Deductions from Gross Total Income - 1 | Commerce & Accountancy Optional Notes for UPSC PDF Download
Introduction
The first step in calculating income is to determine the earnings from each source, considering the expenses associated with generating that income. The total of all income from these sources is called "Gross Total Income". Certain deductions that are not linked to any specific source are then subtracted from the Gross Total Income to arrive at the "Total Income" subject to tax.
To break it down:
- Income from Salaries
- Income from House Property
- Profit and Gains of Business and Profession
- Income from Capital Gains
- Income from Other Sources
Gross Total Income is then reduced by deductions under Chapter VI-A (Section 80C to 80U).
Key points:
- Taxpayers must claim deductions themselves.
- The sum of allowed deductions cannot exceed Gross Total Income.
- If the deductions exceed Gross Total Income, they are restricted to the Gross Total Income.
- Taxpayers must provide proof of claimed deductions upon request.
- If an association of persons or body of individuals is allowed deductions under a specific section, individual members cannot claim deductions under the same section to avoid duplication.
- Section 80C allows deductions up to Rs. 1,50,000 for individuals or HUFs.
- If eligible for deductions under multiple subsections of Section 80 (80C to 80U), the total of all subsections can be claimed, but the total under 80C cannot exceed Rs. 1,50,000 or Gross Total Income, whichever is lower. However, deductions under other subsections up to 80U can still be claimed if Gross Total Income exceeds Rs. 1,50,000.
In summary, the aggregate of deductions between 80C to 80U cannot exceed Gross Total Income, but any amount within that range can be claimed.
Deductions to promote savings
- Section 80C enables certain investments and expenses to be exempt from tax. This provision allows for a deduction in the case of specified qualifying amounts paid or deposited by an individual or Hindu Undivided Family (HUF) taxpayer (assessee) only.
- This deduction is available based on specified qualifying investments/contributions/deposits/payments (Gross Qualifying Amount) made by the taxpayer during the previous year. Specified contributions towards life insurance premiums, annuity plans of Life Insurance Corporation or any other insurer, and the following schemes have been notified: New Jeevan Dhara, New Jeevan Dhara-I, New Jeevan Akshay, New Jeevan Akshay-I, and New Jeevan Akshay-II, Provident Funds, Superannuation Fund, National Savings Scheme, 1992, Sukanya Samriddhi Account, Unit-Linked Insurance Plan (ULIP), Mutual Funds, pension plans, payment of principal amount of home loans, payment of tuition fees, amount invested in approved debentures and equity shares, 5 years Tax Saving Fixed Deposits, subscription in Bonds issued by National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD), amount deposited in the senior citizens saving scheme, 2004, may all or some of them or only one of them (as the case may be) from the total of Gross Qualifying Amount.
- The maximum deduction available under this Section is Rs. 1,50,000/-. The surrender value received by the assessee or his nominee on the prematurely annuity plan shall be taxable in the hands of the recipient in the year of the receipt.
- Section 80CCC allows an individual and Non-resident individual also to avail of a deduction for the amount deposited by him in an annuity plan of the Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC) or any other insurer for receiving the pension from the fund set up by LIC or any other insurer referred to in Section 10(23AAB).
- The amount allowed under this Section is Rs. 1,50,000 or the actual amount deposited, whichever is less. The amount received by the assessee or by the nominee as a pension will be taxable in the year of its receipt. Where a deduction under Section 80CCC has been allowed, a deduction under Section 80C will not be available in respect of payment made towards the annuity plan.
Deduction in Respect of Contribution to Pension Scheme of Central Government (Section 80-CCD)
Eligibility:
- This deduction is available only to individual assesses who have been appointed on or after January 1, 2004, by the Central Government or any other employer and have deposited a sum in a pension account notified by the central government or have contributed to a pension scheme in the previous year.
Quantum of Deduction:
- An individual employed by the Central Government on or after January 1, 2004, or by any other employer, or any other individual, who has paid or deposited any amount in his account under a pension scheme notified or as may be notified by the Central Government in the previous year, shall be allowed a deduction of the whole of the amount so paid or deposited, not exceeding:
- 10% of his salary in the previous year, in the case of an employee, and
- 20% of his gross total income in the previous year, in the case of any other assessee.
- If an assessee deposits in the Atal Pension Yojana, deduction shall be granted (Notification no. 50529 (E), dated 19-02-2016).
- The maximum deduction shall be Rs. 1,50,000.
- Where the Central Government or any other employer makes any contribution to his account, referred to in sub-Section (1), the assessee shall be allowed a deduction in the computation of his total income of the whole amount contributed by the Central Government or any other employer, not exceeding 10% (14% if the employer is the Central Government) of his salary in the previous year.
