Judiciary Exams Exam > Judiciary Exams Notes > Important Acts and Laws for Judiciary Exams > Difference Between Flexible and Rigid Constitutions
Difference Between Flexible and Rigid Constitutions | Important Acts and Laws for Judiciary Exams PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Meaning of Flexible and Rigid Constitutions |

|
| Key Differences Between Flexible and Rigid Constitutions |

|
| Nature of Indian Constitution: Rigid and Flexible |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Introduction
Constitutions serve as the fundamental framework for governance in any nation, profoundly influencing its legal and political landscape. Among the prevailing models, flexible and rigid constitutions stand out as distinct approaches, each with its own implications for how a country's legal system responds to societal shifts while maintaining stability.
This analysis will examine the disparities between flexible and rigid constitutions across essential dimensions.
Meaning of Flexible and Rigid Constitutions
- Flexible and rigid constitutions represent contrasting approaches to constitutional design. A flexible constitution is characterized by its adaptable and easily modifiable framework, enabling adjustments to societal changes with relative ease. This type of constitution often blurs the distinction between ordinary laws and constitutional laws, allowing for swift modifications.
- Conversely, a rigid constitution features a more stringent amendment process, requiring specialized procedures. It prioritizes stability by making amendments complex and deliberate, thereby protecting core principles.
- Rigidity ensures the constitution's resilience against impulsive changes, providing a stable foundation. Both models have their advantages, with flexibility catering to dynamic societies and rigidity serving as a robust safeguard against hasty alterations.
Question for Difference Between Flexible and Rigid Constitutions
Try yourself:
What is a flexible constitution characterized by?View Solution
Key Differences Between Flexible and Rigid Constitutions
Amendment Procedures
- Flexible constitutions allow for easy amendments, similar to altering ordinary laws, enabling swift adjustments in response to societal needs or public opinion changes.
- Rigid constitutions resist easy amendments, requiring complex procedures to preserve their sanctity and make amendments challenging.
Adjustability to Changing Needs
- Flexible constitutions can adapt to evolving societal needs without being bound by ordinary laws, ideal for developing countries seeking progress.
- Rigid constitutions are less adaptable, emphasizing stability over immediate adaptability due to their superior status over ordinary law.
Symbolism and Efficiency
- Flexible constitutions are seen as advantageous for developing nations, symbolizing adaptability and growth with societal maturity.
- Rigid constitutions are perceived as symbols of national efficiency, embodying a sense of reverence and commitment as sacred documents.
Reflection of Public Opinion
- Flexible constitutions can reflect changing public opinion, ensuring the document remains dynamic and capable of addressing contemporary challenges.
- Rigid constitutions may not necessarily reflect public opinion changes, often representing the views of their framers and prioritizing stability.
Growth and Expansion
- Flexible constitutions metaphorically grow with societal maturity, incorporating changes and adapting to evolving norms.
- Rigid constitutions do not metaphorically grow, emphasizing permanence and unchanging principles as sacred documents.
 |
Download the notes
Difference Between Flexible and Rigid Constitutions
|
Download as PDF |
Download as PDF
Assumption of Perfection
- Flexible constitutions acknowledge imperfection and the need for change, while rigid constitutions assume perfection and prioritize stability.
Adaptability in Federal Systems
- Flexible constitutions are more suitable for federal systems, accommodating adjustments to the rights of constituent units and fostering cooperation.
- Rigid constitutions provide stability and integration in federal setups, preventing violations of constituent units' jurisdictions.
Protection of Minority Rights
- Flexible constitutions, with their potential for frequent changes, may overlook safeguarding minority rights effectively.
- Rigid constitutions effectively protect minority rights by resisting frequent amendments, maintaining a stable framework for fundamental rights.
Here is a table showing the difference between flexible and rigid constitutions are: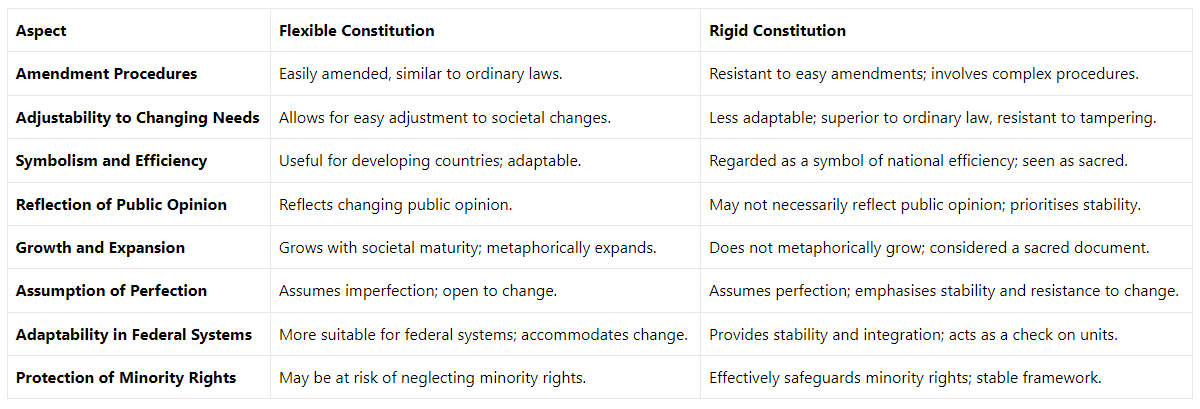
Nature of Indian Constitution: Rigid and Flexible
- The Indian Constitution possesses a distinctive blend of rigidity and flexibility, showcasing a unique structural design.
- While certain segments, notably concerning fundamental rights, demonstrate rigidity by necessitating a specialized amendment process, the Constitution also embodies adaptability.
- The amendment procedure, although specific in nature, allows for adjustments to suit the evolving societal requirements.
- This dual characteristic mirrors a well-thought balance, recognizing the importance of upholding fundamental principles while accommodating the changing needs of a dynamic society.
- The Indian Constitution's amalgamation of rigid and flexible components underscores its robustness and capacity to adjust over the nation's historical journey.
Conclusion
- The decision between a flexible and rigid constitution goes beyond merely establishing a legal framework; it requires a deep understanding of a nation's developmental phase, political stability, and anticipated societal shifts. Each element, including procedures for amendments, adaptability, and symbolic significance, contributes to the overarching narrative of how a constitution operates within a specific society.
- Flexibility might be indispensable for nations undergoing rapid transitions, while stability and permanence could hold equal importance for others. An in-depth examination of these elements enhances our understanding of constitutional design, revealing the delicate equilibrium between adaptability and stability in the governance of diverse nations.
Question for Difference Between Flexible and Rigid Constitutions
Try yourself:What is a key difference between flexible and rigid constitutions?
View Solution
The document Difference Between Flexible and Rigid Constitutions | Important Acts and Laws for Judiciary Exams is a part of the Judiciary Exams Course Important Acts and Laws for Judiciary Exams.
All you need of Judiciary Exams at this link: Judiciary Exams
|
207 docs|219 tests
|
FAQs on Difference Between Flexible and Rigid Constitutions - Important Acts and Laws for Judiciary Exams
| 1. What is the nature of the Indian Constitution - rigid or flexible? |  |
| 2. What are the key differences between flexible and rigid constitutions? |  |
Ans. Flexible constitutions can be easily amended and changed, while rigid constitutions have a more difficult amendment process.
Related Searches






















