JEE Advanced Previous Year Questions (2018 - 2024): Electrochemistry | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
2024
Q1: In a conductometric titration, a small volume of titrant of higher concentration is added stepwise to a larger volume of titrate of much lower concentration, and the conductance is measured after each addition.The limiting ionic conductivity (Λ₀) values (in mS m² mol⁻¹) for different ions in aqueous solutions are given below:
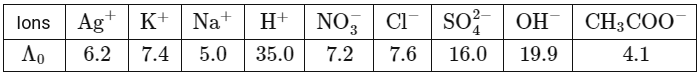 For different combinations of titrates and titrants given in List-I, the graphs of 'conductance' versus 'volume of titrant' are given in List-II.
For different combinations of titrates and titrants given in List-I, the graphs of 'conductance' versus 'volume of titrant' are given in List-II.
Match each entry in List-I with the appropriate entry in List-II and choose the correct option.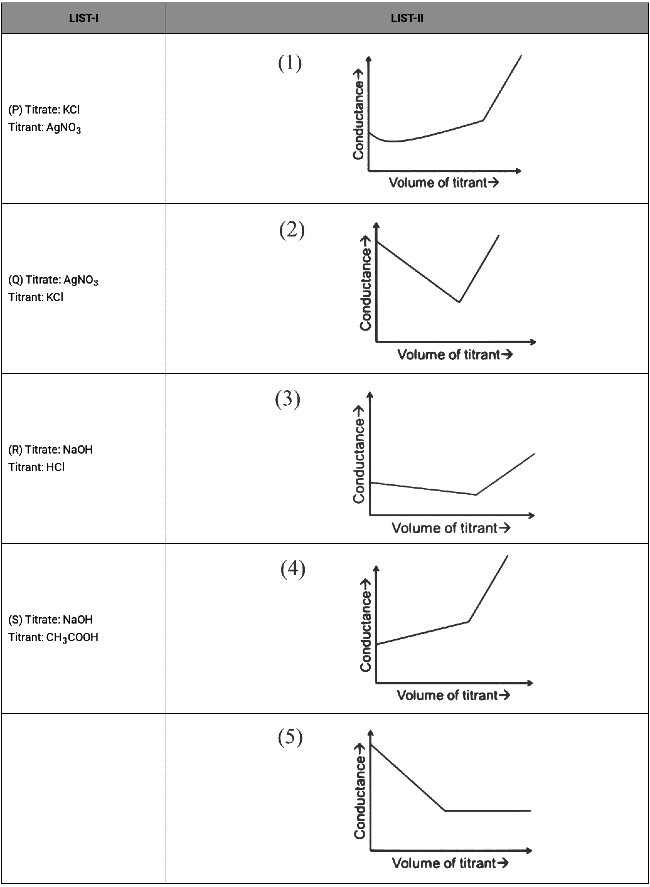 (a) P-4, Q-3, R-2, S-5
(a) P-4, Q-3, R-2, S-5
(b) P-2, Q-4, R-3, S-1
(c) P-3, Q-4, R-2, S-5
(d) P-4, Q-3, R-2, S-1 [JEE Advanced 2024 Paper 1]
Ans: (c)
Option (P):
On adding AgNO₃ solution to KCl solution precipitation of AgCl will occur due to which Cl⁻ already present will be replaced by NO₃⁻ ions. So conductance of solution will decrease till equivalence point. After complete precipitation of AgCl, further added AgNO₃ will increase the number of ions in resulting solution so conductance will increase.
Option (Q):
On adding KCl solution to AgNO₃ solution precipitation of AgCl will occur due to which already present Ag⁺ ions will be replaced by K⁺ ions in solution. So conductance of solution will increase. After complete precipitation of AgCl further added KCl will increase the number of ions in resulting solution so conductance will increase further.
Option (R):
On adding HCl solution to NaOH solution, OH⁻ will be replaced by Cl⁻ ions so conductance of solution decreases. After complete neutralisation further added HCl will increase number of ions in the solution. So conductance will increase further.
Option (S):
On adding CH₃COOH solution to NaOH solution OH⁻ will be replaced by CH₃COO⁻ ions, so conductance of solution decreases. After complete neutralisation further added CH₃COOH will remain undissociated because it is a weak acid and there is also common ion effect on acetate ions. So number of ions in solution will remain almost constant therefore conductance of solution will remain constant.