- An assessee referred to in sub-Section (1), whether or not received any deductions under sub-Section (1), shall be allowed a deduction to the extent of:
- the whole amount paid or deposited in the previous year, or
- Rs. 50,000, whichever is less.
The following amount withdrawn from the pension scheme shall be exempt to the extent given below:
- Any payment from the national pension system trust to an employee on account of closure or his opting out of the pension scheme referred to in Section 80CCD, to the extent it does not exceed 60% of the total amount payable to him at the time of the closure or his opting out, shall be exempt from tax as per Section 10(12A).
- Any payment from the national pension scheme trust to an employee under the pension scheme referred to in Section 80CCD, on partial withdrawal made out of his account in accordance with the terms and conditions specified under the Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority Act, 2013, and the regulations made thereunder, to the extent it does not exceed 25% of the amount of contributions made by him.
No deduction shall be allowed under Section 80C in respect of amounts on which deduction has been claimed under Section 80CCD (1) and 80CCD (1B).
Deductions For Specific Personal Expenses
Deduction for Medical Insurance Premium (Section 80 D)
- Eligibility: The scheme is applicable to individuals (Resident or non-resident) and H.U.F.
Conditions for deduction:
- The insurance scheme must be framed by the General Insurance Corporation of India and approved by the Central Government or any other insurer and approved by the Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority (IRDA), India.
- Deduction is allowed in respect of any amount out of chargeable to tax income by any mode of payment (Cheque, draft, electronic system of bank ECS, NEFT, or RTGS) other than cash (for preventive checkup cash payment allowed) towards an insurance policy taken on the health of the assessee or spouse or dependent children or parents and for H.U.F., Non-senior citizen.
- Any contribution made to the Central Health Scheme of the Central Government.
Quantum of Deduction: In the case of an individual,
Note: Salary includes dearness allowance if the terms of employment so provide, but excludes all other allowances and perquisites.
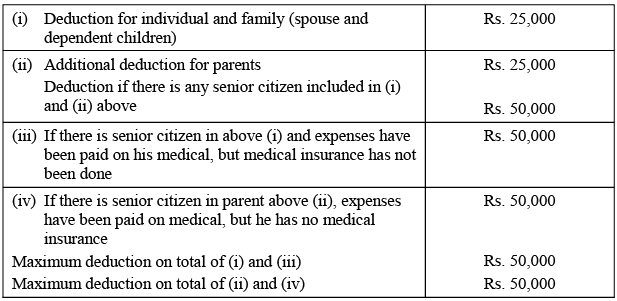
ii) In case of H.U.F,

Note: i) Senior citizen means an individual resident in India, who is of age of 60 years or more at any time during the relevant previous year. ii) Health insurance shall be as per any scheme framed by General Insurance Corporation of India established under Section 9 of general insurance business (Nationalization) Act, 1972 and approved by Central Government or any scheme notified by Central Government or any other insurer approved by Insurance regulatory and development authority established under sub Section (1) of Section (3) of Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority Act, 1999.
Deduction for Handicapped Dependent (Section 80-DD)
- Eligibility: This deduction is available to a resident individual and HUF.
Conditions for deduction:
- Deduction is allowed for expenditure incurred on medical treatment (including nursing), training, and rehabilitation of a handicapped relative who is dependent on the taxpayer and is not dependent on any other person for support or maintenance.
- The individual/HUF must have deposited money under a scheme of the Life Insurance Corporation approved by the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT).
The assessee must submit a copy of the certificate issued by a medical authority every year along with the income tax return in the prescribed form under Section 139 for the year for which the deduction is claimed.
Quantum of Deduction: The deduction will be allowed for a fixed sum of Rs. 75,000/- and for severe disability, it is Rs. 1,25,000/-. This deduction is irrespective of actual expenditure.
Note:
- A handicapped relative refers to a relative suffering from eminent physical disability (including blindness) or mental retardation of the nature specified in IT Rules and certified as such by a physician, surgeon, oculist, or psychiatrist working in a Government hospital. This disability should significantly reduce such person's capacity for normal work or engaging in gainful employment or occupation.
A person suffering from any of the disabilities mentioned below, certified by a medical authority as not less than 40%, is eligible: blindness, low vision, leprosy cured, hearing impairment, locomotor disability, mental disability, mental illness. - A person with severe disability is one who has 80% or more disabilities as referred to in sub-Section (4) of Section 56 of the Persons with Disabilities (Equal Opportunities, Protection of Rights, and Full Participation) Act, 1995, or as mentioned in (f) above.
