Difference Between Review and Revision | Civil Law for Judiciary Exams PDF Download
Overview of Legal Procedures
- When a party is discontent with a court decree, they can appeal to a higher judicial authority for redress.
- An appeal entails a comprehensive re-examination of the dispute by the higher court.
- Exceptions exist for situations involving technical or procedural errors, where seeking a fresh legal proceeding is unnecessary.
Key Concepts: Review and Revision
- Review and Revision are provisions under Sections 114 and 115 of the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908.
- Review allows for a reevaluation of a case within the same court, offering a more accessible means of correcting errors.
- Revision provides a mechanism to rectify decisions based on jurisdictional errors or grounds of injustice.
Understanding Review
- Review permits a court to reconsider its own decision.
- It is typically invoked in cases where there is an apparent error that needs correction.
- For example, if a judgment overlooks crucial evidence, a review can be sought to rectify this oversight.
Explaining Revision
- Revision is a process where a higher court can examine the legality of a decision.
- It is usually invoked to correct jurisdictional errors or decisions that result in manifest injustice.
- For instance, if a lower court exceeded its jurisdiction in a ruling, revision can be sought to remedy this issue.
Significance of Review and Revision
- These provisions ensure that legal errors can be rectified without the need for completely new legal actions.
- They promote fairness and provide avenues for correcting mistakes within the existing legal framework.
Judicial Review under Section 114 of the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908
- Judicial Review Overview: Judicial review, as defined in Section 114 of the Code of Civil Procedure (CPC), serves as a significant process allowing a case to be reexamined by the same court and judge who issued the original decision.
- Review Application: After a judgment is pronounced, the court typically concludes its involvement in the case. However, the option for a review application provides an avenue for parties to contest the decision within the same court.
- Review Meaning: In simple terms, 'review' signifies a reconsideration or reevaluation. Section 114 empowers the court to revisit its judgment, rectifying any errors present in the decision.
Objective of Review
- Purpose of Review: The review process in the legal system is designed to rectify and prevent miscarriages of justice by allowing the court to reconsider its prior decisions.
Grounds for Review
- New Matter or Evidence: If new and substantial evidence emerges after the judgment, the court can review its decision based on Order 47, Rule 1.
- Mistake or Error: Review is permissible when errors, whether factual or legal, are apparent on the record, as clarified by the Supreme Court in Thungabhadra Industries Limited v. Government of AP.
- Sufficient Reason: Any reason based on the grounds specified in the rule, such as inaccuracies in the judgment or failure to consider critical issues, can warrant a review to prevent injustice.
Review: Not an Inherent Right
- Review Authority: The power to review is not inherent but granted by law to rectify substantial errors through the review process.
Limitation Period for Review
- Filing Deadline: Parties have thirty days from the date of the judgment to submit a review application, emphasizing the importance of timely recourse within the legal framework.
Revision under Section 115 of CPC 1908
Overview of Revision under Section 115
- Section 115 of the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908, grants the High Court the power of revision.
- Revision involves a thorough review and re-examination of a matter to ensure accuracy and correctness.
Objectives of Revision
- The main goal of Section 115 is to prevent arbitrary, illegal, or irregular actions by lower courts.
- It allows the High Court to ensure that lower courts operate within the boundaries of the law and contribute to justice.
Scope of Revisional Authority
- The High Court can rectify jurisdictional errors made by lower courts.
- Parties can seek redress for non-appealable orders through revision.
- The High Court can initiate revision proceedings on its own without a formal application.
Limitation Period and Grounds for Revision
- Revision applications must be filed within 90 days, primarily focusing on jurisdictional issues.
Key Highlights of Section 115
- Referral to High Court: Lower courts can seek guidance from the High Court on points of law.
- Review vs. Revision: Review corrects errors by the same court, while revision involves the High Court correcting jurisdictional errors.
- Role of High Court: Section 115 empowers the High Court to maintain justice by rectifying jurisdictional errors.
In essence, Section 115 of the CPC 1908 empowers the High Court with revisional jurisdiction, allowing it to correct jurisdictional errors made by subordinate courts. This provision aims to ensure the proper administration of justice by preventing arbitrary actions and ensuring that legal proceedings align with the law. Moreover, it provides an avenue for parties to rectify non-appealable orders within a limited time frame. The High Court can intervene suo motu, and its role includes overseeing lower courts to uphold fairness and integrity in legal processes.
