Environment and Ecology: February 2024 Current Affairs | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
UN World Restoration Flagships

Overview
The United Nations has designated seven initiatives across Africa, Latin America, the Mediterranean, and Southeast Asia as the World Restoration Flagships of the intergovernmental organization.
About UN World Restoration Flagships
The World Restoration Flagship is a component of the UN Decade on Ecosystem Restoration, spearheaded by the UN Environment Programme (UNEP) and the Food and Agriculture Organization. Its objective is to prevent, halt, and reverse ecosystem degradation worldwide. Initiatives awarded by the UNEP and FAO become eligible for technical and financial assistance from the UN.
These awards recognize initiatives that contribute to global commitments to restore one billion hectares of land. The seven recognized initiatives include:
- Restoring Mediterranean Forests Initiative: This initiative involves Lebanon, Morocco, Tunisia, and Türkiye. It employs a unique approach that has safeguarded and restored natural habitats and vulnerable ecosystems, resulting in approximately two million hectares of restored forests since 2017.
- Living Indus Initiative: Following the devastating 2022 climate change-induced floods, this initiative gained approval from the Pakistan parliament. Its official launch occurred at the 27th Conference of Parties to the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change in Sharm el-Sheikh. It grants the Indus River the status of a living entity with rights, serving as a model for river protection efforts globally.
- Acción Andina Social Movement: Led by Peruvian conservation non-profit ECOAN, this movement aims to protect and restore one million hectares of forest area.
- Sri Lanka Mangrove Regeneration Initiative: A science-driven program co-led by local communities, focusing on restoring the natural balance in the ecosystem.
- Terai Arc Landscape Initiative: This initiative seeks to restore forests in critical corridors of the Terai Arc Landscape, involving collaboration with local communities acting as citizen scientists, anti-poaching units, and forest guards. Notably, it has contributed to the increase of the tiger population in the shared landscape of India and Nepal to 1,174.
- Regreening Africa’s Agriculture: Expected to benefit over 600,000 households.
- Growing Forests in Africa's Drylands Initiative: Aiming to expand from 41,000 restored hectares today to 229,000 hectares by 2030.
Climate Change and Wheat Blast

Wheat Blast (WB)
- It is a fungal disease caused by the pathogen Magnaporthe oryzae pathotype Triticum (MoT).
- It was first identified in Brazil in 1985.
- It is a fast-acting and devastating disease that poses a significant threat to wheat crops, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions.
Symptoms
- Progressive bleaching of heads, where infected spikes show a silvery appearance with a green canopy, turning partially or fully bleached in severe cases.
- Infected plants exhibit discoloured stems and leaves with dark brown lesions and visible dark grey fungal spores.
How does it spread?
- It spreads via infected seeds, posing a threat to new crops as the fungus can persist within them.
- Airborne spores are key in wheat blast transmission, traveling long distances and swiftly infecting nearby wheat fields upon release.
- Infected crop residues containing the fungus aid in disease spread by surviving and infecting new plants under favorable conditions.
- Warmer temperatures and prolonged leaf moisture aid wheat blast pathogen spread, fostering disease growth.
- Also, international wheat trade has been a cause in some countries like Bangladesh and Zambia.
Implications
- It leads to significant yield reductions, with projections indicating a potential 13% global wheat production decrease.
- Vulnerable regions like South America and Africa could face up to 75% of their wheat acreage at risk by 2050.
- WB can incur significant economic losses in certain countries.
- Vulnerable wheat-growing regions in Bangladesh, India, and Pakistan could incur potential losses of 886 thousand metric tons of wheat production, amounting to USD 132 million annually.
- E.g. During the 2016 outbreak, an estimated total wheat production loss of approximately 8,205 tons, worth USD 2.1 million, was recorded.
- Vulnerable wheat-growing regions in Bangladesh, India, and Pakistan could incur potential losses of 886 thousand metric tons of wheat production, amounting to USD 132 million annually.
- E.g. During the 2016 outbreak, an estimated total wheat production loss of approximately 8,205 tons, worth USD 2.1 million, was recorded.
- The spread of WB poses a threat to global food security, particularly in regions experiencing growing wheat consumption.
Way Forward
- Develop and promote wheat varieties resistant to WB.
- wheat varieties resistant to WB
- Combine race non-specific resistance genes to enhance durability.
- race non-specific resistance
- Fungicide spray applications can help manage WB.
- Fungicide spray applications
- Strictly regulate the movement of contaminated plant material and farm equipment.
- Implement practices to break the disease cycle.
- break the disease cycle
- Properly manage crop residues to reduce disease transmission.
