UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 1st March 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-II
Appointment of Lokpal chairperson
Subject: Polity and Governance

Why in News?
Recently, the former SC judge A.M. Khanwilkar has been appointed as Lokpal chairperson.
More details on the news:
- The Lokpal has been working without its regular Chief after Justice Pinaki Chandra Ghose completed his term on May 27, 2022. Justice Pradip Kumar Mohanty, a judicial member of the Lokpal, is currently the acting chairperson.
- Former High Court judges Lingappa Narayana Swamy, Sanjay Yadav and Ritu Raj Awasthi have been appointed as judicial members of the Lokpal.
About Lokpal:
- The Lokpal is established up under the Lokpal and Lokayuktas Act 2013 to investigate corruption allegations against public functionaries.
- Former Supreme Court Justice Pinaki Chandra Ghose assumed office as the first Lokpal chairperson in March 2019.
- India is a signatory to the United Nations Convention against Corruption. The establishment of Lokpal reflects the government’s commitment to clean and responsive governance by combating corruption.
Composition of Lokpal:
- The Lokpal consists of a chairperson and eight members – four judicial and four non-judicial.
- Appointed by the President of India for a 5-year term or until they reach 70 years of age, whichever comes first.
- Appointment Process: The President appoints the Chairperson and Members based on recommendations from a Selection Committee comprising the Prime Minister, Speaker of the House of the People, Leader of Opposition in the House of the People, Chief Justice of India or a nominated Supreme Court Judge, and an eminent jurist nominated by the President.
Lokpal’s Jurisdiction:
- The Lokpal investigates corruption allegations against current or former Prime Ministers, Union Ministers, Members of Parliament, and officials in Groups A, B, C, and D of the Union Government.
- It extends to chairpersons, members, officers, and directors of entities established by an Act of Parliament or funded by the Union or State government.
- The jurisdiction includes societies, trusts, or bodies receiving foreign contributions exceeding ₹10 lakh (approximately US$14,300 as of 2019)
Source: Hindustan Times
Cross-Voting in Rajya Sabha Elections
Subject: Polity and Governance
Why in News?
Recent Rajya Sabha elections in Uttar Pradesh, Himachal Pradesh, and Karnataka have been marred by instances of cross-voting, prompting concerns over the integrity of the electoral process.
Why discuss this?
- Understanding the legal framework governing Rajya Sabha elections and the implications of cross-voting is crucial in addressing these concerns and upholding democratic principles.
Rajya Sabha Elections and Cross-Voting
- Constitutional Provision: Article 80 of the Constitution mandates the indirect election of Rajya Sabha representatives by the elected members of State Legislative Assemblies.
- Historical Context: Rajya Sabha elections were traditionally uncontested until 1998, when cross-voting in Maharashtra marked a departure from this trend.
Legal Provisions and Precedents
- Open Ballot System: An amendment to the Representation of the People Act, 1951 in 2003 introduced open ballot voting for Rajya Sabha elections, aimed at curbing cross-voting.
- Tenth Schedule (Anti-Defection Law): Introduced in 1985, this Schedule disqualifies legislators who voluntarily give up party membership or vote against party instructions. However, it does not apply to Rajya Sabha elections.
- Court Rulings: The Supreme Court, in cases such as Kuldip Nayar versus Union of India (2006), upheld the open ballot system while clarifying that voting against party candidates in Rajya Sabha elections does not invoke disqualification under the Tenth Schedule.
Current Challenges and Legal Remedies
- Cross-Voting Impact: Instances of cross-voting undermine the democratic process and erode electoral integrity.
- Judicial Intervention: The Supreme Court may initiate suo moto proceedings or review existing judgments to address the issue of cross-voting.
- Disqualification Criteria: Voting against party lines in Rajya Sabha elections may be considered voluntary defection, warranting disqualification under the Tenth Schedule.
Way Forward
- Upholding the Intent: Instances of cross-voting undermine the transparency aimed at by the open ballot system, raising questions about the effectiveness of existing mechanisms.
- Judicial Intervention: The Supreme Court’s commitment to safeguarding democracy provides hope for addressing cross-voting issues through suo moto Public Interest Litigation or appeals against disqualification rulings.
- Revisiting Precedents: There is scope for the court to reinterpret its previous rulings in light of evolving circumstances, potentially aligning the consequences of cross-voting with the principles of the Tenth Schedule.
- Deterrent Measures: Clarifying that cross-voting may constitute grounds for disqualification under the Tenth Schedule could serve as a deterrent against future instances.
Conclusion
- Upholding the principles of free and fair elections requires addressing the challenge of cross-voting in Rajya Sabha elections.
- Judicial intervention and enforcement of existing laws are essential to safeguarding the integrity of the electoral process and preserving democratic norms.
Source: The Hindu
GS-III
Jacaranda Bloom
Subject: Environment

