UPSC Daily Current Affairs - 5th April 2024 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS-I
Glacial Lake Outburst Floods
Subject: Geography

Why in News?
The Uttarakhand government has set up two expert teams to assess the danger posed by five potentially hazardous glacial lakes in the area.
- These lakes are at risk of Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs), which have caused numerous disasters in the Himalayan states recently.
Background
- The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA), operating under the Union Ministry of Home Affairs, has pinpointed 188 glacial lakes in the Himalayan states that could potentially breach due to heavy rainfall, with thirteen in Uttarakhand.
About Glacial Lake Outburst Floods
- GLOFs are catastrophic events triggered by the sudden release of water from glacial lakes - large bodies of water situated in front of, on top of, or beneath a melting glacier.
- As glaciers retreat, they leave depressions that fill with meltwater, forming lakes. These lakes, dammed by unstable ice or debris, can become increasingly dangerous as the glacier recedes.
- Factors like glacial calving and events such as avalanches or landslides can destabilize the boundary around a glacial lake, leading to a GLOF event.
- GLOFs can discharge vast amounts of water, sediment, and debris downstream with significant force, causing destruction to infrastructure and posing risks to life and livelihoods.
Causes of GLOFs
- Glacial calving: Large ice chunks breaking off into the lake, displacing water suddenly.
- Avalanches or landslides: Events impacting the stability of the lake boundary, resulting in rapid water discharge.
Impact of GLOFs
- Submerging valleys, destroying infrastructure like roads and buildings, and causing significant loss of life and livelihoods.
- Rising global temperatures and rapid development in vulnerable areas have contributed to the increase in GLOF events in the Himalayan region.
Notable GLOF Events in Uttarakhand
- June 2013: Devastating event in Kedarnath valley resulting in numerous fatalities.
- February 2021: Flash floods in Chamoli district due to a glacier lake burst.
Source: Indian Express
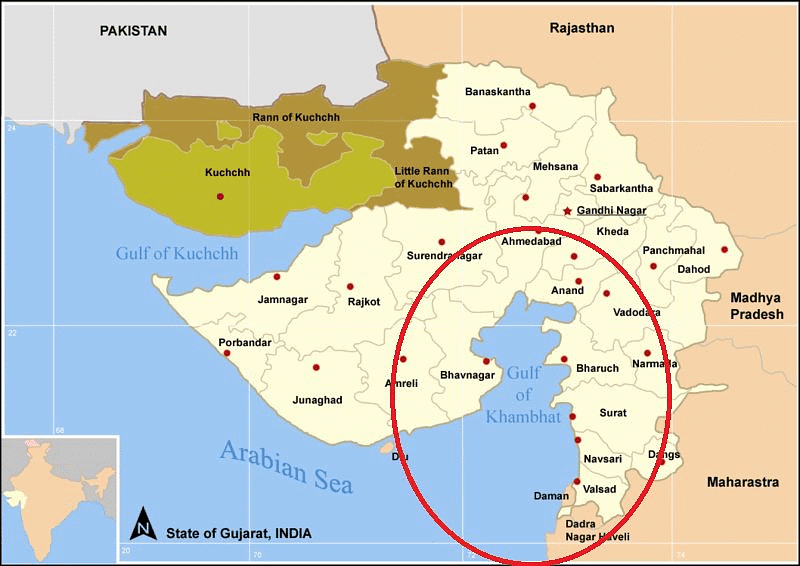
Gulf of Khambhat
Subject: Geography
Why in News?
The Indian Coast Guard (ICG) recently conducted a rescue operation to save a fisherman stranded 50 kilometers off the coast in the Gulf of Khambhat.
Description
The Gulf of Khambhat, also known as the Gulf of Cambay, is a significant inlet of the Arabian Sea situated along the western coast of India, specifically in the state of Gujarat. It serves as a natural division between the Kathiawar Peninsula and the southeastern region of Gujarat.
Geographical Features
- The periphery of the Gulf of Khambhat encompasses extensive estuarine habitats.
- It receives the drainage of several rivers including the Narmada, Tapti, Mahi, and Sabarmati, resulting in the deposition of alluvium across vast areas, linking Saurashtra with Gujarat's mainland.
- The Gulf is characterized by its shallow depth, abundant shoals, and sandbanks. Additionally, there are vast intertidal mud and sand flats located in the deltas of the Mahi and Sabarmati rivers.
- Small inlets in the western part of the Gulf harbor coral reefs.
