Tenses | English Olympiad for Class 3 PDF Download
Simple Present Tense
Tenses inform us about when an action occurs relative to the present moment. Verbs change form to match the tense.
There are three primary tenses:
- Present Tense: Describes actions happening now or those that occur regularly.
- Past Tense: Refers to actions completed before the present moment.
- Future Tense: Indicates actions that will occur after the present moment.
Each of these tenses has four variations:
- Simple
- Continuous
- Perfect
- Perfect Continuous
Simple Present Tense:
The present simple tense is used
- To describe actions that occur regularly.
- To state permanent facts or universal truths.
- To discuss habits.
- To describe persistent situations that do not change.
E.g.
- The Sun rises from the east.
- I go to school.
- The Taj Mahal is in Agra.
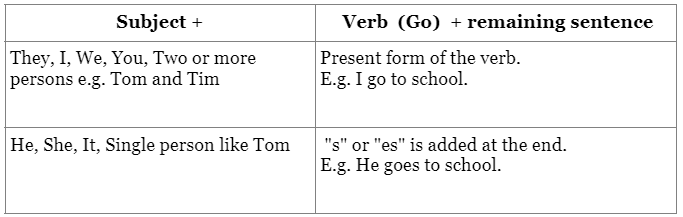
Rules:
Affirmative form
1. Add "s" or "es" when the subject (who is doing the action) is a singular and third person.
E.g.
- Incorrect: He go to school.
- Correct: He goes to school. ("He" is singular third person so "s" or "es" should be added to the verb "go")
2. When the subject is plural or first or second person then present form of the verb is used as it is.
E.g.
- Incorrect: They goes to school.
- Correct: They go to school.
Negative form:
1. Use "does not" when the subject is a singular third person.
E.g.
- Incorrect: My brother do not go to school.
- Correct: My brother does not go to school.
2. Use "do not" when the subject is first person, second person or plural.
E.g.
- Incorrect: Amit and Sumit does not go to school.
- Correct: Amit and Sumit do not go to school.

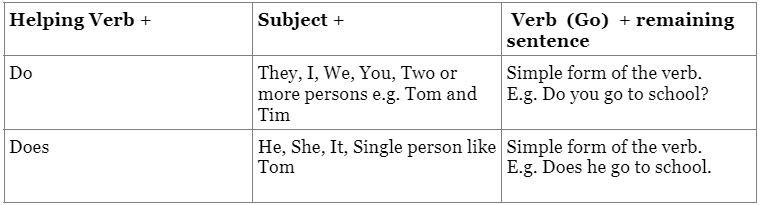
Simple Questions:
1. Bring helping verb in front, keeping the entire sentence same.
2. Use "does" when the subject is a singular third person.
E.g.
- Incorrect: Do he go to school?
- Correct: Does he go to school?
3. Use "do" when the subject is first person, second person or plural.
E.g.
- Incorrect: Does they go to school?
- Correct: Do they go to school?
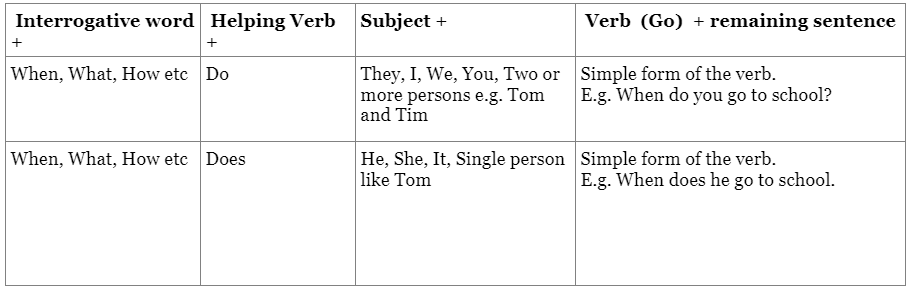
Questions for gathering information:
- The sentence will begin with a question word (e.g., what, when, where, how).
- This will be followed by a helping verb and then the complete sentence.
- Use "does" when the subject is a singular third person.
E.g.
- Incorrect: When do he go to school?
- Correct: When does he go to school?
4. Use "do" when the subject is first person, second person or plural.
E.g.
- Incorrect: How do they go to school?
- Correct: How do they go to school?
Usage of which is slightly different:
- Which + Object + Helping Verb + Rest of the sentence.
- Which book do you like?
- Which school do you go to?
or
In which school do you study?
Simple Past Tense
Tenses inform us about when an action occurs relative to the present moment, and verbs change form accordingly.
There are three primary tenses:
- Present Tense: Describes actions happening now or those that occur regularly.
- Past Tense: Refers to actions completed before the present moment.
- Future Tense: Indicates actions that will occur after the present moment.
Each of these tenses has four variations:
- Simple
- Continuous
- Perfect
- Perfect Continuous
Past Simple Tense:
The past simple tense is used:
- To refer to events that occurred before the current moment in time.
- To describe things that existed before the current moment in time.
- To denote a completed action in the past.
E.g.
- I went to school yesterday.
- He ate fruits in the breakfast.
Rules:
Affirmative form
1. Replace normal form of the verb with past form of the verb.
E.g.
- Incorrect: He wents to school.
- Correct: He went to school.
- Correct: They went to school.