Why in News?
The early onset bloom of jacaranda set off alarm bells among residents and scientists in Mexico City.
About Jacaranda Bloom:
- It’s also known by its synonym Jacaranda acutifolia.
- It is a deciduous tree, Jacaranda mimosifolia comes from the Bignoniaceae family.
- Blue jacaranda is native of Brazil and North West Argentina.
- These are hardy trees that grow well in tropical climes, well-drained soil and plenty of sun to showcase their lavender touch.
- They are widely grown in warm parts of the world and in greenhouses for their showy blue or violet flowers and attractive, oppositely paired, compound leaves.
- Uses: In Brazil, its wood is used to make guitars. It has no edible use, its bark and root has medicinal advantages.
- It is also recommended as an alternative wood carving tree species, especially in Kenya.
- Ecological significance: They attract more hummingbirds and bees than many native trees, so a change in flowering could lead to a decrease in these populations.
- Concern: Some jacarandas began blooming in early January, when they normally awaken in spring.
Source: The Hindu
BioTRIG
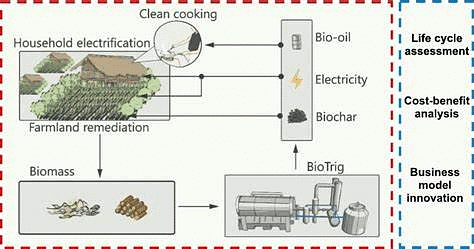
Why in News?
A recent study has claimed that BioTRIG, a new waste management technology could help rural Indians.
About BioTRIG:
- It is a new waste management technology based on the pyrolysis system.
- It works by sealing the waste inside an oxygen-free chamber and heating it above 400 degrees Celsius. Useful chemicals are produced in the process.
- In the study, the researchers outlined that three products of pyrolysis — bio-oil, syngas and biochar fertiliser — could help rural Indians live healthier and greener lives.
- Significance
- The syngas and bio-oil facilitate heat and power the pyrolysis system in future cycles and surplus electricity is utilized to power local homes and businesses.
- The clean-burning bio-oil to replace dirty cooking fuels in homes and using biochar to store carbon, while improving soil fertility.
- Computer simulations showed that the BioTRIG system could also be effective in real-world applications.
- It could help reduce greenhouse gas emissions from communities by nearly 350 kg of CO2-eq per capita per annum.
- It could help rural Indians cut indoor air pollution, improve soil health, and generate clean power
What is Pyrolysis?
- It is a kind of chemical recycling that turns leftover organic materials into their component molecules.
- It works by sealing the waste inside an oxygen-free chamber and heating it to more than 400 degrees Celsius, producing useful chemicals in the process.
Source: Down to Earth
International Big Cat Alliance
Subject: Environment

Why in News?
The Union Cabinet formally announced the establishment of International Big Cat Alliance (IBCA) with one-time budgetary support of Rs 150 crore from the Central Government until 2028.
About International Big Cat Alliance:
- It is an initiative launched by Prime Minister of India in April 2023 in Mysuru commemorating the 50th anniversary of Project Tiger.
- The objective of the IBCA is to ensure cooperation for the conservation of seven big cats: lion, tiger, leopard, cheetah, snow leopard, jaguar, and puma. Five of these cats, apart from jaguar and puma, are found in India.
- Membership: It is open to 97 'range' countries, which contain the natural habitat of these big cats, as well as other interested nations, international organizations, etc.
- It aims for mutual cooperation among countries for mutual benefit in furthering the conservation agenda.
- It would have a multipronged approach in broad basing and establishing linkages manifold in several areas and help in knowledge sharing, capacity building, networking, advocacy, finance and resources support, research and technical support, education and awareness.
- Governance Structure:
- A General Assembly consisting of all member countries.
- A Council of at least seven but not more than 15 member countries elected by the General Assembly for a term of 5 years, and a Secretariat.
- Upon the recommendation of the Council, the General Assembly will appoint the IBCA Secretary General for a specific term.
- Funding: It has secured Government of India's initial support of Rs. 150 crore for five years (2023-24 to 2027-28).
Source: PIB
India’s Leopard Population rises to 13,874
Subject: Environment

