JEE Advanced Previous Year Questions (2019 - 2024): Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
2024
Q1: Based on VSEPR model, match the xenon compounds given in List-I with the corresponding geometries and the number of lone pairs on xenon given in List-II and choose the correct option.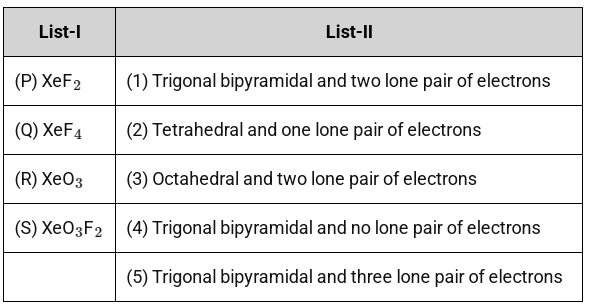 (a) P-5, Q-2, R-3, S-1
(a) P-5, Q-2, R-3, S-1
(b) P-5, Q-3, R-2, S-4
(c) P-4, Q-3, R-2, S-1
(d) P-4, Q-2, R-5, S-3 [JEE Advanced 2024 Paper 1]
Ans: (b)
XeF₂
- 2 sigma bonds and 3 lone pairs on Xe
- Number of hybrid orbitals = 5
- Hybridisation: sp³d
- Geometry: Trigonal bipyramidal
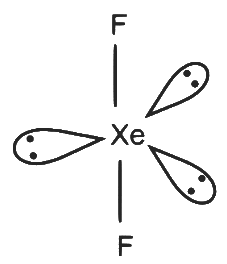
P - 5
XeF₄
- 4 sigma bonds and 2 lone pairs on Xe
- Number of hybrid orbitals = 6
- Hybridisation: sp³d²
Geometry: Octahedral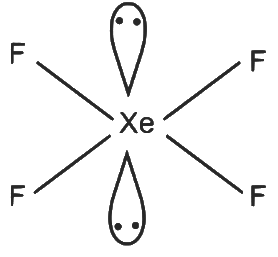 Q - 3
Q - 3
XeO₃
- 3 sigma bonds and 1 lone pair on Xe
- Number of hybrid orbitals = 4
- Hybridisation: sp³
- Geometry: Tetrahedral
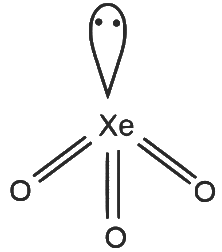
R - 2
XeO₃F₂
- 5 sigma bonds and 0 lone pairs on Xe
- Number of hybrid orbitals = 5
- Hybridisation: sp³d
Geometry: Trigonal bipyramidal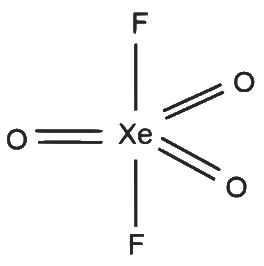 S - 4
S - 4
Q2: The option(s) in which at least three molecules follow the Octet Rule is(are):
(a) CO₂, C₂H₄, NO and HCl
(b) NO₂, O₃, HCl and H₂SO₄
(c) BCl₃, NO, NO₂ and H₂SO₄
(d) CO₂, BCl₃, O₃ and C₂H₄ [JEE Advanced 2024 Paper 1]
Ans: (a), (d)
The octet rule states that atoms tend to combine in such a way that they each have eight electrons in their valence shell, giving them the same electronic configuration as a noble gas. Let's examine each option to determine which molecules follow the octet rule.
Option A: CO₂, C₂H₄, NO and HCl
- CO₂: Carbon dioxide follows the octet rule. Carbon forms double bonds with two oxygen atoms, allowing it to have 8 electrons in its valence shell.
- C₂H₄: Ethylene follows the octet rule. Each carbon forms a double bond with the other carbon and single bonds with two hydrogen atoms, resulting in 8 electrons in the valence shell of the carbons.
- NO: Nitric oxide does not follow the octet rule. It has an odd number of electrons, making it a free radical.
- HCl: Hydrogen chloride follows the octet rule. Chlorine has 8 electrons in its valence shell when bonded with hydrogen.
Thus, three molecules CO₂, C₂H₄, and HCl follow the octet rule here.
Option B: NO₂, O₃, HCl and H₂SO₄
- NO₂: Nitrogen dioxide does not follow the octet rule. It has an odd number of electrons.
