is √2 + √6 + √11 [JEE Advanced 2024 Paper 2]
Ans: (a), (c)
Line: x - 11 = y - 32 = z - 21,
(x, y, z) = (λ + 1, 2λ + 3, λ + 2)
Put in L₁ : x - y + 3z = 6
(λ + 1) - (2λ + 3) + 3(λ + 2) = 6
2λ = 2 ⇒ λ = 1
Q = (2, 5, 3)
line: x - 21 = y - 42 = z - 61,
(x, y, z) = (t + 2, 5 - t, 3t + 3)
Put in L₂ : 2x - y + z = -4
2(t + 4) - (5 - t) + (3t + 3) = -4
6t = -6 ⇒ t = -1
R = (1, 6, 0)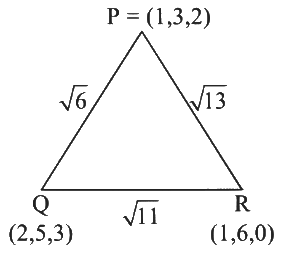 Perimeter = √6 + √13 + √11
Perimeter = √6 + √13 + √11
Centroid = (4/3, 14/3, 5/3)
Q5: Let ℝ³ denote the three-dimensional space. Take two points P = (1, 2, 3) and Q = (4, 2, 7). Let dist(X, Y) denote the distance between two points X and Y in ℝ³. Let S = {X ∈ ℝ³ : (dist(X, P))² - (dist(X, Q))² = 50} and T = {Y ∈ ℝ³ : (dist(Y, Q))² - (dist(Y, P))² = 50}.
Then which of the following statements is (are) TRUE?
(a) There is a triangle whose area is 1 and all of whose vertices are from S.
(b) There are two distinct points L and M in T such that each point on the line segment LM is also in T.
(c) There are infinitely many rectangles of perimeter 48, two of whose vertices are from S and the other two vertices are from T.
(d) There is a square of perimeter 48, two of whose vertices are from S and the other two vertices are from T. [JEE Advanced 2024 Paper 1]
Ans: (a), (b), (c), (d)
S = {X : (XP)² - (XQ)² = 50}
T = {Y : (YQ)² - (YP)² = 50}
For finding S ≡ X(x, y, z) and for T ≡ Y(x, y, z),
((x - 1)² + (y - 1)² + (z - 1)²) - ((x - 4)² + (y - 2)² + (z - 7)²) = 50
⇒ S = {(x, y, z) : 6x + 8z = 105}
T = {(x, y, z) : 6x + 8z = 5}
Since S and T both are planes;
(A) There exists a triangle in plane S whose area = 1 (always).
(B) L & M lies on plane T, hence line segment joining L & M will lie on plane T.
(C) Distance between S & T
d = | (105 - 5) / 10 | = 10
Hence for a rectangle of perimeter 48, it can exist.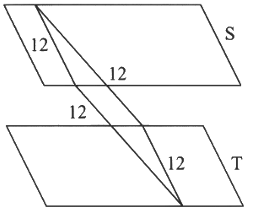 There will be infinite such rectangle possible.
There will be infinite such rectangle possible.
(D) For square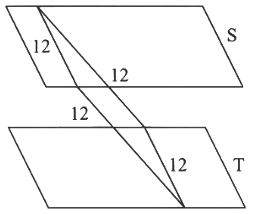 Hence Answers A, B, C, D are correct.
Hence Answers A, B, C, D are correct.
2023
Q1: Let the position vectors of the points P, Q, R and S be 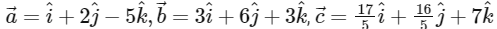 and
and 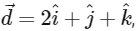 respectively. Then which of the following statements is true?
respectively. Then which of the following statements is true?
