Relevancy and Admissibility | Civil Law for Judiciary Exams PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Relevancy |

|
| Admissibility |

|
| Distinguishing Between Relevancy and Admissibility |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Relevancy
Relevancy is a crucial concept in legal evidence, denoting the importance and connection of specific information to the issues under consideration in a legal case. It essentially means that relevant evidence enhances the probability of a fact's existence compared to the absence of that evidence. The Indian Evidence Act, while not explicitly defining relevancy, details in Sections 5 to 55 the different ways in which facts can be interlinked, forming the basis for determining relevance.
Significance of Relevancy
- Relevancy serves as a vital bridge between evidence presented and the facts requiring proof.
- It establishes a correlation between various facts as stipulated in the Evidence Act.
Principles of Relevancy
- Nothing should be admitted unless logically verified in relation to the matters needing proof.
- Verified and probative evidence should be admitted unless legally excluded.
Exclusion of Relevant Evidence
- A court may exclude relevant evidence if its probative value is outweighed by risks like unfair bias or confusion.
- This exclusion ensures fairness and a just determination of facts.
Indian Evidence Act Framework
- Sections 5 to 55 of the Indian Evidence Act offer a detailed framework for determining relevancy between facts.
- It specifies how facts can be associated and deems a fact irrelevant if not connected as per the Act.
Relevancy, as per the Indian Evidence Act, isn't a subjective judgment but is rooted in legally defined ways in which facts can be linked in a legal context.
Admissibility
- Admissibility refers to the court's acceptance of relevant evidence, based on criteria set by the legal system.
- The judge ultimately decides whether evidence is admissible, as specified in Section 136 of the Evidence Act.
- Before presenting evidence, the judge can question its relevance and alignment with legal requirements.
- Evidence is admitted if the judge is convinced of its relevance under Sections 6 to 55 of the Evidence Act.
- The key aspects of admissibility include the judge's authority in determining relevancy and admissibility.
- If someone wants to prove a fact, the judge may ask for an explanation of its relevance.
- The judge will only admit the demonstrated fact if satisfied with the explanation, ensuring it aligns with legal requirements.
Distinguishing Between Relevancy and Admissibility
Definition of Relevancy and Admissibility
- Relevance: Refers to the logical connection between facts, showing how one set of facts may affect the existence or non-existence of others. It underscores the inherent relationship between facts.
- Admissibility: Relates to the status of facts deemed legally significant under the Indian Evidence Act, determining evidence eligibility in court based on legal rules rather than logical connections.
Basis of Relevancy and Admissibility
- Relevance: Grounded in logic and human experience, highlighting the natural association between facts and how certain facts can make others more or less likely.
- Admissibility: Rooted in legal principles rather than inherent connections between facts, focusing on conformity with legal rules specified in the Evidence Act.
Legal Framework
- Relevance: Detailed under Sections 5 to 55 of the Indian Evidence Act, outlining ways in which facts may be linked to establish relevance.
- Admissibility: Primarily discussed in Section 56 of the Indian Evidence Act, defining criteria for evidence acceptance in court.
Emphasis
- Relevance: Focuses on identifying essential facts for court consideration, emphasizing the logical link between facts and their significance in proving a case.
- Admissibility: Concentrates on distinguishing admissible from inadmissible facts based on legal criteria rather than intrinsic relevance.
Role in Legal Proceedings
- Relevance: Acts as a guiding principle for courts, assisting in determining evidence that is logically connected to the issues being addressed.
- Admissibility: Serves as an outcome, verifying whether evidence meets legal standards for acceptance, as outlined in the Evidence Act.
Nature of Relevancy and Admissibility
- Relevance: Functions as a causative factor, establishing the logical connection between facts and their impact on the case.
- Admissibility: Acts as an effect resulting from facts meeting legal requirements, indicating evidence suitability for consideration.
Judicial Discretion
- Relevance: Courts have flexibility in determining the relevance of facts, offering room for interpretation based on case specifics.
- Admissibility: In contrast, courts have limited discretion in admissibility, as it is governed by adherence to legal regulations with less room for subjective judgment.
Relation to Establishing Proof
- Relevance: Essential in constructing a case and influencing legal outcomes by bridging presented evidence with required facts.
- Admissibility: Indicates that while admissible facts can vary in relevance, legally relevant facts are admissible, representing a subset of evidence relevant in a legal context.
Here’s a table summarising the differences between relevancy and admissibility: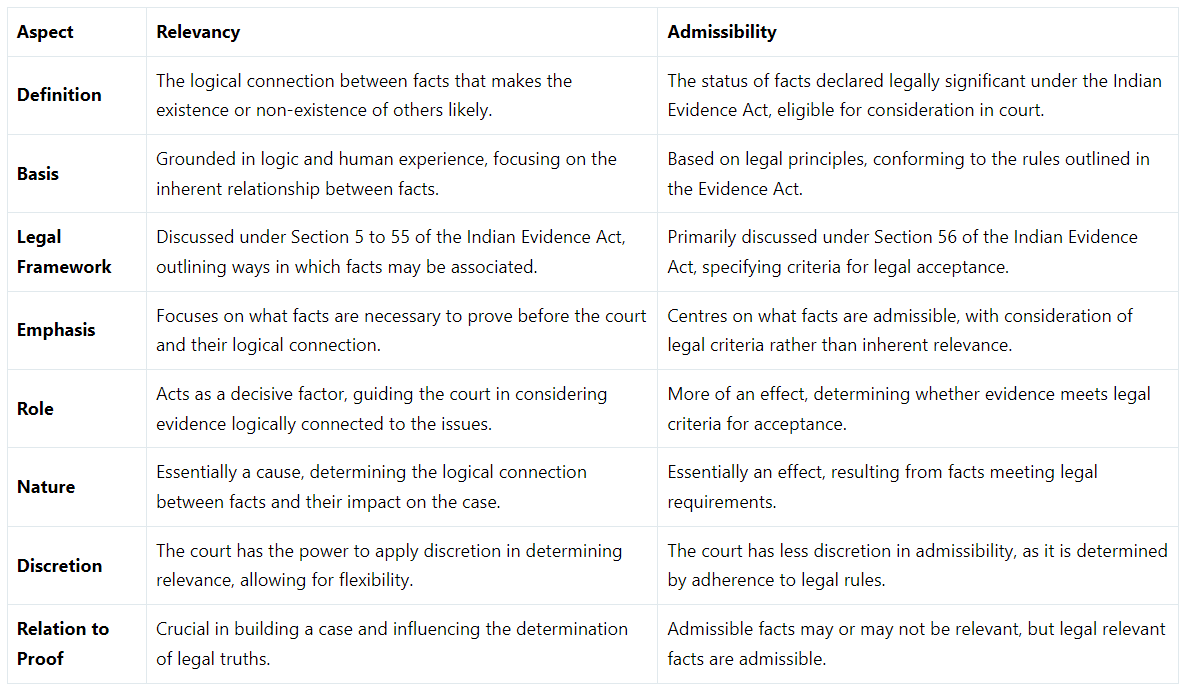
Conclusion
In the legal landscape, the concepts of relevancy and admissibility are closely intertwined, forming the foundation of the approach to evidence. Relevancy serves to establish the connection between facts, highlighting their significance, while admissibility safeguards the court process by ensuring that only relevant evidence meeting specific criteria is considered. This meticulous interplay between relevancy and admissibility is crucial for upholding the integrity and fairness of legal proceedings. It acts as a safeguard, guiding the court in its pursuit of justice and the determination of legal truths by allowing only pertinent and permissible evidence to be presented and considered.
|
363 docs|256 tests
|















