Best Study Material for Year 11 Exam
Year 11 Exam > Year 11 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Reflection of Light
Reflection of Light | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 PDF Download
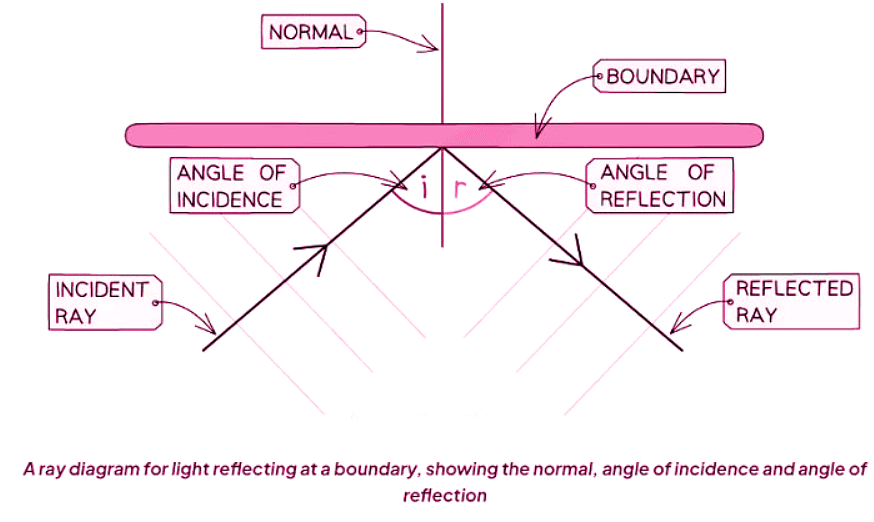
Ray Diagrams
Angles in Ray Diagrams
- Angles are measured between the direction of the wave (ray) and a line perpendicular (at 90 degrees) to the boundary.
- The angle at which the wave approaches the boundary is known as the angle of incidence (i).
- The angle at which the wave leaves the boundary is known as the angle of reflection (r).
Understanding the Normal
- The line perpendicular (at 90 degrees) to the boundary surface is referred to as the normal.
Ray Diagrams for Light Reflection
- When creating a ray diagram for light reflection, use arrows to indicate the direction of the waves.
- An incident ray is depicted with an arrow pointing towards the boundary.
- A reflected ray is illustrated with an arrow pointing away from the boundary.
Incident and Reflected Rays
- An incident ray always points towards the boundary.
- A reflected ray always points away from the boundary.
 |
Download the notes
Reflection of Light
|
Download as PDF |
Download as PDF
Angles of Incidence and Reflection
- The angles of incidence and reflection are commonly denoted as 'i' and 'r', respectively.
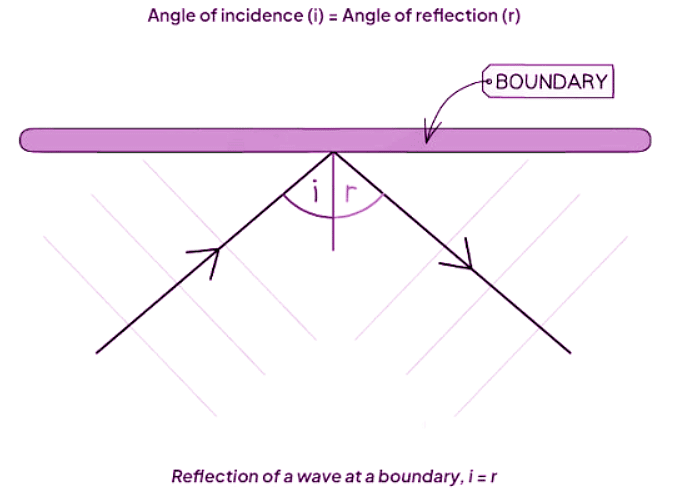
The Law of Reflection
- The law of reflection states that the angle of incidence (i) is equal to the angle of reflection (r).
Question for Reflection of Light
Try yourself:
What is the angle at which the wave leaves the boundary called?View Solution
Reflection in a Plane Mirror
- When an object is placed in front of a mirror, an image of that object is visible in the mirror.
- The image in the mirror is the same size as the object and appears at the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it. It's a virtual image.
- The process of image formation can be understood by creating a ray diagram.
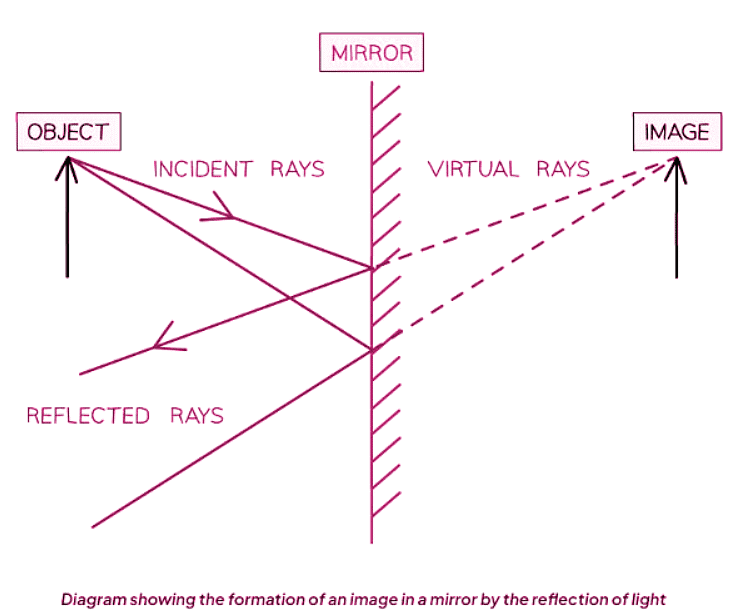
Reflection of Light by a Mirror
- When light from an object hits a mirror, it reflects from it (angle of incidence equals angle of reflection).
- To an observer, the reflected ray appears to have originated from the right-hand side of the mirror.
- The reflected ray can be traced back in this direction, forming a virtual ray.
Virtual Ray Formation
- This process can be repeated for another ray traveling in a slightly different direction.
- An image of the object will appear where these two virtual rays intersect.
- The image formed in the mirror is termed a virtual image.
- A virtual image is created by the divergence of rays from the object and cannot be projected onto a surface like paper.
The document Reflection of Light | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11 is a part of the Year 11 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Year 11 at this link: Year 11
|
127 videos|148 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Reflection of Light - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Year 11
| 1. What is the Law of Reflection? |  |
| 2. How does reflection occur in a plane mirror? |  |
Ans. Reflection in a plane mirror occurs when light rays strike the mirror surface and bounce off at the same angle they hit the mirror, forming an image that is virtual, upright, and laterally inverted.
| 3. What are Ray Diagrams used for in understanding reflection of light? |  |
Ans. Ray Diagrams are used to visually represent the path of light rays as they reflect off surfaces, helping to predict the location and characteristics of images formed by mirrors.
| 4. How does the reflection of light in a plane mirror differ from other types of reflection? |  |
Ans. Reflection in a plane mirror results in a virtual image that is laterally inverted, while reflection off curved surfaces can produce different types of images depending on the shape of the surface.
| 5. What is the significance of understanding the reflection of light in everyday life? |  |
Ans. Understanding reflection of light helps in designing optical devices like mirrors, cameras, and telescopes, and also plays a crucial role in vision and perception of objects around us.
Related Searches




