(a) The points P, Q, R and S are NOT coplanar
(b) 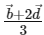 is the position vector of a point which divides PR internally in the ratio 5 : 4
is the position vector of a point which divides PR internally in the ratio 5 : 4
(c) 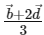 is the position vector of a point which divides PR externally in the ratio 5 : 4
is the position vector of a point which divides PR externally in the ratio 5 : 4
(d) The square of the magnitude of the vector 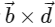 is 95 [JEE Advanced 2023 Paper 2]
is 95 [JEE Advanced 2023 Paper 2]
Ans: (b)
Q2: Let ℓ1 and ℓ2 be the lines 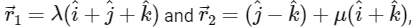 respectively. Let X be the set of all the planes H that contain the line ℓ1. For a plane H, let d(H) denote the smallest possible distance between the points of ℓ2 and H. Let H0 be a plane in X for which d(H0) is the maximum value of d(H) as H varies over all planes in X.
respectively. Let X be the set of all the planes H that contain the line ℓ1. For a plane H, let d(H) denote the smallest possible distance between the points of ℓ2 and H. Let H0 be a plane in X for which d(H0) is the maximum value of d(H) as H varies over all planes in X.
Match each entry in List-I to the correct entries in List-II.

(a) (P)→(2)(Q)→(4)(R)→(5)(S)→(1)
(b) (P)→(5)(Q)→(4)(R)→(3)(S)→(1)
(c) (P)→(2)(Q)→(1)(R)→(3)(S)→(2)
(d) (P)→(5)(Q)→(1)(R)→(4)(S)→(2) [JEE Advanced 2023 Paper 1]
Ans: (b)
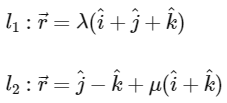
For plane
d(H)= Smallest possible distance between the points of ℓ2 and Plane.
d(H0) = Maximum value of d(H)
For d(H0)
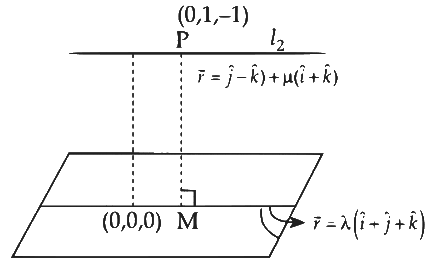
ℓ2 is Parallel to plane containing ℓ1
Equation of plane
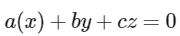
∵ It contain ℓ1
∴ a + b + c = 0 ..........(1)
For largest possible distance between plane (1) and ℓ2 the line ℓ2 must be parallel to plane (1)
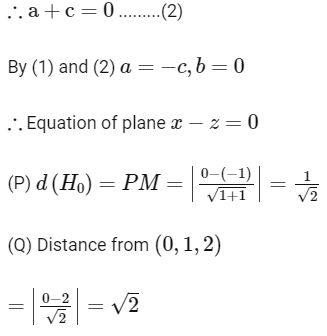

∴ Point of intersection (1, 1, 1) Distance from origin
= 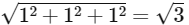
Q3: Let P be the plane 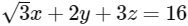 and let
and let 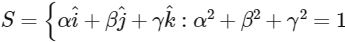 and the distance of (α, β, γ) from the plane P is 7/2. Let
and the distance of (α, β, γ) from the plane P is 7/2. Let 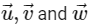 be three distinct vectors in S such that
be three distinct vectors in S such that 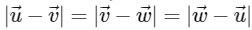 . Let S be the volume of the parallelepiped determined by vectors
. Let S be the volume of the parallelepiped determined by vectors 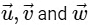 . Then the value of