Q2: An aqueous solution of hydrazine (N₂H₄) is electrochemically oxidized by O₂, thereby releasing chemical energy in the form of electrical energy. One of the products generated from the electrochemical reaction is N₂(g).
Choose the correct statement(s) about the above process
(a) OH⁻ ions react with N₂H₄ at the anode to form N₂(g) and water, releasing 4 electrons to the anode.
(b) At the cathode, N₂H₄ breaks to N₂(g) and nascent hydrogen released at the electrode reacts with oxygen to form water.
(c) At the cathode, molecular oxygen gets converted to OH⁻.
(d) Oxides of nitrogen are major by-products of the electrochemical process. [JEE Advanced 2024 Paper 2]
Ans: (a), (c)
To determine the correct statement(s) regarding the electrochemical oxidation of hydrazine (N₂H₄) by O₂, let's analyze each option in detail.
Option A: OH⁻ ions react with N₂H₄ at the anode to form N₂(g) and water, releasing 4 electrons to the anode. This statement is accurate because in an electrochemical cell, the anode is where oxidation occurs. Hydrazine can be oxidized in the presence of OH⁻ ions to yield nitrogen gas and water, releasing electrons as a part of this redox reaction:
N₂H₄ + 4OH⁻ → N₂ + 4H₂O + 4e⁻
Option B: At the cathode, N₂H₄ breaks to N₂(g) and nascent hydrogen released at the electrode reacts with oxygen to form water. This statement is incorrect because, usually, the cathode is where reduction occurs, not a breaking down of hydrazine. Instead, reduction reactions involve the gain of electrons. Additionally, at the cathode, it's more common for oxygen to be reduced rather than hydrazine itself breaking down.
Option C: At the cathode, molecular oxygen gets converted to OH⁻. This statement is correct. At the cathode in an alkaline medium, oxygen undergoes reduction to form hydroxide ions OH⁻, as depicted by the half-reaction:
O₂ + 2H₂O + 4e⁻ → 4OH⁻
Option D: Oxides of nitrogen are major by-products of the electrochemical process. This statement is incorrect because the primary product from the electrochemical reaction of hydrazine is nitrogen gas (N₂), and not oxides of nitrogen. The formation of oxides of nitrogen would be notable only under different specific conditions not mentioned in this context.
Therefore, the correct statements regarding the electrochemical oxidation of hydrazine by O₂ are:
Option A and Option C.
2023
Q1: Plotting 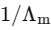 against
against 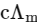 for aqueous solutions of a monobasic weak acid (HX) resulted in a straight line with y-axis intercept of P and slope of S. The ratio P/S is [JEE Advanced 2023 Paper 1]