Deduction for Medical Expenses for Assessee Himself and Dependent Relative (Section 80 DDB)
- Eligibility: This deduction is available to a resident individual or a resident HUF.
- Conditions for deduction: This deduction is allowed for expenditure actually paid on the medical treatment of the individual himself or a dependent in respect of diseases specified in the rules. Specified diseases include neurological diseases, cancer, AIDS, hemophilia, and chronic renal failure.
- Quantum of Deduction: This deduction is allowed up to a maximum of Rs. 40,000. For senior citizens, the deduction is allowed up to a maximum of Rs. 1,00,000. However, if any amount is received under insurance from the insurer for medical treatment, the deduction shall be reduced by the same amount.
Deduction in Respect of Interest on Loan taken for Higher Education (Section 80 E)
- Eligibility: This deduction is available to an individual assessee or any relative who has taken a loan for higher full-time education.
- Conditions for deduction: The assessee is entitled to a deduction in the previous year in which he starts paying the interest on the loan and in seven succeeding previous years or until the full amount of interest is paid (whichever is earlier). This deduction is also available for the purpose of higher education of relatives.
- Quantum of Deduction: This deduction is allowed to an individual in respect of the interest on the loan paid by him in the previous year taken from any financial institution for the purpose of pursuing higher education.
Note:
- Individual, relative includes a spouse, children, or the students for whom the individual is the legal guardian.
- Higher education includes engineering (including architecture), medical science, graduate and postgraduate studies in management or applied science (including mathematics and statistics).
Deduction for Interest on Home Loan (Section 80 EE)
- Eligibility: This deduction is available to individual first-time home buyers.
- Conditions for deduction: The housing loan amount cannot exceed Rs. 35 Lakhs, and the value of the house cannot exceed Rs. 50 Lakhs. The loan should be sanctioned between April 1, 2016, and March 31, 2017. The assessee should not own a second house or any other house on the date of sanction of the loan. This deduction is available over and above the Rs. 2 Lakh limit under Section 24 of the Income Tax Act. Deduction under this Section (80 EE) shall be allowed in computing the total income of the individual for the assessment year beginning on 01.04.2017, and subsequent assessment years.
- Quantum of Deduction: This deduction is available up to Rs. 50,000 on the interest amount on home loans taken from specified financial institutions such as banks and housing finance companies.
Deduction for Interest on Loan taken for certain house Property (Section 80 EEA)
- Eligibility: This deduction is available to individuals who are not eligible to claim any deduction under section 80 EE.
- Conditions for deduction: The loan must be taken for the purpose of acquiring a residential house property. The loan should be sanctioned by a financial institution (i.e., a bank or banking institution or a housing finance company) between April 1, 2019, and March 31, 2022. Additionally, the stamp duty value of the residential house property should not exceed Rs. 45 lakh. The assessee should not own any residential house property on the date of sanction of the loan.
- Quantum of Deduction: If the above conditions are met, the assessee can claim a deduction under section 80EEA. The deduction is available for interest payable on the above loan or Rs. 1,50,000, whichever is less. The deduction is available for the assessment year 2020-21 and subsequent assessment years.
Deduction for Interest on Loan taken for Purchase of Electric Vehicle(Section 80 EEB)
- Eligibility: This deduction is available to an individual who has taken a loan for the purpose of purchasing an electric vehicle.
- Conditions for deduction: The loan must be taken from a financial institution (i.e., a bank or any deposit-taking NBFC or a systematically important non-deposit-taking NBFC). The loan should be sanctioned between April 1, 2019, and March 31, 2023.
- Quantum of Deduction: If the above conditions are met, the assessee can claim a deduction under section 80EEB. The deduction is available for interest payable on the above loan or Rs. 1,50,000, whichever is less. The deduction is available for the assessment year 2020-21 and subsequent assessment years.
Deduction in Respect of Payment of House Rent (Section 80 GG)
- Eligibility: The benefit of this deduction is available to an individual (self-employed or salaried, not receiving house rent allowance from an employer) or an H.U.F. member for rent paid for accommodation (furnished or unfurnished) occupied by him for his own residence, provided that the assessee or his spouse or minor children or H.U.F of which the assessee is a member does not own any residential accommodation at the workplace where the assessee resides currently or at the place where he works or carries on his business or profession.
- Conditions for deduction: If the assessee owns any residential accommodation at any other place and enjoys the concession of self-occupied house with regard to such accommodation, the assessee will not be entitled to a deduction under this Section (80 GG). Details of rent paid should be furnished in form 10 BA.
- Quantum of Deduction: The least of the following shall be allowed as a deduction under this Section (80 GG):
- Rs. 5000/- per month.