. Then the value of 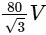 is : [JEE Advanced 2023 Paper 1]
is : [JEE Advanced 2023 Paper 1]
Ans: 45
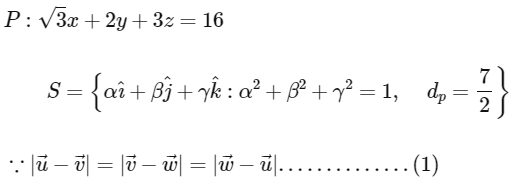
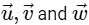 are elements of set S and in set S magnitude of vector is 1
are elements of set S and in set S magnitude of vector is 1
∴ 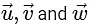 are unit vectors and by equation (1) we can system
are unit vectors and by equation (1) we can system 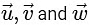 are equally inclined and vertices of equilateral triangle also lying on a circle which is intersection of sphere
are equally inclined and vertices of equilateral triangle also lying on a circle which is intersection of sphere
Distance from Origin to P
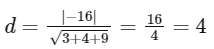

Equation of the plane is
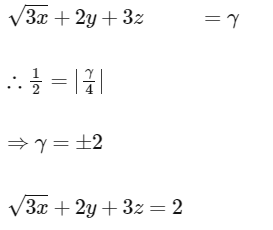
Equation of sphere = 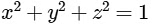
∴ Radius or circle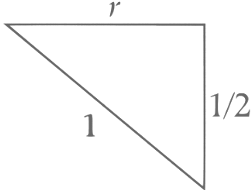
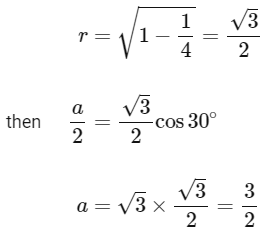
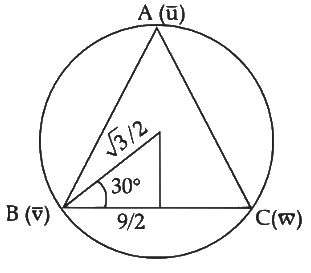
∴ Area or triangle = 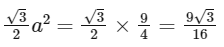
Velocity of Parallelepiped,
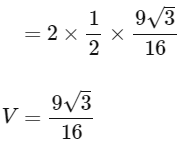
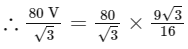
= 45
2022
Q1: Let
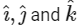 be the unit vectors along the three positive coordinate axes. Let
be the unit vectors along the three positive coordinate axes. Let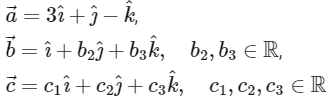
be three vectors such that 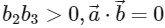 and
and
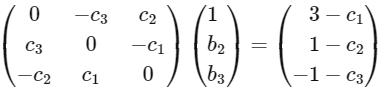
Then, which of the following is/are TRUE?
(a) 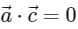
(b) 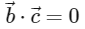
(c) 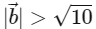
(d) 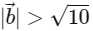 [JEE Advanced 2022 Paper 2]
[JEE Advanced 2022 Paper 2]
Ans: (b), (c) & (d)
Given,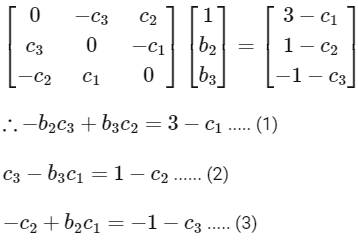
Adding (1), (2) and (3), we get
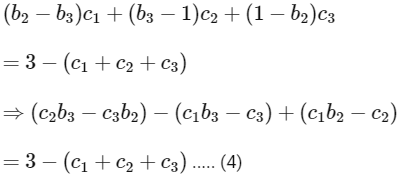
Aso given,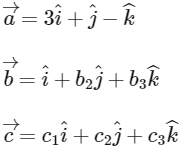
Now,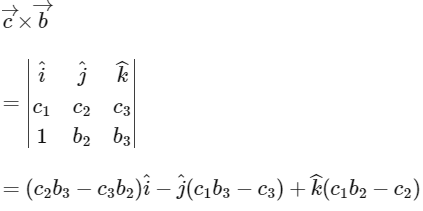
And
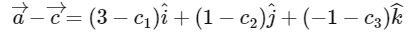
Comparing value of  with equation (4), we get
with equation (4), we get
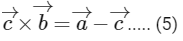
Multiplying both side with 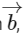 , we get
, we get
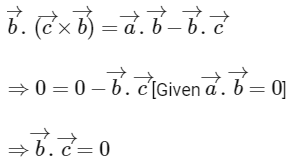
∴ B is correct
As, 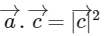
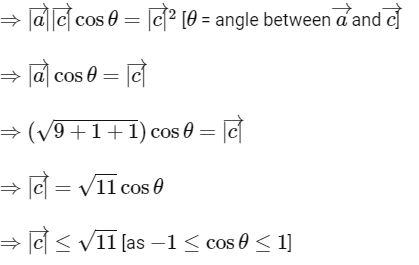
∴ Option (D) is correct.