for aqueous solutions of a monobasic weak acid (HX) resulted in a straight line with y-axis intercept of P and slope of S. The ratio P/S is [JEE Advanced 2023 Paper 1]
[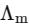 = molar conductivity
= molar conductivity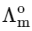 = limiting molar conductivity
= limiting molar conductivity
c = molar concentration
Ka = dissociation constant of HX]
(a) 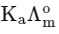
(b) 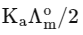
(c) 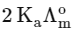
(d) 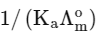
Ans: (a)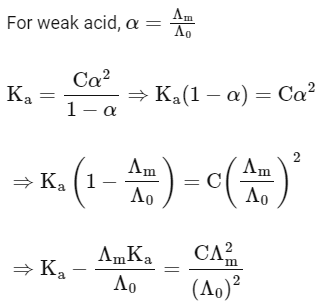
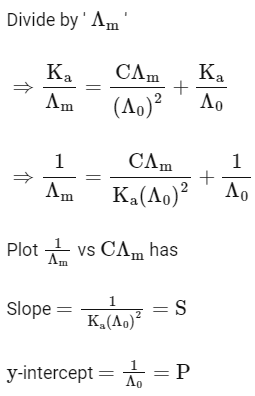
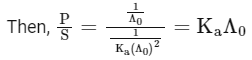
2022
Q1: Consider the strong electrolytes ZmXn , Um YP and Vm Xn . Limiting molar conductivity (Λ0) of Um Yp and Vm Xn are 250 and 440 S cm2 mol−1 , respectively. The value of (m + n + p) is
Given: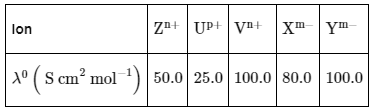 λ0 is the limiting molar conductivity of ions
λ0 is the limiting molar conductivity of ions
The plot of molar conductivity (Λ) of Zm Xn vs c1/2 is given below. [JEE Advanced 2022 Paper 2]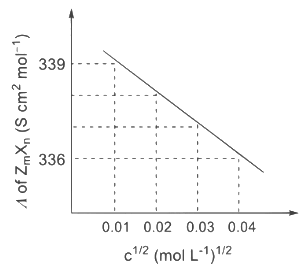 Ans: 7
Ans: 7
Given,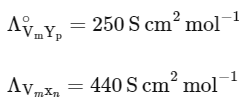
It is also given that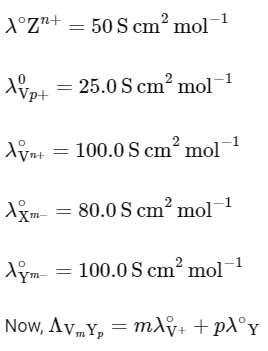
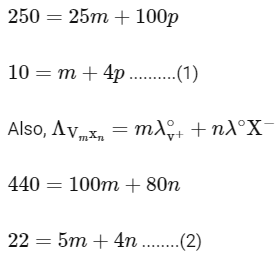
In the question, a graph of ( Λ ) of ZmXn Vs C1/2 is given,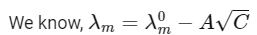
For electrolyte ZmXn and from given curve
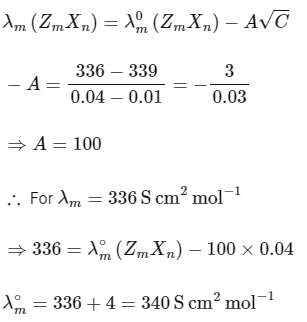
so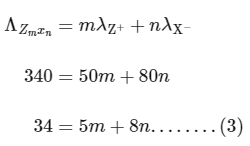
Solving eqn (2) and eqn (3),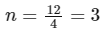
⇒ n = 3
Substituting the value of n in eqn (2), we get,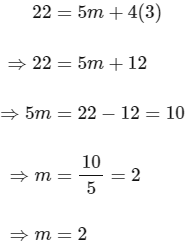
Now, substituting the value of m is eqn (1), we get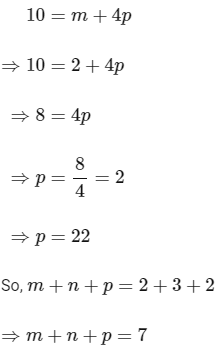
Hence, the required value of m + n + p is 7.
Q2: The reduction potential l (E0 , in V) of MnO4− (aq) / Mn (s) is __________. [JEE Advanced 2022 Paper 1]
[Given: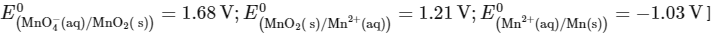
Ans: 0.74 to 0.80
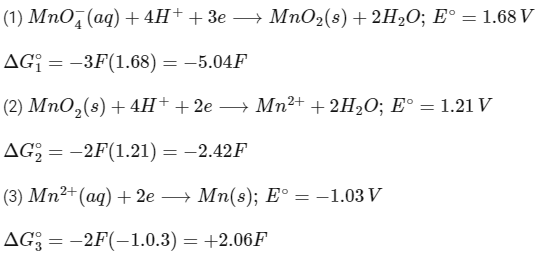
Adding (1), (2) and (3),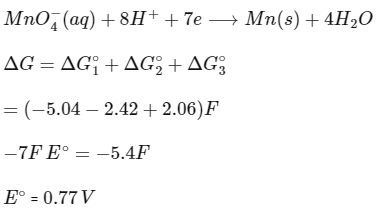
2021
Q1: At 298 K, the limiting molar conductivity of a weak monobasic acid is 4 × 102 S cm2 mol−1. At 298 K, for an aqueous solution of the acid the degree of dissociation is α and the molar conductivity is y × 102 S cm2 mol−1. At 298 K, upon 20 times dilution with water, the molar conductivity of the solution becomes 3y × 102 S cm2 mol−1. [JEE Advanced 2021 Paper 2]
The value of α is __________.