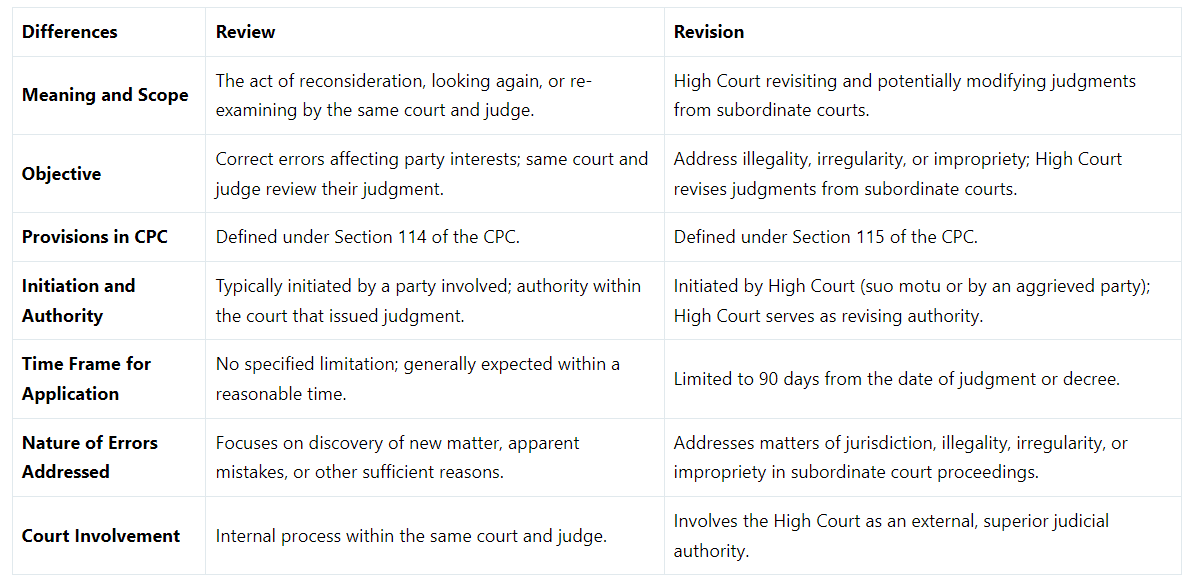
Key Differences Between Review and Revision
1. Meaning and Scope
- Review involves reconsidering or re-examining a legal case by the same court and judge to rectify errors or address overlooked aspects.
- Revision is a broader concept where the High Court revisits and potentially modifies judgments issued by subordinate courts.
2. Objective
- Review aims to correct errors in the court's order that could impact a party's interests.
- Revision addresses instances of illegality, irregularity, or impropriety in subordinate court proceedings.
3. Provisions in CPC
- Review is defined in Section 114 of the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908.
- Revision is governed by Section 115 of the CPC, outlining the High Court's authority to revise judgments.
4. Initiation and Authority
- Review is typically initiated by a party involved in the case, while revision can be initiated by the High Court itself or an aggrieved party.
- The authority for review lies within the same court that issued the original judgment, whereas the High Court serves as the revising authority in revision cases.
5. Time Frame for Application
- No specific limitation period for filing a review application, but it should generally be done within a reasonable time.
- Revision application must be filed within 90 days from the date of the judgment or decree in question.
6. Nature of Errors Addressed
- Review focuses on correcting errors within the original court's judgment, such as new evidence or mistakes on record.
- Revision primarily deals with matters of jurisdiction, addressing illegality, irregularity, or impropriety in subordinate court proceedings.
7. Court Involvement
- Review involves the same court and judge who passed the original decree in the re-examination process.
- Revision brings the High Court as an external, superior judicial authority into the process, offering a fresh perspective on the case.
Table highlighting the key differences between review and revision:
|
363 docs|256 tests
|
FAQs on Difference Between Review and Revision - Civil Law for Judiciary Exams
| 1. What is the Code of Civil Procedure and why is it important in legal procedures? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of review and revision in the legal system? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between judicial review and revision under the Code of Civil Procedure? |  |
| 4. What are some key differences between review and revision under the Code of Civil Procedure? |  |
| 5. What are some frequently asked questions related to review and revision in judiciary exams? |  |





