- 25% of the adjusted total income.
- The actual amount of rent less 10% of the adjusted total income.
Adjusted total income may be calculated by deducting long-term capital gains, short-term capital gains under Section 111 A, and income under Section 115 A or 115 D and deductions from 80 C to 80 U (excluding deduction of 80 GG).
Example: Total Taxable Income Rs. 4,35,000/- Rent paid Rs. 8,000 p.m.
The least of the following shall be allowed as a deduction:
- Rent paid over and above 10% of adjusted total income i.e. Rs. 96,000/-
(12×8,000) – (10% of Rs. 4,35,000/-) Rs. 43,500/- = Rs. 52,500/-. - 25% of adjusted total income i.e. 25% of Rs. 4,35,000/- = Rs. 1,08,750/-
- Rs. 5,000/- p.m. i.e. (Rs. 5000×12) Rs. 60,000/- The least of the (i) or (ii) or (iii) is Rs. 52,500/-. Hence, the deduction allowed is Rs. 52,500/-
Deduction For Encouraging Voluntary Participation In Charitable And Socially Desirable Activities
The Income Tax Act, 1961 allows certain deductions for contributions made to charitable and socially desirable activities. These are explained in Section 80 G.
Deduction in Respect of Donations to Certain Charitable Institutions (Section 80G)
Eligibility: This deduction is available to all assesses who have donated to charitable institutions and special funds.
Conditions for deduction:
- Donations should be given to specified funds or institutions.
- Donations can be made in cash, cheque, or draft, but if the donation amount exceeds Rs. 2,000, it should be given through draft, cheque, or debit card, etc.
- Proof of donation is mandatory to be presented by the assessee.
- Donations should not be for a particular caste, creed, or religion.
Quantum of Deduction: The deductions can be classified as:
- No limit donations, i.e., the entire amount qualifies for deduction.
With limit donations, i.e., the qualifying amount for deduction shall not exceed 10% of the gross total income after deducting:
- Long term capital gains
- Deductions under Sections 80 C to 80 U, except 80 G
- Exempted incomes
- Incomes referred to in Section 115A, 115AB, 115 AC, or 115AD, i.e., income from NRIs and foreign companies, etc., which are taxable at a special rate of tax.
- Short-term capital gains under Section 111A.
Donations can further be classified as:
- Deduction allowed @100% of the qualifying amount.
- Deduction allowed @50% of the qualifying amount.
No limit donations where deduction is allowed @ 100% are as follows:
- The Africa (Public Contributions India) Fund
- The National Foundation for Communal Harmony
- The National/State Blood Transfusion Council and Fund set-up by State Government to provide relief to the poor.
- Andhra Pradesh CM Cyclone relief Fund,1996
- Chief Minister’s or Lt. Governor’s Relief Fund
National Sports Fund set up by Central Government
- National Cultural Fund set up by Central Government
- National children's fund
- State Government's medical relief fund.
- Chief Minister’s earthquake fund Maharashtra.
- Any fund set up by State Government of Gujarat exclusively for providing relief to the victims of the earthquake in Gujarat.
- Any Zila Saksharta Samiti.
- National Illness Assistance Fund.
- The fund for technology development and application set up by the central government.
- The Swachh Bharat Kosh.
- National Defence Fund
- P.M's National Relief Fund.
- The clean Ganga Fund.
- PM's Armenia Earthquake Relief Fund
- National fund for control of Drug Abuse.
- An approved university or educational institution of national eminence.
- Central welfare fund of the Army and defence force and the Indian Naval Benevolent Fund.
- National Trust for Welfare of persons with Autism, Cerebral Palsy, Mental Retardation, and Multiple Disabilities.
No limit donations where deduction is allowed @ 50% are as follows:
- Jawaharlal Nehru Memorial Fund
- PM's Drought Relief Fund
- Indira Gandhi Memorial Trust
- Rajiv Gandhi Foundation
With limit donations where deduction is allowed on 100% of the qualifying amount:
- Any institution approved by the Government/local authority established for the purpose of promoting family planning. Thus, Government or approved local authority or association and approved institutions and association are covered.
- Sum paid by a company to the Indian Olympic Association or any other association established in India for the development of infrastructure for sports in India or for the sponsorship of sports in India. The donation recipient institution or association must be notified by the Central Government.
With limit donations where deduction is allowed on 50% of the qualifying amount:
- Donation to any Recognized Charitable Fund or Institution.
- Donation to the Government or any local authority for charitable purposes (excluding the promotion of family planning).
- Donations to lawfully constituted authority engaged in satisfying the needs of housing requirements or in planning the development and improvement of cities, towns, or villages.
