Who are Cabinet Ministers | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Cabinet’s Function |

|
| Who are the Council of Ministers |

|
| Regulation |

|
| Council of Ministers in State Governments |

|
| Functions of Council of Minister |

|
| Conclusion |

|
Introduction
The Cabinet is the highest decision-making body in India's political and administrative structure. Comprising key ministers who hold crucial portfolios such as defense, home affairs, and education, the Cabinet plays a central role in formulating policies, managing national issues, and ensuring governance runs smoothly. With regular meetings convened to deliberate on critical matters, the Cabinet is a constitutional body that upholds collective responsibility to the public. Its decisions, once made, are binding on all ministers, reinforcing the unified functioning of the government.
Cabinet’s Function
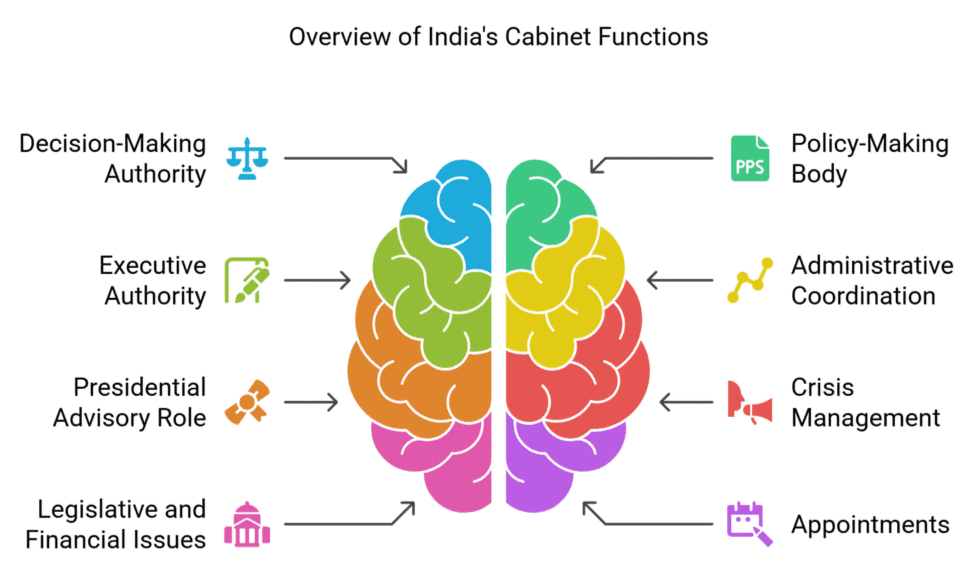
The Cabinet holds several vital functions within India's governance system:
- It is the highest decision-making authority in our political and administrative system.
- It serves as the main policy-making body of the Central Government.
- It acts as the supreme executive authority of the central government.
- The Cabinet is the chief coordinator of the central administration.
- It acts as a consultative body to the president, with its recommendations being legally binding on him.
- The Cabinet is responsible for managing emergency situations and acting as the chief crisis manager.
- It addresses major legislative and financial issues.
- The Cabinet has the authority to appoint constitutional authorities and senior officials within the secretariat.
- It plays a crucial role in determining and managing India’s foreign policies and affairs.
Who are the Council of Ministers
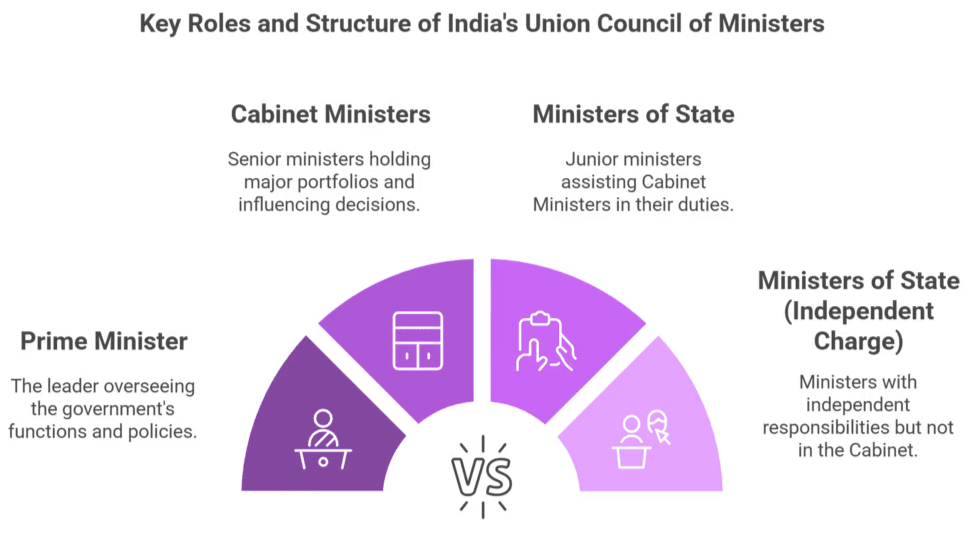
The Union Council of Ministers is an integral part of India's governance structure. It consists of the following components:
- The Prime Minister: The leader of the Council, overseeing the functioning of the government.
- Cabinet Ministers: Senior ministers who hold major portfolios and play a key role in decision-making.
- Ministers of State: Junior ministers responsible for assisting Cabinet Ministers in their work.
- Ministers of State (Independent Charge): Ministers who hold independent responsibilities but are not part of the Cabinet.
The Union Cabinet is a smaller subset of the Council and is responsible for the country’s primary decision-making.
As per Article 352, Union Cabinet members must propose any presidential proclamation of emergency in writing to the President. Furthermore, the Indian Constitution specifies that the total number of ministers in the Council must not exceed 15% of the Lok Sabha's total membership. Ministers must be members of parliament, and failure to maintain membership for six consecutive months leads to automatic revocation of ministerial positions.
Regulation
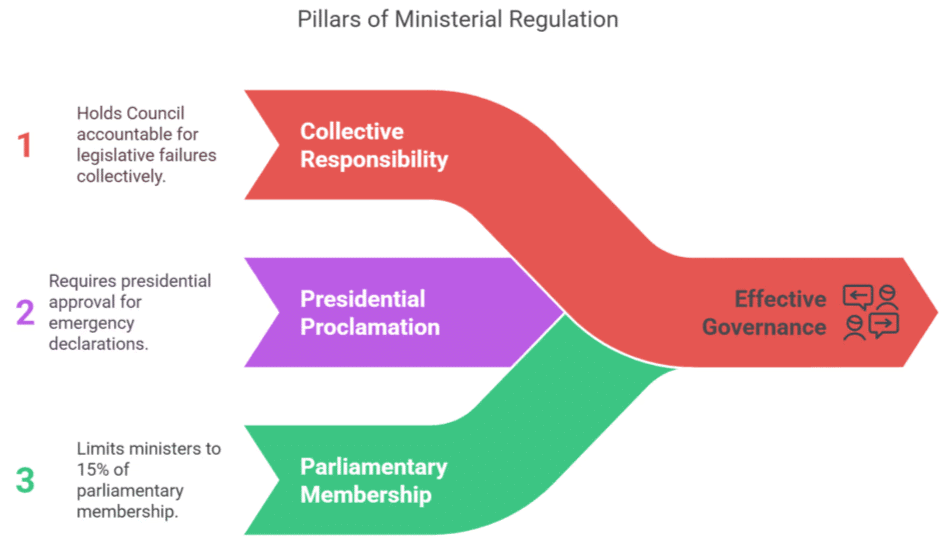