Given, 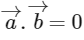
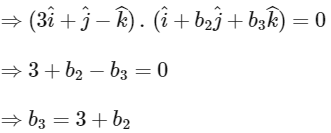
Now,
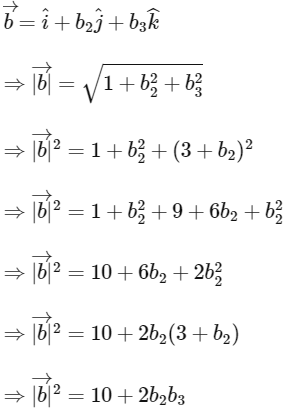
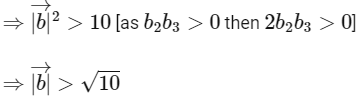
∴ Option (C) is correct.
Q2: Let P1 and P2 be two planes given by
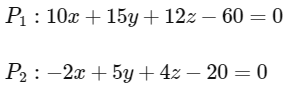
Which of the following straight lines can be an edge of some tetrahedron whose two faces lie on P1 and P2 ?
(a) 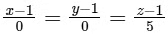
(b) 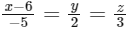
(c) 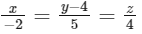
(d) 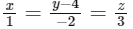 [JEE Advanced 2022 Paper 1]
[JEE Advanced 2022 Paper 1]
Ans: (a), (b) & (d)
P1 and P2 be two planes given by
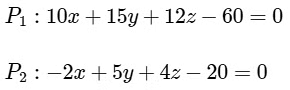
Now finding line of intersection of both the planes,
Let z = λ, then
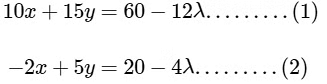
Now solving the eq. (1) and (2) we get,
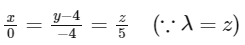
Now any skew line with the line of intersection of given plane can be edge of tertrahedron.
Now using above concept we will solve all options.
For option (A)
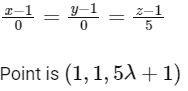
Now satisfying this point in given plane we have,
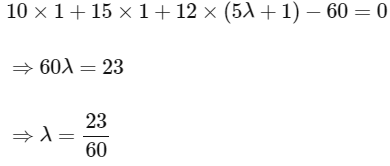
Now we can see line is intersecting the plane P1, at some point.
Now checking for plane (P2)
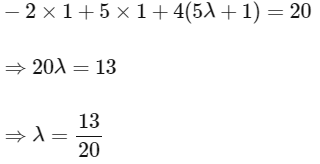
Also intersecting plane (P2)
Hence, it can be the edge of tetrahedron.
For option (B)
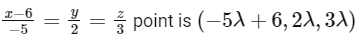
this point is satisfying plane P1
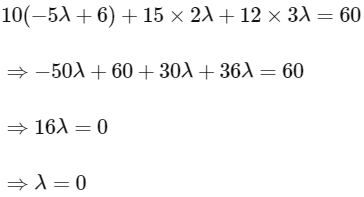
Now checking for plane P2
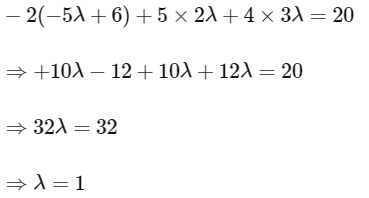
Hence, it can be the edge of tetrahedron.