- manage crop residues
- Use early warning systems to predict disease outbreaks.
- Investigate biological control agents to suppress WB (Beneficial microorganisms or natural enemies can play a role).
Cameroon Adopts Nagoya Protocol

Cameroon’s recent adoption of the Nagoya Protocol marks a significant step towards harnessing its rich biodiversity for sustainable development.
Cameroon’s Biodiversity Wealth
- Biodiversity Hotspot: Cameroon hosts approximately 11,000 species, offering immense genetic resources for research and development.
- Traditional Knowledge: Indigenous communities possess invaluable traditional knowledge associated with biodiversity, contributing to bioprospecting (search for useful products derived from bioresources including plants, microorganisms, animals, etc.).
- Bioprospecting Potential: Bioprospecting projects, such as those focusing on species like Irvingia wombulu, present opportunities for sustainable resource utilization.
About Nagoya Protocol
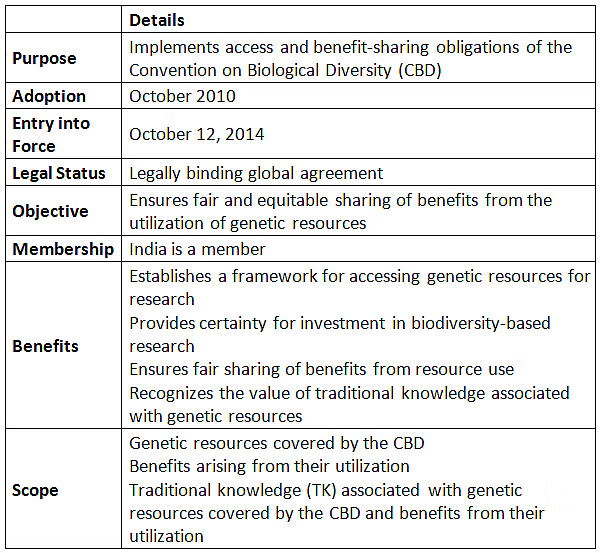
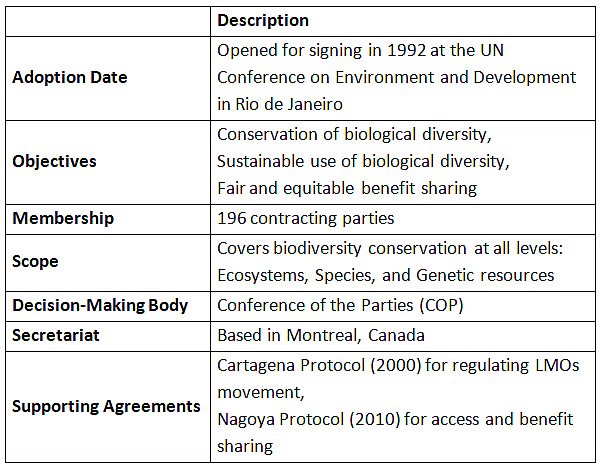
Key Facts about Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)
World’s First Melanistic Tiger Safari in Odisha
 Context
Context
The Odisha Government is embarking on the establishment of a melanistic tiger safari. This initiative will be located near Baripada, the administrative hub of Mayurbhanj district, encompassing the Similipal Tiger Reserve (STR).
About Melanistic Tiger
Melanistic tigers, also known as "black tigers," represent a rare variant of the Bengal tiger. These majestic creatures sport thick black stripes across their bodies, a result of pseudo-melanism—a distinct genetic mutation in Transmembrane Aminopeptidase Q (Taqpep), differing from conventional melanism.
Benefits of Melanistic Tiger Safari
- Awareness Generation: The safari aims to raise awareness about melanistic tigers, garnering international attention.
- Development of Tourism: It is expected to boost tourism revenue and foster local employment opportunities.
Impact on Local Communities and Ecosystem
- Positive Impacts: Increased revenue could enhance local infrastructure, healthcare, and education facilities. Conservation initiatives may offer income through ecotourism and sustainable practices.
- Negative Impacts: Disagreements between the government and local communities may arise regarding the utilization of traditional resources. High tourist influx might lead to the exploitation and degradation of local resources.
Similipal Tiger Reserve (STR)
Situated in Odisha's Mayurbhanj district, STR forms part of the Mayurbhanj Elephant Reserve. Established as a tiger reserve in 1956, it became part of the UNESCO World Network of Biosphere Reserves in 2009. Various indigenous tribes reside near STR, including Kolha, Santhala, Bhumija, Bhatudi, Gondas, Khadia, Mankadia, and Sahara. The reserve's dominant tree species is Sal.