Ans: 0.22
Degree of dissociation = α
Limiting molar conductivity, 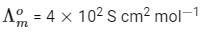
Molar conductivity, 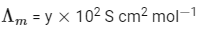
Molar conductivity of dilution, 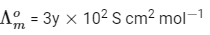
Concentration before dilution = C
Concentration after dilution = C/20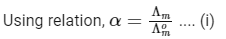
Dissociation constant, 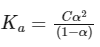
Putting Eq. (i),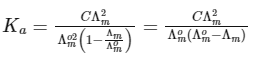
Dissociation constant before dillution,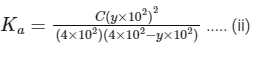
Dissociation constant after dilution,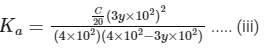
Comparing Eqs. (ii) and (iii),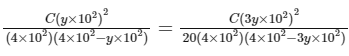
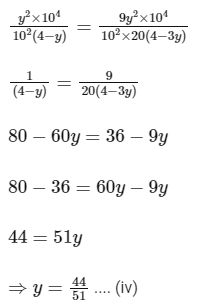
Putting in Eq. (i),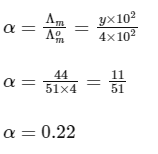
The value of α is 0.22.
Q2: At 298 K, the limiting molar conductivity of a weak monobasic acid is 4 × 102 S cm2 mol−1. At 298 K, for an aqueous solution of the acid the degree of dissociation is α and the molar conductivity is y × 102 S cm2 mol−1. At 298 K, upon 20 times dilution with water, the molar conductivity of the solution becomes 3y × 102 S cm2 mol−1. [JEE Advanced 2021 Paper 2]
The value of y is __________.
Ans: 0.86
Degree of dissociation = α
Limiting molar conductivity, 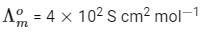
Molar conductivity, 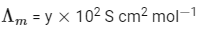
Molar conductivity of dilution, 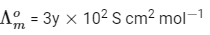
Concentration before dilution = C
Concentration after dilution = C/20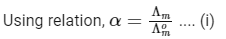
Dissociation constant, 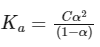
Putting Eq. (i),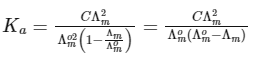
Dissociation constant before dillution,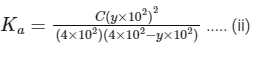
Dissociation constant after dilution,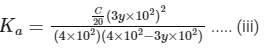
Comparing Eqs. (ii) and (iii),
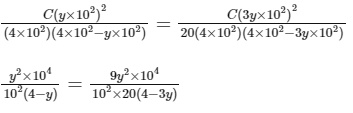
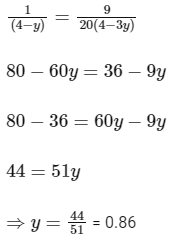
Q3: Some standard electrode potentials at 298 K are given below :
Pb2+ /Pb − 0.13 V
Ni2+ /Ni − 0.24 V
Cd2+ /Cd − 0.40 V
Fe2+ /Fe − 0.44 V
To a solution containing 0.001 M of X2+ and 0.1 M of Y2+, the metal rods X and Y are inserted (at 298 K) and connected by a conducting wire. This resulted in dissolution of X. The correct combination(s) of X and Y, respectively, is(are)
(Given : Gas constant, R = 8.314 JK− mol−1, Faraday constant, F = 96500 C mol−1) [JEE Advanced 2021 Paper 2]
(a) Cd and Ni
(b) Cd and Fe
(c) Ni and Pb
(d) Ni and Fe
Ans: (a, b, c)
Given,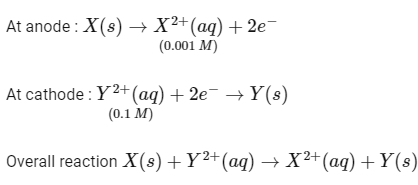
Nernst equation,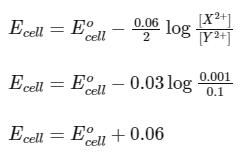
Ecell should be positive for a reaction to be spontaneous.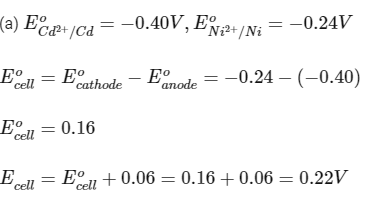
Reaction is spontaneous.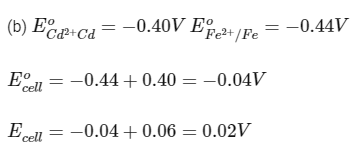
Reaction is spontaneous.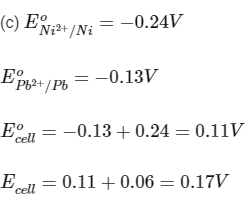
Reaction is spontaneous.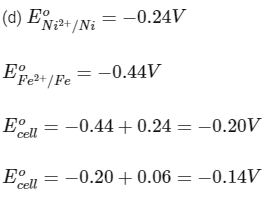
Reaction is non-spontaneous.