- The Gulf's shape and orientation in relation to the southwest monsoon winds contribute to its notable tidal range of 12 meters and the swift entry of tides.
Significant Locations
- On the eastern side of the gulf, you'll find Bharuch, one of India's ancient ports, and Surat, historically linked with early European trade interactions in India.
- The town of Khambhat is situated at the head of the gulf.
Source: The Print
TORNADOS
Subject: Geography

Why in News?
Recently, a tornado struck the Mainaguri area of Jalpaiguri district in West Bengal.
Background
- The tornado caused significant destruction, leading to the loss of five lives and injuring over 300 individuals.
About Tornadoes
- A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that connects the Earth's surface to a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud.
- Tornadoes are funnel-shaped storms with low pressure at the center, being the smallest yet most violent storms.
- They typically occur in middle latitudes due to steep pressure gradients causing rapid air movement towards the center.
Types of Tornadoes
- Multiple-Vortex Tornado: Consists of several smaller whirls rotating around a common center.
- Landspout: Non-supercellular tornado developing over land.
- Waterspout: Spiral funnel-shaped wind current connecting to a large cumulus or cumulonimbus cloud, usually forming over bodies of water.
Occurrence
- Tornadoes are most common in mid-latitudes of both hemispheres during spring and summer when thunderstorms are prevalent.
- These storms convert potential and heat energy into kinetic energy, calming the agitated atmosphere down.
- In India, tornadoes and cyclones occur, with tornadoes being relatively infrequent but causing moderate damage in northwestern and northeastern regions.
Source: Down To Earth
GS-II
Green Elections
Subject: Polity and Governance

Why in News?
The Election Commission of India (ECI) expressed concerns about the environmental risks linked to the usage of non-biodegradable materials in elections.
Background
- Given the current climate crisis, the transition to sustainable practices in all human activities has become crucial and urgent.
Green Elections
- These refer to practices that aim to diminish the environmental impact of electoral processes, incorporating measures like the use of recycled materials, advocating for electronic voting, and urging candidates to embrace sustainable campaign strategies.
Objectives/Aims of Green Elections
- Candidates and parties can opt for sustainable alternatives such as recycled paper, biodegradable banners, and reusable materials.
- Choosing energy-efficient lighting, sound systems, and transportation during rallies can aid in reducing the carbon footprint.
- Utilizing digital platforms for campaigning (websites, social media, and email) diminishes paper consumption and energy use.
Need for a Shift towards Green Elections
- Conventional election procedures have notable environmental repercussions due to factors like emissions from campaign flights, leading to a substantial carbon footprint.
- Dependence on paper-based materials for ballots, campaign literature, and administrative documents results in deforestation and energy-intensive production methods.
- Large-scale election rallies with energy-intensive equipment contribute to increased energy consumption and emissions.
- The use of PVC flex banners, hoardings, and disposable items in campaigns adds to waste generation and environmental impact.
Issues/Challenges in the Adoption of Green Elections
- Ensuring equitable access to new technologies for all voters is essential, necessitating significant efforts in training election officials and educating voters about the new systems.
- Implementing eco-friendly materials and advanced technology often involves substantial initial costs, which may deter governments with limited budgets.
- Traditionally, voting has been tied to physical presence at polling booths, requiring a shift in voter behavior and cultural norms towards modernization.
- Introducing new methods like online voting or blockchain-based systems raises concerns about vote security and public trust.
Source: Hindu
National Medical Commission (NMC)
Subject: Polity and Governance
Why in News?
The Supreme Court recently instructed the National Medical Commission (NMC) to provide information on the stipend status of medical colleges in all States.
About National Medical Commission (NMC)
- The NMC was established through the National Medical Commission Act, 2019, which became effective on September 25, 2020.
- It succeeded the former Medical Council of India (MCI) and is responsible for regulating medical education and professionals in India.
- Key functions include granting recognition to medical qualifications, accrediting medical schools, providing registration to medical practitioners, monitoring medical practices, and evaluating medical infrastructure.
- Headquarters: New Delhi
Functions
- Laying down policies to uphold high quality and standards in medical education and enacting necessary regulations.
- Establishing policies for regulating medical institutions, research, and professionals, and formulating related regulations.
- Assessing healthcare needs, including human resources and infrastructure, and ensuring State Medical Councils' compliance with guidelines.
- Exercising appellate jurisdiction over decisions of the Autonomous Boards.
- Creating policies and codes to enforce professional ethics in the medical field and promote ethical conduct among practitioners.