Humboldt’s Enigma

Context
The phenomenon of mountains contributing disproportionately to global species diversity, termed "Humboldt’s enigma," remains poorly understood.
- Alexander von Humboldt, a renowned polymath explorer active from 1769 to 1859, extensively documented observations across various scientific fields during his explorations.
- His studies, particularly on South America's Chimborazo mountain, laid groundwork for understanding biodiversity patterns.
Humboldt's Contribution
- Humboldt's exploration of plant distribution on mountains emphasized the interplay between environmental factors such as temperature, altitude, humidity, and species occurrence patterns.
- His studies, notably on Chimborazo mountain, highlighted the rich diversity found in mountainous regions.
Humboldt's Enigma
- Contemporary biogeographers coined "Humboldt’s enigma" to challenge the prevailing belief that biodiversity peaks in tropical regions.
- Instead, it identifies mountains like the Eastern Himalaya as unexpectedly diverse areas, prompting further investigation into the factors driving this diversity.
Diversity in Indian Context
- Contrary to expectations, the Eastern Himalaya exhibits exceptional biodiversity, influenced by climate variations, geological factors, and other ecological nuances.
- This region showcases unique biodiversity patterns shaped by its distinct environmental characteristics.
Drivers of Biodiversity in Mountains
- Geological processes act as both "cradles" and "museums" for species, creating new habitats through uplifts and sustaining species over time.
- Coastal tropical sky islands, such as the Shola Sky Islands, exemplify how ancient lineages persist despite changing climates.
Role of Geology
- High geological diversity correlates with biodiversity in mountains, as different rock types influence soil composition and habitat formation.
- Geological heterogeneity fosters species diversification, contributing to overall biodiversity.
Challenges and Unknowns
- Fine-scale species occurrence data are essential for understanding biodiversity patterns, with many regions, like the Eastern Ghats in India, remaining understudied.
- Limited data availability poses challenges in explaining biodiversity variations accurately.
Ongoing Efforts
- National programs like the National Mission on Himalayan Studies aim to address research gaps, employing modern tools such as genetic analysis for comprehensive biodiversity assessments.
- Continued efforts are crucial for deeper insights into biodiversity dynamics.
Conclusion
- "Humboldt’s Enigma" represents a facet of the complex puzzle of mountain biodiversity. Strengthening research initiatives and utilizing modern tools are essential for unraveling mysteries and addressing global challenges related to climate and landscape change.
- Insights gained contribute to a holistic understanding of biodiversity dynamics across ecosystems.
Ramsar Sites in India

Context
The Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change recently declared five additional wetlands as Ramsar sites in India, increasing the total count from 75 to 80 in honor of World Wetlands Day 2024.
- Among these designations, three are situated in Karnataka: Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve, Aghanashini Estuary, and Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve, while the remaining two, Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary and Longwood Shola Reserve Forest, are located in Tamil Nadu.
- Tamil Nadu currently leads with 16 Ramsar sites, followed by Uttar Pradesh with 10.
Understanding the Ramsar Convention
The Ramsar Convention is an intergovernmental treaty established on February 2, 1971, in Ramsar, Iran, aimed at conserving wetlands of international significance. India became a party to this convention on February 1, 1982, under which wetlands meeting specific criteria are recognized as Ramsar sites.
Significance of World Wetlands Day (WWD)
- World Wetlands Day commemorates the adoption of the Ramsar Convention on February 2, 1971, emphasizing the vital role of wetlands in human wellbeing.
- The 2024 theme, "Wetlands and Human Wellbeing," underscores the importance of wetlands in flood control, water purification, biodiversity preservation, and recreational activities, all crucial for human health and prosperity.
Characteristics of Newly Designated Ramsar Sites
- Ankasamudra Bird Conservation Reserve (Karnataka): A human-made village irrigation tank spanning 244.04 acres, serving Ankasamudra village.
- Aghanashini Estuary (Karnataka): Extending over 4801 hectares, formed at the confluence of Aghanashini River and the Arabian Sea, providing diverse ecosystem services and supporting local livelihoods.
- Magadi Kere Conservation Reserve (Karnataka): A 50-hectare human-made wetland primarily constructed for rainwater storage, hosting vulnerable and near-threatened bird species and serving as a significant wintering ground for Bar-headed goose.
- Karaivetti Bird Sanctuary (Tamil Nadu): Utilized by villagers for agriculture, this sanctuary boasts 198 bird species, including notable migratory birds.
- Longwood Shola Reserve Forest (Tamil Nadu): Named after the Tamil word for tropical rainforest, this site supports globally endangered and vulnerable bird species.