Therefore, the correct combinations of X and Y are (a), (b) and (c).
2020
Q1: Consider a 70% efficient hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell working under standard conditions at 1 bar and 298 K. Its cell reaction is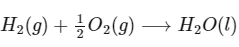
The work derived from the cell on the consumption of 1.0 × 10−3 mole of H2(g) is used to compress 1.00 mole of a monoatomic ideal gas in a thermally insulated container. What is the change in the temperature (in K) of the ideal gas?
The standard reduction potentials for the two half-cells are given below : [JEE Advanced 2020 Paper 1]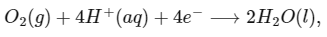
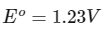
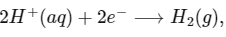
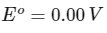
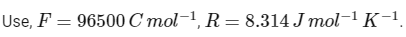
Ans: 13.32
Vessel is insulated, thus q = 0
For the given reaction :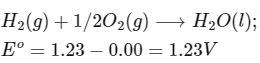
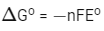
= − 2 × 96500 × 1.23 J/mol
Therefore, work derived from this fuel cell using 70% efficiency and on consumption of 1.0 × 10−3 mol of H2(g)
= 2 × 96500 × 1.23 × 0.7 × 1 × 10−3
= 166.17 J
This work done = change in internal energy (for monoatomic gas, Cv'm = 3R/2),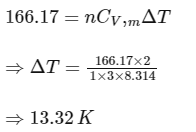
2019
Q1: Molar conductivity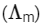 of aqueous solution of sodium stearate, which behaves as a strong electrolyte, is recorded at varying concentrations (C) of sodium stearate. Which one of the following plots provides the correct representation of micelle formation in the solution?
of aqueous solution of sodium stearate, which behaves as a strong electrolyte, is recorded at varying concentrations (C) of sodium stearate. Which one of the following plots provides the correct representation of micelle formation in the solution?
(critical micelle concentration (CMC) is marked with an arrow in the figures) [JEE Advanced 2019 Paper 1]
(a) 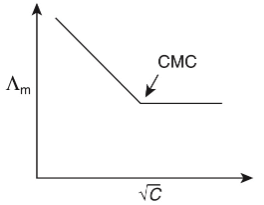
(b)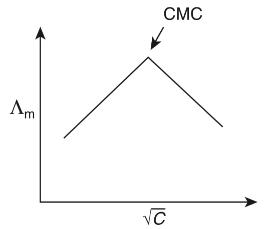
(c) 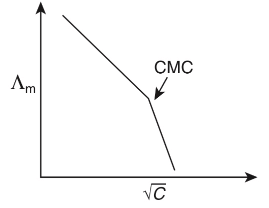
(d) 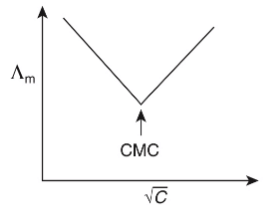
Ans: (c)
At normal or low concentration, sodium stearate (CH3(CH2)16COO-Na+] behaves as strong electrolyte and for strong electrolyte, molar conductance 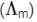 decreases with increase in concentration. Above particular concentration, sodium stearate forms aggregates known as micelles. The concentration is called as CMC. Since, number of ions decreases and hence
decreases with increase in concentration. Above particular concentration, sodium stearate forms aggregates known as micelles. The concentration is called as CMC. Since, number of ions decreases and hence 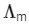 also decreases.
also decreases.
Hence, option (c) is correct.
2018
Q1: Consider an electrochemical cell: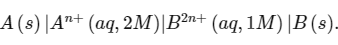
The value of ΔH∘ for the cell reaction is twice that of ΔG∘ at 300 K . If the emf of the cell is zero, the ΔS∘ (in JK−1 mol−1) of the cell reaction per mole of B formed at 300 K is ___________.