- Developing guidelines for determining fees and charges for fifty percent of seats in private medical institutions and universities under the Act's provisions.
Composition
- The NMC comprises 33 members, including the Chairperson (exclusively medical professionals), 10 ex-officio members, and 22 part-time members.
Medical Advisory Council
- Offers a platform for States or UTs to express their perspectives and concerns to the NMC.
- Advises the NMC on measures to establish and maintain minimum standards of medical education.
Autonomous Boards
- Under-Graduate Medical Education Board
- Post-Graduate Medical Education Board
- Medical Assessment and Rating Board
- Ethics and Medical Registration Board
Source: Live Law
 |
Download the notes
UPSC Daily Current Affairs - 5th April 2024
|
Download as PDF |
GS-III
OZONE
Subject: Environment and Ecology
Why in News?
An international team of scientists, including those from India, has found compelling evidence of ozone presence on Jupiter's moon Callisto.
Background
- This discovery has illuminated the intricate chemical processes taking place on icy celestial bodies within our Solar System.
About OZONE
- Ozone, also called trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule represented by the chemical formula O₃.
- It is generated from dioxygen (O₂) due to the impact of ultraviolet (UV) light and electrical discharges in Earth's atmosphere.
- Ozone exists in minimal concentrations across Earth's atmosphere.
- The highest amounts are present in the ozone layer of the stratosphere, where it absorbs the majority of the Sun's ultraviolet (UV) radiation.
- The ozone layer is crucial for safeguarding life on Earth by preventing excessive UV radiation from reaching the surface, which could otherwise harm living organisms severely.
- Finding ozone on Jupiter's moon Callisto indicates the existence of a stable oxygen-rich atmosphere vital for the formation of complex organic molecules and potentially, life.
- The detection of ozone on Callisto carries substantial implications for the moon's potential habitability and the quest for life beyond our planet.
Source: Hindu
Derivatives
Subject: Economy
Why in News?
The RBI delays enforcement of regulations on exchange-traded currency derivatives by one month, prompting traders to close positions.
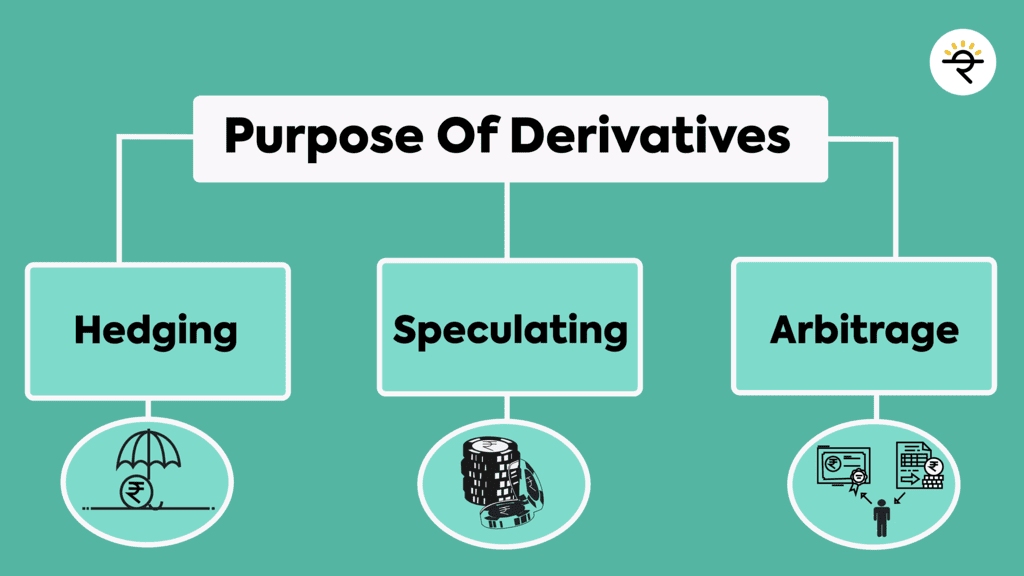
- Definition: Derivatives are financial contracts whose value is based on an underlying asset, group of assets, or benchmark. They are used for various purposes and come with their own set of risks.
- Common Types:
- Futures Contracts: Agreements to buy or sell assets at a predetermined price on a future date. For example, agreeing to buy a certain quantity of oil at a specific price in six months.
- Options Contracts: Provide the holder with the right (but not obligation) to buy or sell an asset at a specified price by a certain date. For instance, having the option to purchase a stock at a set price before a deadline.