Other Conservation Initiatives
At the global level, initiatives like the Montreux Record and World Wetlands Day are significant. Nationally, efforts such as the Wetlands (Conservation and Management) Rules 2017, National Plan for Conservation of Aquatic Ecosystems (NPCA), Amrit Dharohar Capacity Building Scheme, and National Wetland Conservation Programme (NWCP) launched in 1985 aim to safeguard vulnerable wetland ecosystems.
Gentoo Penguins

Over 200 Gentoo penguins were recently discovered deceased in the Falkland Islands, Antarctica, succumbing to the H5N1 Avian Influenza Virus.
Overview of Avian Influenza
- Avian influenza, commonly known as bird flu, is a highly contagious viral infection primarily affecting birds, including both wild and domestic species.
- Originating in Southern China in 1996, the highly pathogenic avian influenza H5N1 virus, scientifically labeled A/goose/Guangdong/1/1996, was first identified in domestic waterfowl.
Transmission and Symptoms in Humans
- While human transmission is rare, the mortality rate of H5N1 avian influenza is approximately 60%.
- Symptoms vary from mild flu-like manifestations to severe respiratory complications and neurological issues.
Avian Influenza in India
- India faced its initial outbreak of Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza (HPAI) H5N1 in 2006, with subsequent annual occurrences.
- H5N8 emerged in November 2016, predominantly affecting wild birds across five states, notably Kerala.
- The disease has spread to 24 states and union territories, prompting the culling of over 9 million birds.
- India's Response: India adopts a "detect and cull" strategy outlined in the National Action Plan for Prevention, Control, and Containment of Avian Influenza (revised - 2021).
- Treatment: Antiviral medications have proven efficacy in reducing severity and mortality rates of avian influenza infections in humans.
Key Facts About Gentoo Penguins
- Scientific Name: Pygoscelis papua
- Characteristics: Recognizable by a distinctive band of white feathers above each eye, a black throat, a prominent brush tail, and a predominantly deep orange or red bill.
- Habitat: Primarily found in the Southern Hemisphere, notably on the Antarctic Peninsula and various sub-Antarctic islands, including a significant presence in the Falkland Islands.
- Behavior: Typically inhabit shorelines for easy access to food and efficient nesting activities.
- Threats: Face predation from various marine and avian predators, historical human practices such as egg collection and hunting, and environmental changes impacting prey availability and habitat suitability.
National Conference on Promotion of Seaweed Cultivation

The Union Minister of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry & Dairying chaired the National Conference on Promotion of Seaweed Cultivation at Koteshwar (Kori Creek), Kutch, Gujarat.
Seaweed Cultivation in India
- A pilot project was conducted at Koteshwar (Kori Creek), Kutch, Gujarat, showcasing various seaweed cultivation methods such as Monoline, tube-net, and rafts by CMFRI, CSMCRI, and NFDB during the aforementioned conference.
About Seaweeds
- Seaweeds, a form of macroscopic algae, thrive in marine, shallow coastal waters, or brackish water habitats, and rocky shores.
- They are classified into four groups based on pigments absorbing specific light wavelengths: Chlorophyta (green algae), Phaeophyta (brown algae), Rhodophyta (red algae), and Blue algae.
- India hosts approximately 434 species of Red Algae, 194 species of Brown Algae, and 216 species of Green Algae, primarily found along the Tamil Nadu and Gujarat coasts, as well as in the Lakshadweep and Andaman & Nicobar Islands.
Application of Seaweed
- Seaweeds serve as a renewable source of food, energy, chemicals, and medicines, with diverse applications in nutrition, industry, healthcare, agriculture, and personal care.
- They are utilized in pharmaceuticals for laxatives, capsules, goitre cancer treatment, bone-replacement therapy, and cardiovascular surgeries.
- Industrially, they provide Agar, Alginates, and Carrageenan for laboratories, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, cardboard, paper, paint, and processed foods.
- Seaweeds play a crucial role in environmental benefits by absorbing carbon dioxide efficiently, akin to Eelgrass, mangroves, and salt marshes.
- The National Institute of Ocean Technology (NIOT) has developed a bioplastic film from marine seaweed and PEG-3000, potentially revolutionizing the plastic industry.
Seaweed Cultivation in India: Status, Importance, and Challenges
- In 2022, global seaweed production reached nearly 35 million tonnes, valued at approximately $16.5 billion, while India's production stood at 34,000 tonnes.
- The Indian government has allocated a Rs 640 crore package to boost seaweed cultivation up to 1.12 million tonnes by 2025.
- India possesses the capability to produce approximately 9.7 million tonnes of seaweed annually, as per the Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute.