For option (D),
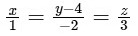
point (λ, −2λ + 4, 3λ) and for λ = 0 point will be (0, −4, 0) which is lying on line of intersection and DR of plane P2 is (−2,5,4) and DR of line is (1,−2,3)
Now line is lying completely on P2
Hence, it can be the edge of tetrahedron.
Q3: Let S be the reflection of a point Q with respect to the plane given by
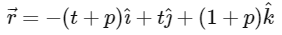
where t, p are real parameters and 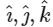 are the unit vectors along the three positive coordinate axes. If the position vectors of Q and S are
are the unit vectors along the three positive coordinate axes. If the position vectors of Q and S are 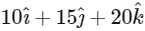 and
and 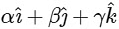 respectively, then which of the following is/are TRUE ?
respectively, then which of the following is/are TRUE ?
(a) 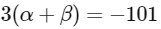
(b) 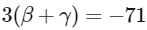
(c) 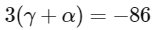
(d)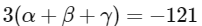 [JEE Advanced 2022 Paper 1]
[JEE Advanced 2022 Paper 1]
Ans: (a), (b) & (c)
Given : equation of plane
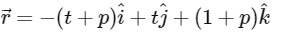
on rearranging we get,
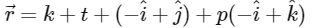
So, equation of plane in standard form is given by
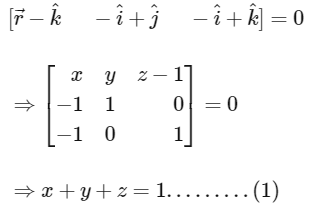
Now given co-ordinate of Q = (10, 15, 20)
And Co-ordinates of 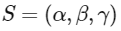
Now using the image formula of point and plane we get,
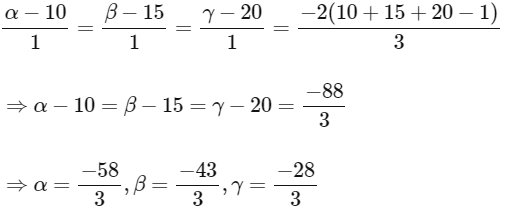
Now solving all options.
2021
Q1: Let α, β and γ be real numbers such that the system of linear equations
x + 2y + 3z = α
4x + 5y + 6z = β
7x + 8y + 9z = γ − 1
is consistent. Let | M | represent the determinant of the matrix
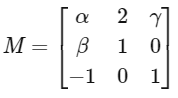
Let P be the plane containing all those (α, β, γ) for which the above system of linear equations is consistent, and D be the square of the distance of the point (0, 1, 0) from the plane P.
The value of | M | is _________. [JEE Advanced 2021]
Ans: 1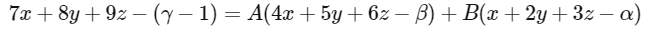
On equating the coefficients,
4A + B = 7 .... (i)
5A + 2B = 8 .... (ii)
and − (γ − 1) = − Aβ − αB ..... (iii)
On solving Eqs. (i) and (ii), we get A = 2 and B = −1
From Eq. (iii), we get
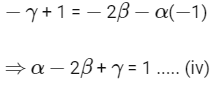
Now, determinant of
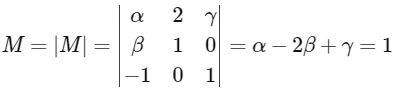 [from Eq. (iv)]
[from Eq. (iv)]
Q2: Let α, β and γ be real numbers such that the system of linear equations
x + 2y + 3z = α
4x + 5y + 6z = β
7x + 8y + 9z = γ − 1
is consistent. Let | M | represent the determinant of the matrix
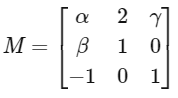
Let P be the plane containing all those (α, β, γ) for which the above system of linear equations is consistent, and D be the square of the distance of the point (0, 1, 0) from the plane P.