(Given: ln (2) = 0.7 , R (universal gas constant) = 8.3 JK−1 mol−1. H , S and G are enthalpy, entropy and Gibbs energy, respectively.) [JEE Advanced 2018 Paper 2]
Ans: -11.62
At 300 K, following electrochemical cell operates: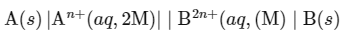
The reactions at:
(i) Anode: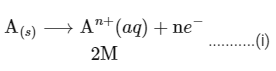
(ii) Cathode :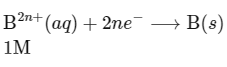
Multiplying equation (i) by 2,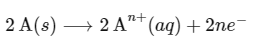
The net electrochemical cell is written as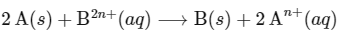
Given : Enthalpy change ( ΔH∘) for cell reaction = 2 × Gibbs free energy than for cell reaction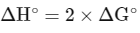
According to the Nernst equation :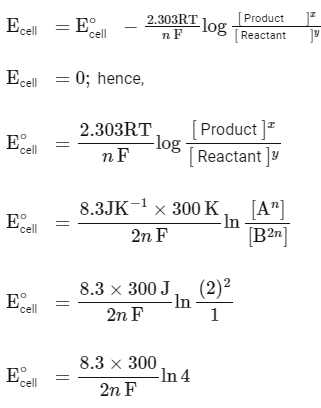
For a spontaneous reaction,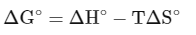
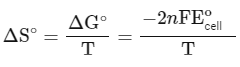
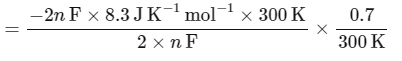
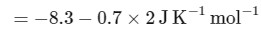
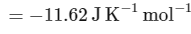
The change in entropy (ΔS∘) per mol of B is 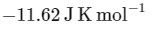
Q2: For the electrochemical cell,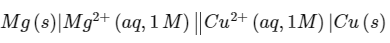 the standard emf of the cell is 2.70 V at 300 K. When the concentration of Mg2+ is changed to x M , the cell potential changes to 2.67 V at 300 K. The value of x is ___________.
the standard emf of the cell is 2.70 V at 300 K. When the concentration of Mg2+ is changed to x M , the cell potential changes to 2.67 V at 300 K. The value of x is ___________.
(given, F/R = 11500 KV-1, where F is the Faraday constant and R is the gas constant, In (10 = 2.30) [JEE Advanced 2018 Paper 1]
Ans: 10
Equation of cell reaction according to the cell notation given, is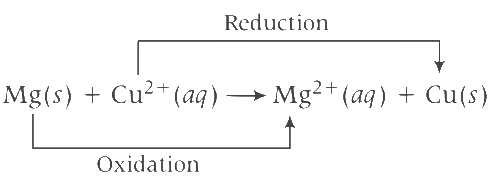 Given, E0cell = 2.70 V, T = 300 K with [Mg2+(aq)] = 1 M and [Cu2+(aq)] = 1 M and n = 2
Given, E0cell = 2.70 V, T = 300 K with [Mg2+(aq)] = 1 M and [Cu2+(aq)] = 1 M and n = 2
Further, Ecell = 2.67 V with [Cu2+(aq)] = 1 M and [Mg2+(aq)] = xM and F/R = 11500 KV−1 where F = Faraday constant, R = gas constant
From the formula,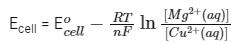
After putting the given values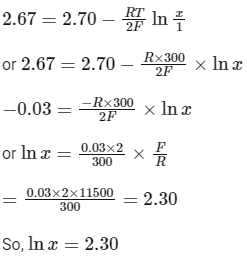
or x = 10 (as given ln (10) = 2.30)
|
361 videos|822 docs|301 tests
|
FAQs on JEE Advanced Previous Year Questions (2018 - 2024): Electrochemistry - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What are the key concepts of electrochemistry that are frequently tested in JEE Advanced? |  |
| 2. How can I prepare effectively for the electrochemistry section of JEE Advanced? |  |
| 3. What types of problems related to electrochemistry are commonly found in JEE Advanced? |  |
| 4. How does the Nernst equation apply to electrochemistry problems in JEE Advanced? |  |
| 5. What role does the understanding of standard electrode potentials play in JEE Advanced electrochemistry questions? |  |
