- Donation to a corporation established by the Government (Central or State) for promoting the interests of the members of the minority community.
- Donation for the renovation and repair of Temples, Mosques, and Gurudwaras, Churches, or any other religious place or historical place notified by the Central Government or State Government and declared national importance places in the Government Gazette.
For applying the qualifying limit, all donations made to funds/institutions covered under C and D above shall be aggregated, and the aggregated amount shall be limited to 10% of the adjusted gross total income.
Adjusted Gross Total Income: It means the ‘Gross Total Income’ as reduced by:
- Long term capital gains, if any, which have been included in the ‘Gross total income’.
- Short term capital gains of the nature referred to in Section 111A (i.e., short term capital gain on the transfer of shares through a recognized stock exchange which are taxable @ 15%.
- All deductions permissible u/s 80C to 80U except the deduction u/s 80G.
- Such income on which income tax is not payable i.e. share from AOP.
- Income referred to in Section 115A, 115AB, 115AC, or 115AD. These Sections relate to incomes of NRIs and foreign companies, etc., which are taxable at a special rate of tax.
Note:
- Donations given in kind do not qualify for deduction.
- Aid to any individual does not qualify for deduction.
- Donation to any charitable institution meant for a particular caste or creed does not qualify for deduction.
- Donation to a political party does not qualify for deduction.
- Cash donation cannot exceed Rs. 2000/. Donations exceeding Rs. 2000/- can be made in any other mode other than cash.
- Payment proof of donation is compulsory.
Contribution to Certain Approved Institutions (Section 80 GGA)
- Eligibility: This deduction is allowed to an assessee whose "Gross Total Income" does not include income chargeable under the head "Profits and gains of business or profession."
Conditions for Deduction:
- Deduction is allowed equal to 100% of the following sums:
- Contribution to an approved scientific research association or to an approved University, College, or other Institution to be used for Scientific Research.
- Contribution to an association or institution having the object of undertaking an approved program of rural development or Contribution to an association or institution which has as its object of training of persons for implementing programs of rural development.
- Contribution to the notified Rural Development Fund or Sums paid to National Urban Poverty Eradication Fund set up and notified by the Central Government. (The assessee shall furnish a certificate as per Section 35CCA)
- Contribution to an approved University, College, Research Association, or Other Institution to be used for Research in Social Science or Statistical Research
- Contribution made to specified public sector company, local authority, or an approved association or institution for carrying out an eligible project or scheme for promoting social and economic welfare or uplift of the public. (The assessee shall furnish a certificate as per Section 35AC)
- Cash donation can be up to Rs. 2,000
Deduction in Respect of Contributions given to Political Parties by Companies (Section 80 GGB)
- From the total income of an Indian company, a 100% deduction of any sum contributed (in the previous year) by it to any political party (Registered under Section 29 A of the Representation of the People Act, 1951) or an Electoral Trust is allowed as a deduction.
- No deduction is allowed in respect of any sum contributed by way of cash.
- Advertisement expenditure made by a company in a magazine owned by a political party is treated as a contribution to a political party. An electoral trust is established for the orderly receipt of the voluntary contributions from any person (or company) for distributing the same to the registered political parties.
Deduction in Respect of Contributions given by any Person to Political Parties (Section 80 GGC)
- From the total income of the assessee (excluding local authority and artificial judicial person wholly or partly funded by the Government), 100% deduction of the sum contributed by him (in the previous year) to a political party (Registered under Section 29 A of the Registration of the People Act, 1951) or an electoral trust is allowed as a deduction.
- However, cash contribution is not allowed as a deduction for the assessee.
- Advertisement expenditure in a magazine owned by a political party is not deductible under this Section. An electoral trust is a non-profit company established for the orderly receipt of contributions from any person for distributing the same to the registered political parties.
Note: Since the assessment year 2005-2006, deductions u/s 80 HH; 80 HHA; 80 HHB; 80 HHBA; 80 HHC; 80 HHD; 80 HHE; 80 HHF, and 80-I are not available.
|
196 videos|219 docs
|
FAQs on Deductions from Gross Total Income - 1 - Commerce & Accountancy Optional Notes for UPSC
| 1. What are some specific personal expenses that can be deducted from gross total income? |  |
| 2. How can individuals encourage voluntary participation in charitable and socially desirable activities through deductions? |  |
| 3. Is there a limit to the amount of deductions that can be claimed for specific personal expenses? |  |
| 4. Are there any conditions that need to be met in order to claim deductions for specific personal expenses? |  |
| 5. How can individuals ensure that they are maximizing their deductions for specific personal expenses? |  |