- O₃: Ozone follows the octet rule. It has a resonance structure that allows each oxygen atom to have 8 electrons in its valence shell.
- HCl: As mentioned, hydrogen chloride follows the octet rule.
- H₂SO₄: Sulfuric acid follows the octet rule. All atoms achieve stable configurations through bonding.
Thus, three molecules O₃, HCl, and H₂SO₄ follow the octet rule in this option.
Option C: BCl₃, NO, NO₂ and H₂SO₄
- BCl₃: Boron trichloride does not follow the octet rule. Boron has only 6 electrons in its valence shell.
- NO: As mentioned, nitric oxide does not follow the octet rule.
- NO₂: As mentioned, nitrogen dioxide does not follow the octet rule.
- H₂SO₄: Sulfuric acid follows the octet rule.
Thus, only one molecule, H₂SO₄, follows the octet rule in this option.
Option D: CO₂, BCl₃, O₃ and C₂H₄
- CO₂: As mentioned, carbon dioxide follows the octet rule.
- BCl₃: As mentioned, boron trichloride does not follow the octet rule.
- O₃: As mentioned, ozone follows the octet rule.
- C₂H₄: As mentioned, ethylene follows the octet rule.
Thus, three molecules CO₂, O₃, and C₂H₄ follow the octet rule in this option.
Conclusion:
The correct options are Option A and Option D, both having at least three molecules that follow the octet rule.
2023
Q1: The correct molecular orbital diagram for F2 molecule in the ground state is : [JEE Advanced 2023 Paper 2]
(a)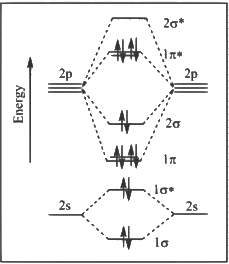
(b)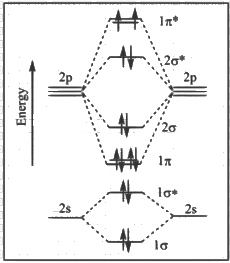
(c)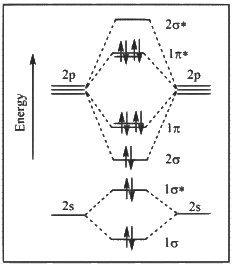
(d)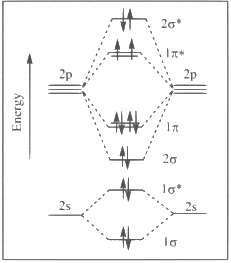
Ans: (c)
(1) Upto 14 electrons, molecular orbital configuration is ->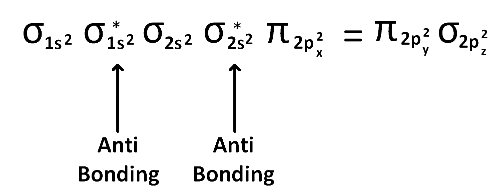 Nb = No of electrons in bonding molecular orbital
Nb = No of electrons in bonding molecular orbital
Na = No of electrons in anti bonding molecular orbital
Here Na = Anti bonding electron = 4 and Nb = 10
(2) After 14 electrons to 20 electrons molecular orbital configuration is ->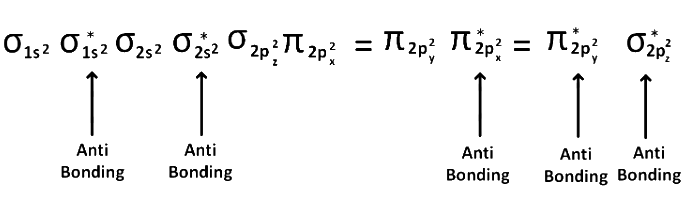 Here Na = 10
Here Na = 10
and Nb = 10
Now from question, in F atom 9 electrons present, so in F2, 9 × 2 = 18 electrons present.
Molecular orbital configuration of F2(18 electrons) is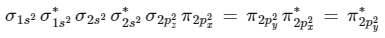
Q2: Among [I3]+, [SiO4]4−, SO2 Cl2 , XeF2, SF4, ClF3, Ni (CO)4 , XeO2 F2, [PtCl4]2− , XeF4 , and SOCl2 , the total number of species having sp3 hybridised central atom is ________. [JEE Advanced 2023 Paper 2]
Ans: 5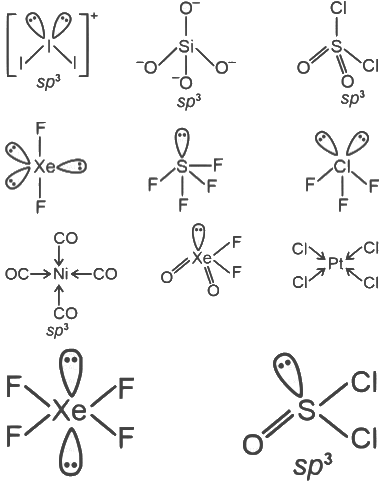
Q3: Consider the following molecules: Br3O8 , F2O, H2S4O6, H2S5O6 , and C3O2. Count the number of atoms existing in their zero oxidation state in each molecule.
