Revision Notes: Thermodynamics | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Introduction to Thermodynamics
- System: The portion of the universe under investigation.
- Open System: A system capable of exchanging both energy and matter with its surroundings.
- Closed System: A system allowing the passage of energy but not mass across its boundary.
- Isolated System: A system that neither exchanges energy nor matter with its surroundings.
- Surroundings: The part of the universe other than the system, interacting with it.
- Boundary: Anything separating the system from its surroundings.
State Variables and Functions
- State Variables: Parameters required to define the state of a system (e.g., pressure, volume, mass, temperature).
- State Functions: Properties depending only on the system's state, not the path (e.g., pressure, volume, temperature).
- Intensive Properties: System properties independent of mass (e.g., temperature, pressure, density, concentration).
- Extensive Properties: System properties dependent on mass (e.g., volume, energy, enthalpy, entropy).
Processes in Thermodynamics
- Process: The path along which the state of a system changes.
- Isothermal Process: Process occurring at a constant temperature.
- Isobaric Process: Process occurring at a constant pressure.
- Isochoric Process: Process occurring at a constant volume.
- Adiabatic Process: Process where no heat transfer occurs between the system and surroundings.
- Cyclic Process: Process where the system returns to its initial state after a series of changes.
- Reversible Process: Process where the system infinitesimally departs from equilibrium, and its direction can be reversed at any moment.
- Irreversible Process: Fast process completed in a single step that cannot be reversed; natural processes typically fall into this category.
Heat, Energy, and Work
Heat (Q)- Energy is exchanged between system and surround in the form of heat when they are at different temperatures.
- Heat added to a system is given by a positive sign, whereas heat extracted from a system is given negative sign.
- It is an extensive property.
- It is not a state function.
Energy
- It is the capacity for doing work.
- Energy is an extensive property.
- Unit : Joule.
Work (W)
- Work = Force × Displacement i.e. dW = Fdx
- Work done on the system is given by positive sigh while work done by the system is given negative sign.
- Mechanical Work or Pressure-Volume Work: work associated with change in volume of a system against an external pressure.
- Work done in reversible process: W=
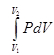
- W = – 2.303 nRT log v2/v1 = –2.303 nRT log p1/p2
- Wok done in isothermal reversible contraction of an ideal gas:
?W = – 2.303 nRT log v2/v1 = –2.303 nRT log p1/p2 - Unit : Joule.
Internal Energy (E or U):
Sum of all the possible types of energy present in the system.
ΔE = heat change for a reaction taking place at constant temperature and volume.
ΔE is a state function.
It is an extensive property.
Value of ΔE is -ve for exothermic reactions while it is +ve for endothermic reactions.
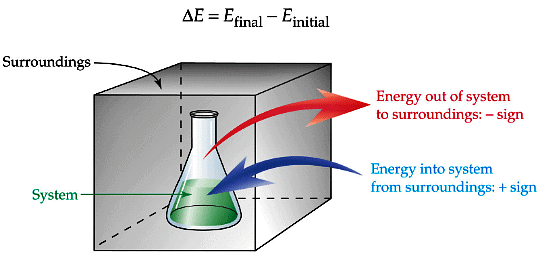
First Law of Thermodynamics
Energy can neither be created nor destroyed although it can be converted from one form to another.
or
Energy of an isolated system is constant.
Mathematical Expression
- Heat observed by the system = its internal energy + work done by the system.
i.e. q = dE + w - For an infinitesimal process
- dq = dE + dw
- Where, q is the heat supplied to the system and w is the work done on the system.
- For an ideal gas undergoing isothermal change ΔE =0.
- so q= -w.
For an isolated system, dq=0
so, dE = - dw
For system involving mechanical work only
ΔE = q - pdV
At constant volume i.e. isochoric process
ΔE = qv
For Isothermal Process
ΔE = 0
or
q = - pdV =-W
For adiabatic process
?q = 0
or
ΔE = W
Enthalpy (H):
- H = E+PV
- At constant pressure:
- dH = dE + pdV
- For system involving mechanical work only
- dH = QP (At constant pressure)
- For exothermic reactions:
- dH = -ve
- For endothermic reactions:
- dH = +ve
Relation between dH and dE:
- dH = dE + dng RT
- Where,
- dng = (Number of moles of gaseous products - Number of moles of gaseous reactants)
Heat Capacity
Heat capacity:
- Amount of heat required to rise temperature of the system by one degree.
C = q / dT
Specific heat capacity
- Heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of a substance by one dgree.