Negative form:
1. Use "did not" and normal form of verb.
E.g.
- Incorrect: My brother does not go to school yesterday.
- Correct: My brother did not go to school yesterday.

Simple Questions:
1. Bring helping verb (did) in front, keeping the entire sentence same. Use the normal form of the verb.
E.g.
- Incorrect: Did he went to school?
- Correct: Did he go to school?

Questions asking information:
1. Sentence will start with question word seeking information like what, when, where, how etc
2. Proceeded by helping verb (did) and then the entire sentence with the normal form of the verb.
E.g.
- Incorrect: When do he went to school?
- Correct: When did he go to school?

Usage of which is slightly different:
- Which + Object + Helping Verb + Rest of the sentence.
- Which book did you buy?
- Which school did you go to?
Future Tense
Tenses play a crucial role in indicating the timing of an action concerning the present moment. The future tense, in particular, helps us talk about actions that are yet to happen.
Three basic tenses:
- Present Tense
- Past Tense
- Future Tense
Each basic tense has 4 other subtenses:
- Simple
- Continuous
- Perfect
- Perfect Continuous
Future Simple Tense:
The future simple tense is used to denote actions that will occur later in relation to the current moment.
Usage:
- To express actions that will happen in the future.
- To make predictions or talk about future events.
Form:
Affirmative:
- Subject + will + base form of the verb
e.g., I will go to the park tomorrow.
Negative:
- Subject + will not (won't) + base form of the verb
e.g., She won't be late for the meeting.
Questions:
- Will + subject + base form of the verb + ?
e.g., Will you come to the party?
Future Continuous Tense:
The future continuous tense is used to describe ongoing actions that will happen at a specific future time.
Usage:
- To talk about actions that will be in progress at a certain point in the future.
- To speculate about future activities.
Form:
Affirmative:
- Subject + will be + present participle (verb + -ing)
e.g., They will be studying at this time tomorrow.
Negative:
- Subject + will not (won't) be + present participle
e.g., She won't be working next weekend.
Questions:
- Will + subject + be + present participle + ?
e.g., Will you be sleeping when I arrive?
Future Perfect Tense:
- The future perfect tense is used to indicate the completion of an action by a certain future time.
Usage:
- To express actions that will be completed before a specific point in the future.
- To talk about something that will happen before another action in the future.
Form:
Affirmative:
- Subject + will have + past participle
e.g., By next year, she will have graduated.
Negative:
- Subject + will not (won't) have + past participle
e.g., They won't have finished their project by then.
Questions:
- Will + subject + have + past participle + ?
e.g., Will you have completed the assignment by Monday?
Future Perfect Continuous Tense:
The future perfect continuous tense is used to describe actions that will continue up to a certain point in the future and will be completed by that time.
Usage:
- To emphasize the duration of an action that will be ongoing until a specified future time.
- To indicate an action that will have been happening for some time in the future.
Form:
Affirmative:
- Subject + will have been + present participle
e.g., By next month, they will have been living in this city for five years.
Negative:
- Subject + will not (won't) have been + present participle
e.g., She won't have been working here for long by then.
Questions:
- Will + subject + have been + present participle + ?
e.g., Will you have been waiting for long when I arrive?
These different forms of the future tense allow us to express a variety of future actions, durations, and completions, providing clarity and context in communication.
|
35 videos|57 docs|97 tests
|
