- Swaps: Agreements to exchange cash flows based on financial variables. An example includes exchanging fixed interest rate payments for variable rate payments.
- Forwards: Customized agreements between two parties to buy or sell an asset at an agreed price on a future date. This could involve agreeing to purchase a specific quantity of wheat at an established price in three months.
- Underlying Assets: Derivatives are often based on assets like stocks, bonds, commodities, currencies, interest rates, and market indexes.
- Purposes: They are utilized for speculation, hedging against risks, and gaining exposure to different assets or markets.
- Profit Motive: The fundamental idea behind engaging in derivative contracts is to make profits by predicting the future value of the underlying asset.
- Types:
- Exchange-Traded Derivatives: Standardized contracts traded on exchanges.
- Over-the-Counter Derivatives: Customized contracts traded directly between parties without an intermediary.
Source: Times of India
RBI defers exchange traded currency derivatives norms
Subject: Economy

Why in News?
RBI has postponed the enforcement of its new regulations for the exchange traded currency derivatives (ETCD) market to May 3 from the initial date of April 5.
- Market participants expressed concerns over joining the ETCD market, leading to increased volatility in the forex market as the April 5 deadline neared.
Exchange Traded Derivatives (ETD)
- About ETDs
- ETDs are standardized financial contracts traded on stock exchanges in a regulated manner.
- These contracts derive their value from the performance of underlying assets like stocks, bonds, commodities, or currencies.
- Regulated by market regulators such as SEBI in India.
- Examples of ETDs
- Futures Contracts
- Futures contracts involve "lock in" agreements to buy or sell assets like wheat or oil at pre-set prices on specified future dates.
- For instance, a farmer might use a futures contract to fix a price for their wheat crop before harvesting.
- Options Contracts
- Options contracts offer holders the right (but not obligation) to buy or sell assets at specific prices within defined timeframes.
- For example, an investor might buy a call option on a stock, allowing them to purchase it at a set price within the next six months.
- Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs)
- ETFs are investment funds traded on stock exchanges, containing portfolios of assets like stocks, bonds, or commodities.
- ETFs qualify as exchange-traded derivatives as their value stems from underlying assets they hold.
- Futures Contracts
- Types of ETDs
- Stock ETDs
- Stock derivatives, such as stock forwards and stock options, are exclusively traded on the BSE and NSE in India.
- Index ETDs
- These derivatives operate on major stock indices, offering index forwards and options for purchase or sale.
- Index options mandate cash settlement, unlike stock options allowing cash or stock delivery.
- Currency ETDs
- These derivatives enable trading based on currency price movements on stock exchanges.
- Contrary to OTC derivatives, ETDs allow only standardized contracts for specified currency pairs.
- For example, trading in Indian Rupee vs. United States Dollar or Indian Rupee vs. Euro.
- Commodity ETDs
- These derivatives are based on price fluctuations of various commodities and are traded at exchanges like MCX in India.
- Examples of standardized contracts include gold, crude oil, silver, natural gas, copper, zinc, etc.
- Bond ETDs
- Bond ETDs involve trading bonds and are facilitated on platforms like the NSE in India.
- Stock ETDs
- Background: New norms published by RBI
- In January 2024, RBI introduced new regulations for managing foreign exchange risks, initially set to be effective on April 5, 2024.
- The new rules stipulate that only traders with genuine forex exposure can engage in currency derivatives trading.
- Traders use currency futures to hedge against potential losses from adverse exchange rate movements.
- It is essential for users to confirm the existence of valid underlying exposure that hasn't been hedged through other derivative contracts.
- The circular from Jan 5 upholds previous regulations, including the need for proof of exposure for trades exceeding $100 million.
- The recent circular mandates exchanges to ensure that clients trade only against documented exposures.
- Current scenario and concerns
- Currency traders were previously free to participate in the derivative market with or without declaring underlying exposure.
- Traders utilize currency derivatives to manage forex risks effectively.
- Challenges and Oppositions
- Anticipated Dip in ETD Volume
- Potential Impact on Market Liquidity
- Speculation and Market Regulation
Source: Times of India
|
39 videos|4566 docs|979 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs - 5th April 2024 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs) and how do they occur? |  |
| 2. How does the Gulf of Khambhat impact the surrounding region? |  |
| 3. What are the key features of TORNADOS and how do they form? |  |
| 4. How can Green Elections contribute to environmental conservation and sustainability? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the National Medical Commission (NMC) in the healthcare sector? |  |


