The value of | D | is _________. [JEE Advanced 2021]
Ans: 1.5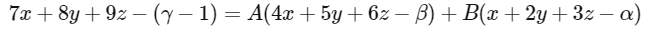
On equating the coefficients,
4A + B = 7 .... (i)
5A + 2B = 8 .... (ii)
and − (γ − 1) = − Aβ − αB ..... (iii)
On solving Eqs. (i) and (ii), we get A = 2 and B = −1
From Eq. (iii), we get
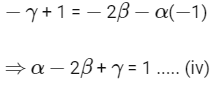
Now, determinant of
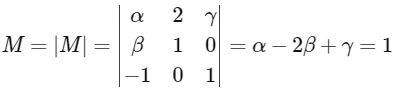 [from Eq. (iv)]
[from Eq. (iv)]
Equation of plane P is given by x −2y + z = 1
Hence, perpendicular distance of the point (0, 1, 0) from the plane
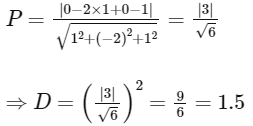
2020
Q1: Let α2 + β2 + γ2 ≠ 0 and α + γ = 1. Suppose the point (3, 2, −1) is the mirror image of the point (1, 0, −1) with respect to the plane αx + βy + γz = δ. Then which of the following statements is/are TRUE?
(a) α + β = 2
(b) δ − γ = 3
(c) δ + β = 4
(d) α + β + γ = δ` [JEE Advanced 2020 Paper 2]
Ans: (a), (b) & (c)
Since, the point A(3, 2, −1) is the mirror image of the point B(1, 0, −1) with respect to the plane αx + βy + γz = δ, then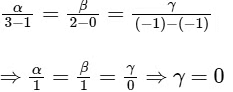
it is given that 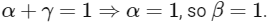
And, the mid-point of AB, M(2, 1, −1) lies on the given plane, so
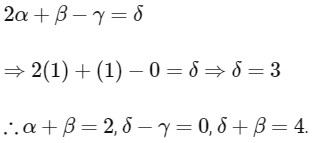
Q2: Let a and b be positive real numbers. Suppose 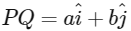 and
and 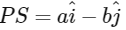 are adjacent sides of a parallelogram PQRS. Let u and v be the projection vectors of
are adjacent sides of a parallelogram PQRS. Let u and v be the projection vectors of 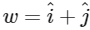 along PQ and PS, respectively. If |u| + |v| = |w| and if the area of the parallelogram PQRS is 8, then which of the following statements is/are TRUE?
along PQ and PS, respectively. If |u| + |v| = |w| and if the area of the parallelogram PQRS is 8, then which of the following statements is/are TRUE?
(a) a + b = 4
(b) a − b = 2
(c) The length of the diagonal PR of the parallelogram PQRS is 4
(d) w is an angle bisector of the vectors PQ and PS [JEE Advanced 2020 Paper 2]
Ans: (a) & (c)
Given vectors 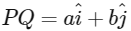 and
and 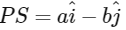 are adjacent sides of a parallelogram PQRS.
are adjacent sides of a parallelogram PQRS.
