UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly > The Hindu Editorial Analysis- 3rd April 2024
The Hindu Editorial Analysis- 3rd April 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC PDF Download

Poll campaigns in India must reflect climate issues
Why in News?
Recently, the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) released its report on the State of the Global Climate 2023, pointing out that the heat content of the world's oceans had hit a new high in 2023.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Record Ocean Heat Content: In 2023, the heat content of the world's oceans peaked, marking the highest level ever documented. This surge is primarily linked to human-induced climate influences like greenhouse gas emissions and alterations in land usage.
- Regional Disparities in Ocean Temperature Changes:
- Varying Trends: While a significant portion of the global oceans are witnessing a rise in temperature, certain localized areas, such as the subpolar North Atlantic Ocean, are undergoing cooling effects.
- Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC): The cooling phenomena in the subpolar North Atlantic Ocean are intricately connected to the deceleration of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC). This circulation system facilitates the movement of water within the Atlantic Ocean, transporting warm water northwards and cold water towards the south.
Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC)
- AMOC, or Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation, represents a crucial system of ocean currents within the Atlantic Ocean. It plays a significant role in redistributing heat around the Earth.
- This circulation mechanism operates by transporting warm water towards the north and cold water towards the south within the Atlantic Ocean.
Key Points:
- AMOC is a complex system of ocean currents in the Atlantic Ocean.
- It helps regulate the Earth's climate by moving warm and cold waters.
- AMOC acts like a conveyor belt, transferring warm waters from the tropics towards the North Atlantic region. This process warms up the atmosphere in Europe, making it milder than expected for its latitude.
- Conversely, the colder waters that flow southwards help maintain the equilibrium by cooling the southern regions.
Importance:
- AMOC's functioning is crucial for maintaining global climate stability by regulating the distribution of heat.
- Changes in AMOC can have far-reaching effects on weather patterns, sea levels, and marine ecosystems globally.
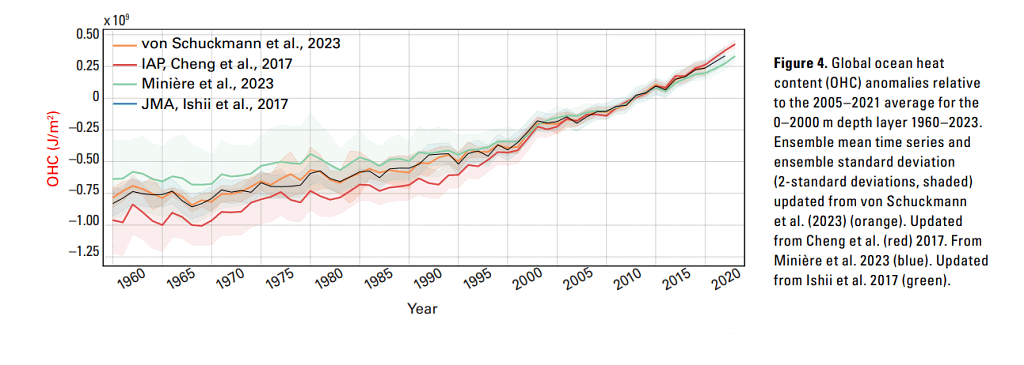 Global Climate Trends in 2023
Global Climate Trends in 2023
- Global Average Sea-Surface Temperatures: In 2023, the world witnessed record-high global average sea-surface temperatures, surpassing previous records in multiple months. Areas such as the eastern North Atlantic, the Gulf of Mexico, the Caribbean, the North Pacific, and significant parts of the Southern Ocean experienced exceptional heating.
- Marine Heatwaves and Ocean Acidification: The global ocean faced extensive Marine Heatwave occurrences, with coverage peaking at 32%, significantly exceeding the previous record of 23% in 2016. By the end of 2023, a substantial portion of the ocean between 20° S and 20° N had been under heatwave conditions since early November. The North Atlantic bore a broad band of severe and extreme marine heatwaves, with temperatures soaring 3°C above average. These events have had detrimental impacts on marine ecosystems and coral reefs. Furthermore, ocean acidification has intensified due to increased carbon dioxide absorption by the oceans.
- Global Mean Near-Surface Temperature: The global mean near-surface temperature in 2023 stood at 1.45 ± 0.12 °C above the pre-industrial average from 1850-1900, marking it as the warmest year on record. Each month from June to December set new temperature records. The continual temperature rise is attributed to heightened concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
- Glacial Retreat and Antarctic Sea Ice Loss: Glaciers globally experienced unprecedented ice loss, primarily driven by extensive melting in western North America and Europe. Antarctic sea ice reached a historic low for the satellite era, and Arctic sea ice remained well below normal levels.