Their sum is _______. [JEE Advanced 2023 Paper 2]
Ans: 6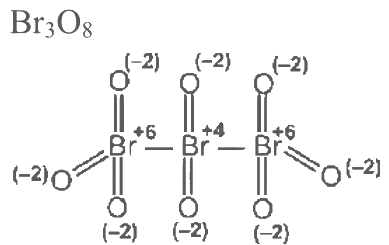 Number of atoms with zero oxidation state =0
Number of atoms with zero oxidation state =0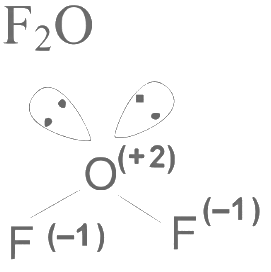 Number of atom with zero oxidation state = 0
Number of atom with zero oxidation state = 0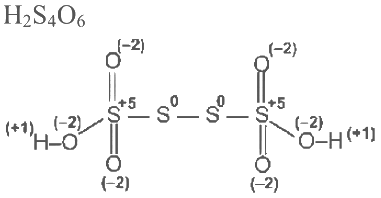 Number of atoms where zero oxidation state = 3
Number of atoms where zero oxidation state = 3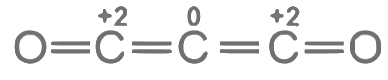 Number of atoms with zero oxidation state =1
Number of atoms with zero oxidation state =1
∴ Total atom with zero oxidation number state are 6.
2020
Q1: With respect to hypochlorite, chlorate and perchlorate ions, choose the correct statement(s). [JEE Advanced 2020 Paper 1]
(a) The hypochlorite ion is the strongest conjugate base.
(b) The molecular shape of only chlorate ion is influenced by the lone pair of electrons of Cl.
(c) The hypochlorite and chlorate ions disproportionate to give rise to identical set of ions.
(d) The hypochlorite ion oxidises the sulphite ion.
Ans: (a, b, d)
(a) Order of acid strength different oxyacids of chlorine are :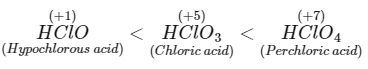 Weak acid have strong conjugate base thus hypochlorite ion has strongest conjugate base. Therefore, statement (a) is correct.
Weak acid have strong conjugate base thus hypochlorite ion has strongest conjugate base. Therefore, statement (a) is correct.
(b) Hypochlorite ion is linear and perchlorate ion is tetrahedral and there is no effect of lone pair on hypochlorite ion. Thus, statement (b) is correct.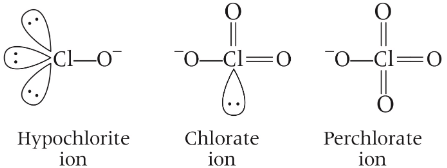 (c) In the disproportionation reaction, chlorate ion Cl(+5) is oxidised to perchlorate, Cl(+7) and reduce to chloride, Cl(−1).
(c) In the disproportionation reaction, chlorate ion Cl(+5) is oxidised to perchlorate, Cl(+7) and reduce to chloride, Cl(−1).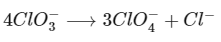
While in hypochlorite ion, chlorite ion Cl(+1) is oxidised to chlorate, Cl(+5) and reduced to chloride, Cl(−1) ion.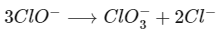
Thus, statement (c) is incorrect.
(d) The hypochlorite ion oxidises the sulphite ion to sulphate ion, because HOCl is the strongest oxidising Cloxyacids,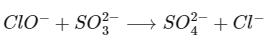
Thus, statement (d) is correct.
