Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Radiation
Radiation | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
Thermal Radiation
- Every object emits thermal radiation.
- The emission of thermal radiation increases with the temperature of the object.
- Thermal radiation corresponds to the infrared portion of the electromagnetic spectrum.
- Thermal radiation constitutes the sole means by which heat can traverse through a vacuum.
- It is the mechanism through which heat from the Sun reaches us across the vacuum of space.
- The ability of an object to emit and absorb thermal radiation is influenced by its color.
Thermal Equilibrium
- When an object absorbs thermal radiation, it experiences a rise in temperature.
- With increasing temperature, the object also emits more thermal radiation.
- A body's temperature elevates when it absorbs radiation at a faster rate than it emits radiation.
- Ultimately, the object will reach a state of equilibrium where it absorbs and emits radiation at an equal rate.
- At this juncture, the object achieves thermal equilibrium.
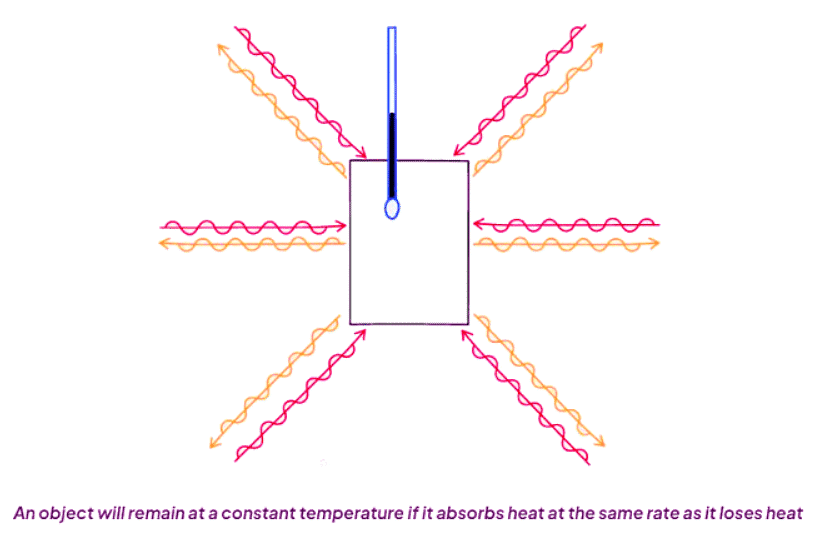
- If an object receives energy at a slower rate than it releases energy, it will lose heat and cool down.
- Conversely, if the rate of energy transfer from an object is slower than the rate at which it gains energy, the object will warm up.
- This process invariably progresses towards achieving thermal equilibrium.
Question for Radiation
Try yourself:
What is the relationship between an object's temperature and the emission of thermal radiation?View Solution
Effects of Different Surfaces
The emission of thermal radiation from an object is influenced by various factors:
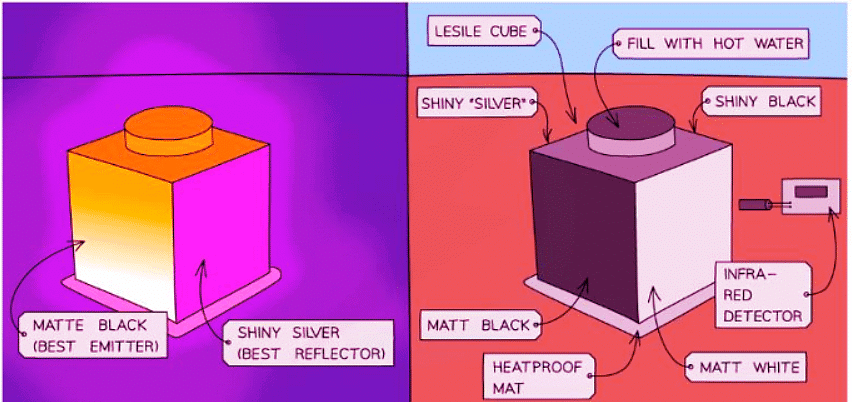
- Surface Color: Dark-colored surfaces emit more radiation.
- Texture: Shiny surfaces emit less radiation.
- Surface Area: Objects with greater surface area emit more radiation due to increased area for emission.

- Black objects excel at absorbing thermal radiation. For instance, black clothing can make you feel warmer in sunny conditions. They are also proficient at emitting thermal radiation, which explains why chargers for laptops and car radiators are often black - aiding in cooling processes.
- Shiny objects, in contrast, reflect thermal radiation, absorbing minimal heat. Although they emit low levels of radiation, they take longer to cool down compared to black objects.
 An image of a hot object taken in both Infrared and visible light. The black surface emits more thermal radiation (infrared) than the shiny surface
An image of a hot object taken in both Infrared and visible light. The black surface emits more thermal radiation (infrared) than the shiny surface
The document Radiation | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
127 videos|148 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Radiation - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. How does the surface of an object affect its thermal radiation? |  |
| 2. Can you give examples of surfaces with high emissivity values? |  |
Ans. Surfaces such as black paint, asphalt, and oxidized metals have high emissivity values, meaning they can efficiently emit and absorb thermal radiation.
| 3. How does the color of a surface affect its thermal radiation properties? |  |
Ans. The color of a surface affects its thermal radiation properties as darker colors tend to have higher emissivity values, making them better at emitting and absorbing heat compared to lighter colors.
| 4. Are there any practical applications of understanding the effects of different surfaces on thermal radiation? |  |
Ans. Yes, understanding how different surfaces interact with thermal radiation is crucial in various industries such as building construction, solar energy systems, and thermal insulation materials.
| 5. How can we measure the emissivity of a surface in order to predict its thermal radiation properties? |  |
Ans. Emissivity can be measured using a spectrometer or infrared camera to analyze the surface's ability to emit thermal radiation at different wavelengths.
Related Searches




