Importance of Seaweed Cultivation
- Seaweed cultivation serves as an additional income source for coastal communities, addressing scarcity concerns and conserving natural populations while being eco-friendly.
Challenges in Cultivation
- Challenges include overexploitation of seabeds, manpower shortages during paddy harvesting seasons, technological limitations, and an information deficit regarding alternative raw material sources.
2500-year-old Solution to Fight Climate Change
Why in News?
Researchers from the Birbal Sahni Institute of Palaeosciences have recently uncovered evidence suggesting that India possesses a 2500-year-old remedy for combating climate change. Through an extensive analysis spanning millennia, they shed light on the adaptive strategies employed by ancient societies at the historic site of Vadnagar.
Key Highlights of the Report
- Climate Adaptation Over Millennia: In Gujarat's semi-arid region, Vadnagar stands as a testament to a resilient agricultural economy that endured over 2500 years despite the erratic nature of monsoon rains. This endurance is evident across historic, medieval, and post-medieval periods, reflecting the community's ability to thrive amidst climatic fluctuations.
- Resilient Crop Economy: During the post-medieval era, spanning from 1300 to 1900 CE, Vadnagar's inhabitants cultivated a robust crop economy, primarily relying on small-grained cereals such as millets, which are adept at coping with adverse conditions like weakened monsoons. This agricultural shift underscores the community's adaptive response to environmental challenges.
- Diversification of Food Crops: The diversification of food crops and socio-economic practices enabled ancient societies to navigate the challenges posed by unpredictable precipitation patterns and periods of drought, showcasing their resilience in the face of climatic adversity.
- Significance of the Study: This study underscores the importance of understanding historical climate patterns and human responses, challenging the notion that past famines and societal collapses were solely attributable to climate deterioration. Insights gleaned from the research can inform contemporary climate change adaptation strategies, emphasizing the value of historical perspectives in addressing modern challenges.
India's Climate Change Mitigation Initiatives
- National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC): Launched in 2008, NAPCC aims to foster low-carbon and climate-resilient development in India through eight national missions, each targeting specific facets of climate change mitigation and adaptation.
- Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC): India's commitments to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing resilience to climate change, including pledges to reduce emissions intensity and expand renewable energy sources by 2030.
- National Adaptation Fund on Climate Change (NAFCC): Established in 2015, NAFCC provides financial assistance to state governments for implementing adaptation projects across various sectors to bolster climate resilience.
- State Action Plan on Climate Change (SAPCC): Encourages states and union territories to develop tailored strategies for addressing climate change, aligning with the objectives of NAPCC and NDC while addressing localized climate challenges.
Snow Leopard Population Assessment in India
Why in News?
The Union Minister of Environment, Forest and Climate Change unveiled the report on the Snow Leopard Population in India during the National Board for Wildlife meeting in New Delhi.
- This report marks a significant milestone in the Snow Leopard Population Assessment in India (SPAI) Program.
About the Snow Leopard
- The snow leopard, a member of the Felidae family within the order Carnivora, inhabits the mountainous regions of Central and South Asia. Classified as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List, it plays a crucial role as a top predator and indicator of ecosystem health.
- However, threats such as poaching and habitat loss jeopardize its survival.
What is the Snow Leopard Population Assessment in India (SPAI) Program?
Led by the Wildlife Institute of India (WII) with support from snow leopard range states and conservation partners, the SPAI Program employed a comprehensive two-step methodology to assess snow leopard distribution and abundance across India's potential range.
Findings of the SPAI Program
- The SPAI Program estimates India's wild snow leopard population at 718 individuals, spread across two Union Territories and four states in the Himalayan Mountain range.
- These numbers highlight India's significant role in global snow leopard conservation efforts.
Significance of the SPAI Program
- The SPAI Program fills critical knowledge gaps regarding snow leopard populations in India, facilitating informed conservation strategies.
- Regular assessments offer insights into coexistence dynamics between local communities and snow leopards, aiding in the formulation of effective conservation measures.
|
164 videos|800 docs|1155 tests
|
FAQs on Environment and Ecology: February 2024 Current Affairs - General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce
| 1. What are some of the UN World Restoration Flagships mentioned in the article? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of the World’s First Melanistic Tiger Safari in Odisha? |  |
| 3. What is Humboldt’s Enigma mentioned in the article? |  |
| 4. How does the 2500-year-old Solution mentioned in the article help fight climate change? |  |
| 5. What is the focus of the National Conference on Promotion of Seaweed Cultivation mentioned in the article? |  |




