so area of parallelogram PQRS =
|PQ × PS| = 2ab = 8 (given)
∴ ab = 4 ......(i)
According to the question,
|u| = |projection vector of 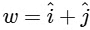 along PQ|
along PQ|
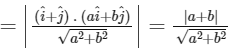
and, similarly, |v| = |projection vector of 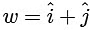 along PS|
along PS|
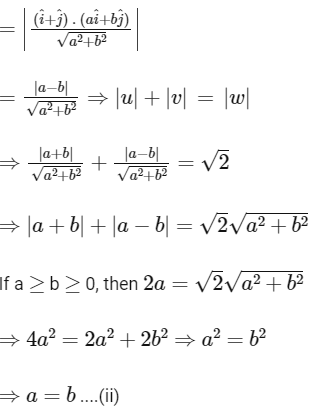
From Eqs. (i) and (ii), we get
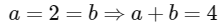
and the length of diagonal PR
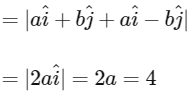
And, the angle bisector of vector PQ and PS is along the vector
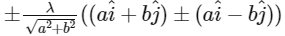
2019
Q1: Three lines 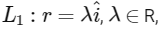
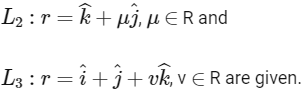
For which point(s) Q on L2 can we find a point P on L1 and a point R on L3 so that P, Q and R are collinear?
(a) 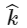
(b) 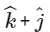
(c) 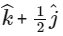
(d) 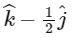 [JEE Advanced 2019 Paper 2]
[JEE Advanced 2019 Paper 2]
Ans: (c) & (d)
Given lines,
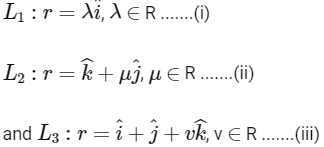
Now, let the point P on L1 = (λ, 0, 0)
the point Q on L2 = (0, μ, 1), and
the point R on L3 = (1, 1, v)
For collinearity of points P, Q and R, there should be a non-zero scalar 'm', such that PQ = m PR
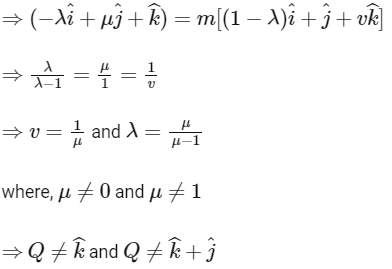
Hence, Q can not have coordinator (0, 0, 1 ) and (0, 1, 1)
Hence, options (c) and (d) are correct.
Q2: Let L1 and L2 denote the lines
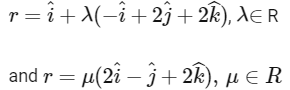
respectively. If L3 is a line which is perpendicular to both L1 and L2 and cuts both of them, then which of the following options describe(s) L3?
(a) 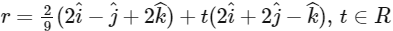
(b) 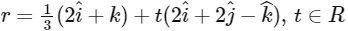
(c) 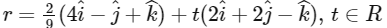
(d) 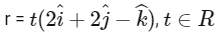 [JEE Advanced 2019 Paper 1]
[JEE Advanced 2019 Paper 1]
Ans: (a), (b) & (c)
Given lines,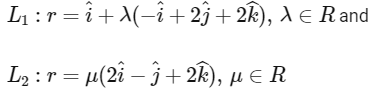
and since line L3 is perpendicular to both lines L1 and L2.
Then a vector along L3 will be,
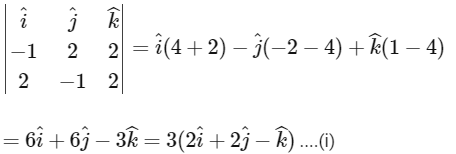
Now, let a general point on line L1.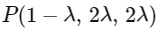 and on line L2 as
and on line L2 as 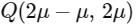 and let P and Q are point of intersection of lines L1, L3 and L2, L3, so direction ratio's of L3
and let P and Q are point of intersection of lines L1, L3 and L2, L3, so direction ratio's of L3
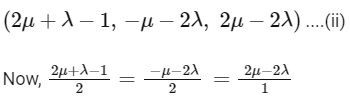
[from Eqs. (i) and (ii)]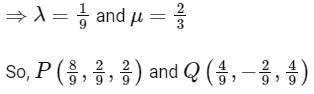
Now, we can take equation of line L3 as 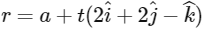 , where a is position vector of any point on line L3 and possible vector of a are
, where a is position vector of any point on line L3 and possible vector of a are
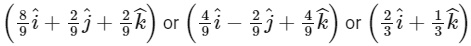
Hence, options (a), (b) and (c) are correct.
