Modes of Preservation of Fossils | Geology Optional for UPSC PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Unaltered remains |

|
| Permineralization |

|
| Carbonization |

|
| Replacement |

|
| Recrystallization |

|
| Internal Molds |

|
| External Molds |

|
| Casts |

|
Unaltered remains
- Unaltered remains refer to fossils that are preserved in their original mineral composition, despite potential compression or separation due to burial sediments.
- It is crucial to understand the expected mineralogy of a fossil organism to determine the preservation mode applicable to the specimen.
- Examples of common fossil mineralogy:
- Calcite (CaCO3): Foraminifera, coccolithophores, sponges, corals, brachiopods, trilobites, molluscs, echinoderms
- Aragonite (CaCO3): Modern corals, molluscs
- Quartz (SiO2): Radiolarians, diatoms, sponges
- Hydroxyapatite Ca5(PO4)3: Vertebrate bone and teeth
- In rare cases, soft tissues like skin, feathers, or fur can be preserved, often found in materials like amber or glacial ice rather than sediments.
Fossils can form in various ways, depending on the conditions and materials involved. Let's explore some of the different types of fossilization processes:
Permineralization
- Definition: Permineralization is a process where mineral crystals fill open spaces within porous tissues after the organism has been buried.
- Process: Groundwater carrying dissolved minerals flows through the fossil. As the water evaporates, minerals fill the available spaces.
- Common Minerals: Quartz, calcite, and iron oxides are frequently involved in permineralization. These minerals are often found in sedimentary rocks.
- Organisms Involved: Vertebrate bones, wood, and some shells can undergo permineralization for preservation.
- Petrifaction: This is a specific type of permineralization, such as petrified wood, where minerals fill pores and replace organic material in plant tissues.
- Detail Preservation: Permineralized fossils retain high detail, preserving internal structures and the original organism's three-dimensional shape.
- Density: Due to crystal growth in previously open spaces, permineralized fossils are denser and heavier than their original forms.

Carbonization
- Process: When soft tissues are rapidly buried in calm water, they undergo pressure and temperature changes during lithification. This process affects the remaining organic material, leading to the release of volatile compounds.
- Result: After the release of volatiles, a dark carbon film, which is chemically stable, remains.
- Preservation: Carbonization can preserve intricate details of delicate soft tissues, such as individual cell structures in plants, fish scales, insect wings, and even internal organs.
Replacement
- Process: Under high pressure and temperature deep within the Earth's crust, fluids containing mobile chemical ions are released from sediments. These fluids engage with buried fossils, causing the original mineral or organic material to dissolve entirely.
- Replacement: The dissolved material is then substituted with different ions that are deposited from the moving fluids.
- Common Minerals: Silica and pyrite are commonly involved in the replacement process.
- Decomposition: The decomposition of organic matter requires the presence of bacteria, which aid in sulfur reduction and the formation of iron sulfide mineral, pyrite.
- Preservation: Through replacement, a significant amount of the original organism's structure can be preserved.
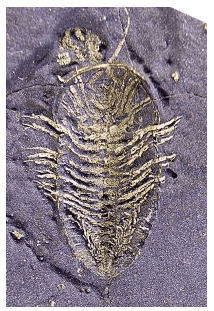
Recrystallization
- Recrystallization is a crucial process for preserving fossils made of aragonite, a mineral that is commonly found but chemically unstable over long periods.
- Marine invertebrates like molluscs and modern corals produce aragonite as their skeletal material due to their metabolic processes.
- Aragonite, a polymorph of CaCO3, can exhibit the beautiful "mother of pearl" appearance in the nacreous layer inside shells.
- Once aragonite is removed from the living organism, it is less chemically stable than calcite. This instability prompts it to spontaneously recrystallize into calcite after burial.
- The transformation into calcite enhances the shell's longevity, increasing the chances of its preservation in the geological record and subsequent discovery by geologists.
- During recrystallization, while the crystal structure changes, the fundamental chemical composition of the mineral remains the same. The same atoms are simply rearranged into a more stable form.
- Recrystallization maintains the general shape of the fossil, but it may result in the loss of finer details as new crystals develop.
Internal Molds
- Definition: Internal molds are created when the internal space of an organism is filled with sediment that eventually hardens, preserving the internal shape of the organism.