The Council of Ministers operates under the principle of collective responsibility to the Lok Sabha, India's lower house of Parliament. The key regulations governing their actions include:
- Collective Responsibility: If the Lok Sabha rejects a bill introduced by a minister, the entire Council of Ministers is held responsible, not just the minister. When the Lok Sabha loses confidence in the government, the entire Council must resign.
- Presidential Proclamation: Under Article 352, Union Cabinet members must submit a written proposal to the President for any emergency proclamation.
- Parliamentary Membership: The total number of ministers in the Council must not exceed 15% of the Lok Sabha’s total membership. Ministers are required to be members of parliament, and failure to maintain this membership results in the loss of their position.
Council of Ministers in State Governments
In addition to the Union Cabinet, each state in India is also governed by its own Council of Ministers, as outlined in Articles 163, 164, and 167. These councils follow similar rules and procedures as the Union Council of Ministers. The Supreme Court of India, under Article 142, exercised its powers in March 2020 to remove a minister in the state of Manipur, marking a significant legal intervention.
Functions of Council of Minister
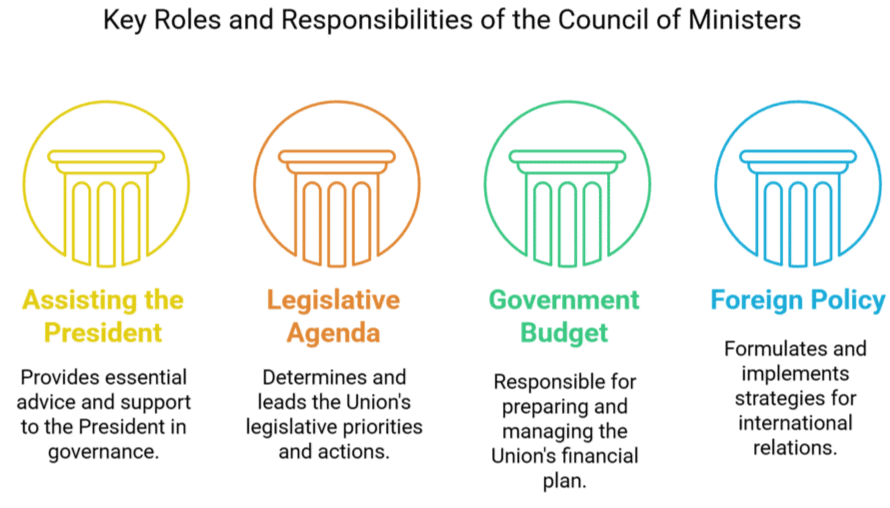
The Council of Ministers performs several key roles within the Indian government, including:
- Assisting and Advising the President: The Council helps the President in executing his duties by advising on various matters of national importance.
- Legislative Agenda: It plays a crucial role in determining the Union’s legislative agenda and takes the lead in introducing and passing government legislation.
- Union Government Budget: The Council is responsible for preparing the Union Government’s budget and making grant requests.
- Foreign Policy Formulation: It is in charge of formulating and implementing India’s foreign policy. The President’s emergency powers are also largely exercised by the Ministers.
Conclusion
The Prime Minister leads the Council of Ministers and helps the President carry out important duties. The Cabinet, made up of senior ministers, is responsible for making and implementing policies in India, both within the country and internationally. The Council of Ministers manages key issues like emergencies, laws, and finances. All ministers are accountable to the Lok Sabha, ensuring the government remains responsible to the people. The Cabinet's organized way of working helps India run smoothly and protects the country's interests.
|
164 videos|800 docs|1158 tests
|
FAQs on Who are Cabinet Ministers - General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce
| 1. What is the role of the Cabinet in a government? |  |
| 2. Who are the members of the Council of Ministers? |  |
| 3. What are the main functions of the Council of Ministers? |  |
| 4. How does the Council of Ministers operate in state governments? |  |
| 5. What distinguishes Cabinet Ministers from other ministers? |  |