Cs = Heat capacity / Mass in grams
Molar heat capacity
- Heat required to raise the temperature of 1 g of a substance by one dgree.
Cm = Heat capacity / Molar mass.
Heat capacity of system at constant volume:
- Cv = (dE/dT)v
Heat capacity of system at constant pressure:
- Cp = (dE/dT)p
- Cp – Cv = R
Variation Of Heat Of Reaction With Temperature:
- dCP = (dH2 - dH1)/(T2-T1) & dCV = (dE2 - dE1)/(T2-T1
Bomb Calorimeter
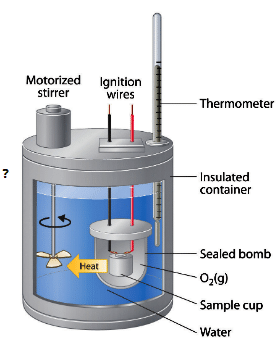
- Heat exchange = Z × ΔT
- Z–Heat capacity of calorimeter system
- ΔT– Rise in temp.
- Heat changes at constant volumes are expressed in ΔE and Heat changes at constant
- pressure are expressed in dH.
Enthalpies of Reactions
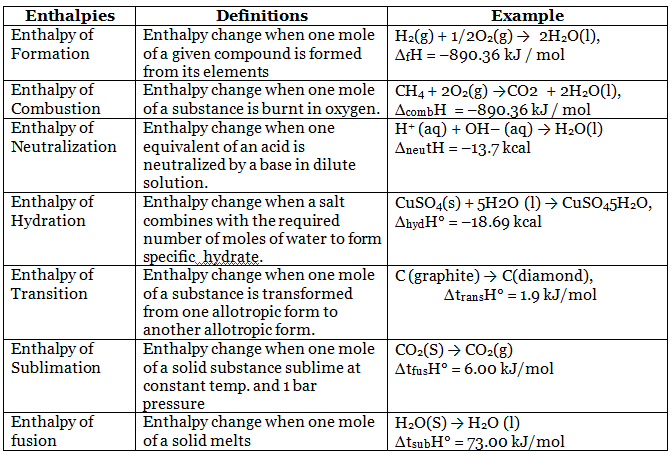
Hess’s Law of constant heat summation:
?The total enthalpy change of a reaction is the same, regardless of whether the reaction is completed in one step or in several steps.
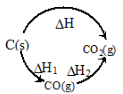
According to Hess’s law: ΔH = ΔH1 + ΔH2
Born–Haber Cycle
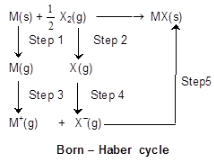
Applying Hess’s law we get
ΔH1 + 1/2 ΔH2 + ΔH3 + ΔH4 + ΔH5 = ΔHf (MX) (Lattice energy)
Lattice energy: The change in enthalpy that occurs when 1 mole of a solid crystalline substance is formed from its gaseous ions.
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Statement:
It is impossible to take heat from a hot reservoir and convert it completely into work by a cyclic process without transferring a part of it to a cold reservoirs.
Mathematically:
ΔS = qrev/T
Where,
ΔS is entropy change.
- Entropy is the degree of randomness thus it increases with increase in randomness of particles of the system i.e. ΔS is positive for melting of ice.
- At equilibrium, ΔS = 0
- For a spontaneous process, ΔS > 0
- Entropy change in an isothermal reversible expansion of a gas
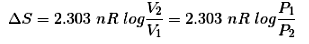
Spontaneous Processes
These type of physical and chemical changes occur of its own under specific circumstances or on proper initiations. For example: Flow of liquids from higher to lower level.
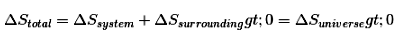
Gibbs Free Energy(ΔG)
- ΔG = ΔH - TΔS
- ΔG = nRT ln Keq
- ΔG = nFEcell
- At equilibrium, ΔG = 0
- For spontaneous process, ΔG < 0
Bond Energies
- Average amount of energy required to break one mole bonds of that type in gaseous molecules.
- H–OH(g) → 2H(g) + ½O(g) ΔH = 498 kJ
- O–H(g) → H2(g) + ½O2 (g) ΔH = 430 Kj
- ΔHO–H = (498 + 430)/2 = 464 kJ mol–1
Efficiency of a Heat Engine (Carnot Cycle)
W = R (T2 – T1) ln v2/v1
q2 = RT2 ln v2/v1
W = q2 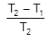
Efficiency (h). h =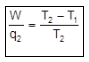
|
361 videos|822 docs|301 tests
|





