- Increased Frequency and Intensity of Extreme Weather Events: Various extreme weather events like heatwaves, floods, droughts, wildfires, and tropical cyclones significantly impacted all inhabited continents. For instance, Mediterranean Cyclone Daniel caused devastating flooding in Greece, Bulgaria, Tϋrkiye, and Libya, with a notable loss of life in Libya. Tropical Cyclones Freddy and Mocha in early 2023 had severe consequences across Madagascar, Mozambique, Malawi, and the Bay of Bengal region.
- Renewable Energy Surge: The year 2023 witnessed a substantial surge in renewable energy generation, with a nearly 50% increase in renewable capacity additions compared to the previous year. This growth signifies the potential for achieving decarbonization goals and transitioning towards cleaner energy sources to combat climate change.
- Climate Financing Challenges: Despite a significant increase in global climate-related finance flows to nearly USD 1.3 trillion in 2021/2022, representing a doubling from 2019/2020 levels, these investments only account for approximately 1% of global GDP. There exists a substantial financing gap to meet climate goals. For a 1.5°C pathway, annual climate finance investments need to escalate more than sixfold to reach close to USD 9 trillion by 2030 and an additional USD 10 trillion by 2050. Adaptation finance remains inadequate, with a widening gap in global adaptation financing compared to the required amounts for developing countries until 2030.
Climate Financing Challenges
- Between 2021 and 2022, global financial flows related to climate issues nearly doubled, reaching close to USD 1.3 trillion. However, these tracked finance flows only represent around 1% of the global Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
- There exists a substantial financial disparity. In a typical scenario aimed at a 1.5°C trajectory, annual investments in climate finance must increase by over sixfold, amounting to nearly USD 9 trillion by 2030 and an additional USD 10 trillion by 2050.
- Despite reaching a record high of USD 63 billion in 2021-22, resources for adaptation remain insufficient. The global adaptation funding gap is widening, falling significantly short of the approximately USD 212 billion annually required up to 2030 in developing nations alone.
- In 2021/2022, global climate-related finance flows amounted to nearly USD 1.3 trillion, almost doubling in comparison to the levels seen in 2019/2020. Despite this increase, the total tracked climate finance flows only represent around 1% of the global GDP.
- There exists a substantial financing gap. In a typical scenario aiming for a 1.5°C pathway, the annual climate finance investments must increase by over sixfold, reaching close to USD 9 trillion by 2030 and an additional USD 10 trillion by 2050.
- Adaptation finance remains inadequate. While adaptation finance peaked at USD 63 billion in 2021-22, it falls significantly short of the estimated USD 212 billion required per year up to 2030 solely for developing countries.
Exploring the Social and Economic Consequences of Weather and Climate Hazards
- Weather and Climate Hazards Impact Agriculture and Food Security: Severe weather events like droughts and floods can devastate crops, leading to food shortages and increased prices. For instance, prolonged droughts in regions like East Africa have resulted in failed harvests, contributing to food insecurity.
- Health Risks Amplified by Extreme Weather: Extreme temperatures, storms, and changing disease patterns linked to climate change can pose significant health risks. Heatwaves, for example, can lead to heat-related illnesses and even fatalities, especially among vulnerable populations such as the elderly and children.
- Displacement and Migration Due to Climate-Induced Disasters: Catastrophic events like hurricanes, wildfires, and rising sea levels force communities to relocate, leading to displacement and migration. This can strain resources in host areas and create social tensions. For instance, Hurricane Katrina in 2005 displaced thousands of people from New Orleans, highlighting the challenges of climate-induced migration.
- Economic Losses and Infrastructure Damage: Weather and climate hazards can result in substantial economic losses due to damaged infrastructure, disrupted supply chains, and increased insurance costs. The destruction caused by events like hurricanes and typhoons requires significant investments in rebuilding and recovery efforts, impacting local economies and livelihoods.
World Meteorological Organization (WMO):
- The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is an intergovernmental body comprising 192 Member States and Territories. India stands as one of the members of WMO.
- Originating from the International Meteorological Organization (IMO), which emerged subsequent to the 1873 Vienna International Meteorological Congress, WMO was formally established through the ratification of the WMO Convention on March 23, 1950.
- With a focus on meteorology (weather and climate), operational hydrology, and related geophysical sciences, WMO serves as the specialized agency of the UN in these areas.
- The headquarters of WMO is situated in Geneva, Switzerland.
The document The Hindu Editorial Analysis- 3rd April 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly - UPSC is a part of the UPSC Course Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
38 videos|5269 docs|1114 tests
|
Related Searches