- Example: Think of making a sandcastle by filling a bucket with wet sand, flipping it over, and lifting the bucket. The shape left in the sand resembles an internal mold.
- Occurrence in Geology: Internal molds are often found in organisms like bivalves, brachiopods, or snails with a single open chamber that allows sediment to fill the space. This method of preservation can reveal details such as muscle scars, but identifying mollusks may be difficult without the original shell.
Geopetal Structures:
- Formation: Small cavities within shells can retain sediment, forming pockets that may close with minerals over time, resulting in geopetal structures.
- Geological Significance: Geopetal structures serve as indicators of the 'up' direction during the deposition of sedimentary layers. This aids geologists in understanding the effects of tectonic processes.
Visual Clue Interpretation:
- Crystal Variations: Examining differences in infilled calcite crystals can help indicate the 'up' direction in a geological formation. Variations in crystal sizes can provide valuable information in this regard.
External Molds
An external mold is a type of fossil that captures the shape of an organism's outer surface. This happens when a fossil gets pressed into soft sediment. Over time, the original hard parts of the organism can be washed away by water currents, or they might dissolve after being buried and compacted.
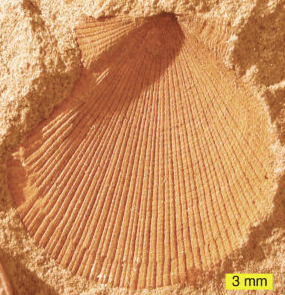
When scientists find external molds, they see a version of the organism's exterior, but it's not an exact copy. Instead, it shows negative relief, which means that raised areas on the mold represent indentations on the original fossil, and depressed areas represent raised parts.
- Fossil Trackways: These are a specific type of external mold and include famous dinosaur tracks.
- Creation by Hard Shells or Bones: Most external molds are formed by hard shells or bones, but there have been discoveries of external molds of dinosaur skin, indicating that soft tissues can also be preserved this way under the right conditions.
- Bioimmuration: This is another method of creating external molds, where other organisms encrust the exterior surfaces of an organism. For instance, if barnacles encrust a piece of wood and the wood later decays, an impression of the wood will be left on the barnacle. Bioimmuration can involve a succession of encrusting organisms, such as barnacles, corals, brachiopods, sponges, and others. This process provides valuable insights into past ecological situations when the original hard substrate is removed, leaving behind the encrusting organisms.
Casts
- Casts are 3D replicas of organisms, created by filling in molds with sediment to recreate the original shape.
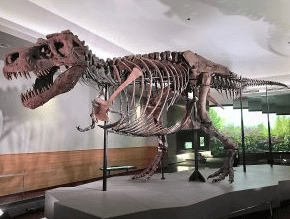
- The process begins with preserving an organism as an external mold, which can also apply to open burrows seen in trace fossils.
- Once the mold is made, it is filled with sediment, producing a detailed replica that mimics the original fossil's form.
- Although some intricate details might be lost during casting, these replicas still provide valuable information about the organism.
- Interestingly, many fossil skeletons displayed in museums are casts, not fakes.
- These casts are made from original fossils for various reasons: the originals can be extremely heavy, fragile, or require special preservation conditions.
- Casts also facilitate sharing specimens among museums and allow ongoing studies of the original fossils.
|
64 videos|135 docs
|
FAQs on Modes of Preservation of Fossils - Geology Optional for UPSC
| 1. What is permineralization and how does it occur in fossil preservation? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between carbonization and replacement in fossil preservation? |  |
| 3. How do internal molds and external molds contribute to our understanding of ancient organisms? |  |
| 4. What role does recrystallization play in the fossilization process? |  |
| 5. Why are casts considered important in the study of fossils? |  |




