Why in News?
The Union Minister for Environment, Forest, and Climate Change, released the report on the Status of Leopards in India at New Delhi.
About the Fifth Cycle of Leopards Estimation
- The fifth cycle leopard population estimation was conducted by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) and Wildlife Institute of India (WII), in collaboration with State Forest Departments.
- It covered 18 States of India, and focused on about 70% of the animals’ expected habitat.
- The estimation focused on forested habitats within 18 tiger states, covering major tiger conservation landscapes. Non-forested and high Himalayan regions were excluded.
- A comprehensive foot survey spanning 6,41,449 km and camera traps at 32,803 locations resulted in 85,488 photo-captures of leopards, providing valuable insights into their distribution and abundance.
Key Findings
- Population Estimate: India’s leopard population is estimated at 13,874 individuals, signifying stability compared to the 2018 estimate. Notably, this estimation covers 70% of leopard habitat, excluding areas like the Himalayas and semi-arid regions.
- Regional Trends: While Central India witnesses a stable or slightly growing population, regions like the Shivalik hills and Gangetic plains experience a decline. Overall, there’s a 1.08% per annum growth in sampled areas.
- State-wise Distribution: Madhya Pradesh houses the largest population of leopards in the country – 3907 (2018: 3421), followed by Maharashtra (2022: 1985; 2018: 1,690), Karnataka (2022: 1,879 ; 2018: 1,783) and Tamil Nadu (2022: 1,070; 2018: 868).
- Habitats: Tiger Reserves or sites with highest leopard population are, Nagarajunasagar Srisailam (AP), followed by Panna (MP), and Satpura (AP).
- Declining Trends: While Uttarakhand reported a 22% decline in the big cat numbers — reportedly due to poaching and man-animal conflict, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam and West Bengal saw a collective 150% rise to 349 animals.
Source: The Hindu
Context Windows in AI Conversations
Subject: Science and Technology

Why in News?
In conversations with AI chatbots like ChatGPT, the text the AI can “see” or “read” at any given moment is determined by its context window.
- The context window, measured in tokens, defines the amount of conversation the AI can process and respond to during a chat session.
What are Context Windows?
- Tokens: Basic units of data processed by AI models, tokens represent words, parts of words, or characters.
- Tokenisation: The process of converting text into vectors (format suitable) for input into machine learning models.
- Example: For English text, one token is roughly equivalent to four characters. Thus, a context window of 32,000 tokens translates to around 128,000 characters.
Importance of Context Windows
- Recall and Understanding: Context windows enable AI models to recall information from earlier in the conversation and understand contextual nuances.
- Generating Responses: They help AI models generate responses that are contextually relevant and human-like in nature.
Functioning of Context Windows
- Sliding Window Approach: Context windows work by sliding a window over the input text, focusing on one word at a time.
- Scope of Information: The size of the context window determines the scope of contextual information assimilated by the AI system.
Context Window Sizes
- Advancements: Recent AI models like GPT-4 Turbo and Google’s Gemini 1.5 Pro boast context window sizes of up to 128K tokens and 1 million tokens, respectively.
- Benefits: Larger context windows allow models to reference more information, maintain coherence in longer passages, and generate contextually rich responses.
Challenges and Considerations
- Computational Power: Larger context windows require significant computational power during training and inference, leading to higher hardware costs and energy consumption.
- Repetition and Contradiction: AI models with large context windows may encounter issues such as repeating or contradicting themselves.
- Accessibility: The high resource requirements of large context windows may limit access to advanced AI capabilities to large corporations with substantial infrastructure investments.
Conclusion
- Context windows play a vital role in enabling AI chatbots to engage in meaningful conversations by recalling context and generating relevant responses.
- While larger context windows offer benefits in terms of performance and response quality, they also pose challenges related to computational resources and environmental sustainability.
- Balancing these factors is essential for the responsible development and deployment of AI technologies.
Source: Business Standard
|
55 videos|5389 docs|1141 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs- 1st March 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What is the significance of the appointment of Lokpal chairperson? |  |
| 2. What is cross-voting in Rajya Sabha Elections? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of the Jacaranda Bloom? |  |
| 4. What is BioTRIG and its relevance in the field of biology? |  |
| 5. How has India's Leopard Population increased to 13,874 and what are the conservation efforts being taken? |  |
