Q2: Consider the following compounds in the liquid form :
O2, HF, H2O, NH3, H2O2, CCl4, CHCl3, C6H6, C6H5Cl
When a charged comb is brought near their flowing stream, how many of them show deflection as per the following figure? [JEE Advanced 2020 Paper 2]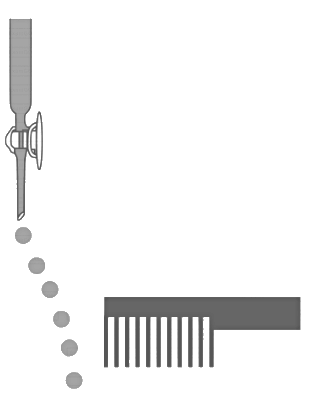 Ans: 6
Ans: 6
Only polar liquid will be attracted towards charged comb due to the formation of electrically charged droplets in the polar liquid stream, induced by a nearby charged object. Hence, liquid showing deflection are HF, H2O, NH3, H2O2, CHCl3, C6H5Cl.
Q3: The structure of a peptide is given below.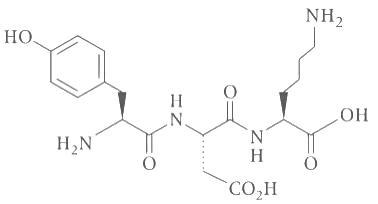 If the absolute values of the net charge of the peptide at pH = 2, pH = 6, and pH = 11 are and |Z3|, respectively, then what is |Z1| + |Z2| + |Z3| ? [JEE Advanced 2020 Paper 2]
If the absolute values of the net charge of the peptide at pH = 2, pH = 6, and pH = 11 are and |Z3|, respectively, then what is |Z1| + |Z2| + |Z3| ? [JEE Advanced 2020 Paper 2]
Ans: 5
At pH = 2,
There are two − NH2 group, and + 1 charge on each group because all amino groups exist in the form of − NH3⊕.
Therefore, |Z1| = 2.
At pH = 6,
NH2 of lysine (+ 1) (pH = 9.47) and COOH (− 1) of glutamic (pH = 3.08) acid, so because of dipolar ion exists, therefore |Z2| = 0.
At pH = 11,
COOH of glutamic acid has (− 1), COOH of lysine (− 1) and OH of phenol (− 1).
Therefore, |Z3| = | − 3| = 3 (All COOH and OH exist in the form of − COO − and − O −).
∴ |Z1| + |Z2| + |Z3| = 2 + 0 + 3 = 5
2019
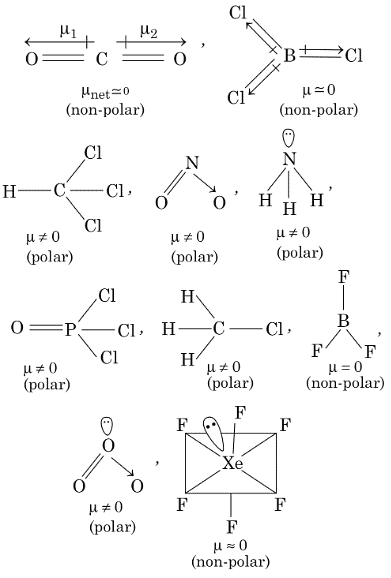
Q1: Each of the following options contains a set of four molecules. Identify the option(s) where all four molecules posses permanent dipole moment at room temperature. [JEE Advanced 2019 Paper 1]
(a) SO2, C6H5Cl, H2Se, BrF5
(b) BeCl2, CO2, BCl3, CHCl3
(c) NO2, NH3, POCl3, CH3Cl
(d) BF3, O3, SF6, XeF6
Ans: (a, c)
The molecules which gives permanent dipole moment are polar in nature.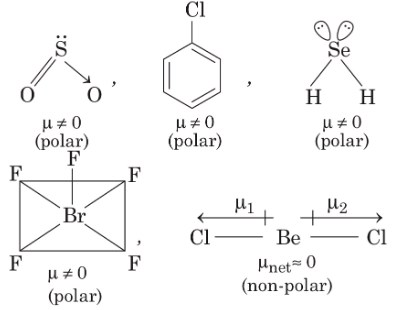
|
334 videos|651 docs|300 tests
|
FAQs on JEE Advanced Previous Year Questions (2019 - 2024): Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What is the significance of hybridization in chemical bonding? |  |
| 2. How do you determine the molecular geometry of a compound? |  |
| 3. What are the differences between ionic and covalent bonds? |  |
| 4. How do lone pairs affect molecular shape? |  |
| 5. What is the role of electronegativity in determining bond polarity? |  |
