2018
Q1: Let P1 : 2x + y − z = 3 and P2 : x + 2y + z = 2 be two planes. Then, which of the following statement(s) is(are) TRUE?
(a) The line of intersection of P1 and P2 has direction ratios 1, 2, −1
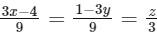 is perpendicular to the line of intersection of P1 and P2
is perpendicular to the line of intersection of P1 and P2Ans: (c) & (d)
We have,
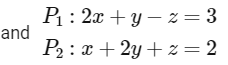
Here, 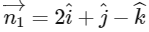
and 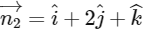
(a) Direction ratio of the line of intersection of P1 and P2 is 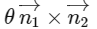
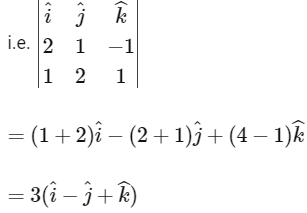
Hence, statement a is false.
(b) We have,
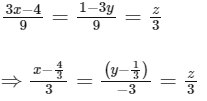
his line is parallel to the line of intersection of P1 and P2.
Hence, statement (b) is false.
(c) Let acute angle between P1 and P2 be θ.
We know that,
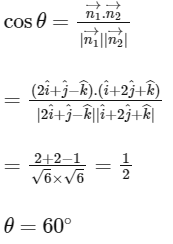
Hence, statement (c) is true.
(d) Equation of plane passing through the point (4, 2, −2) and perpendicular to the line of intersection of P1 and P2 is
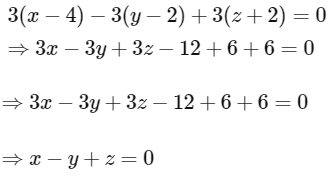
Now, distance of the point (2, 1, 1) from the plane x − y + z = 0 is
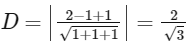
Hence, statement (d) is true.
Q2: Let P be a point in the first octant, whose image Q in the plane x + y = 3 (that is, the line segment PQ is perpendicular to the plane x + y = 3 and the mid-point of PQ lies in the plane x + y = 3) lies on the Z-axis. Let the distance of P from the X-axis be 5. If R is the image of P in the XY-plane, then the length of PR is _____. [JEE Advanced 2018 Paper 2]
Ans: 8
Let P(α, β, γ) and R is image of P in the XY-plane.
∴ R(α, β, -γ)
Also, Q is the image of P in the plane x + y = 3
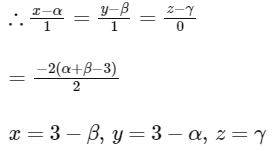
Since, Q is lies on Z-axis
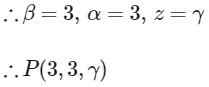
Given, distance of P from X-axis be 5
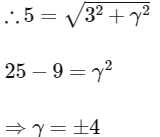
Then, 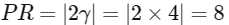
|
176 videos|582 docs|160 tests
|
FAQs on JEE Advanced Previous Year Questions (2018 - 2024): Vector Algebra and 3D Geometry - Mathematics (Maths) for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What are the key topics covered in Vector Algebra and 3D Geometry for JEE Advanced? |  |
| 2. How important is Vector Algebra and 3D Geometry for JEE Advanced preparation? |  |
| 3. What types of questions can be expected from Vector Algebra and 3D Geometry in JEE Advanced? |  |
| 4. How can I effectively study Vector Algebra and 3D Geometry for the JEE Advanced exam? |  |
| 5. Are there any specific JEE Advanced previous year questions that focus on Vector Algebra and 3D Geometry? |  |





















