Class 10 Exam > Class 10 Notes > Physics for GCSE/IGCSE > Circuit Diagrams & Circuit Components
Circuit Diagrams & Circuit Components | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 PDF Download
Circuit Components
Circuit symbols are vital in circuit diagrams, representing various components and their functions within a circuit.
- Each component in a circuit has a specific role and behavior that influences the flow of electricity.
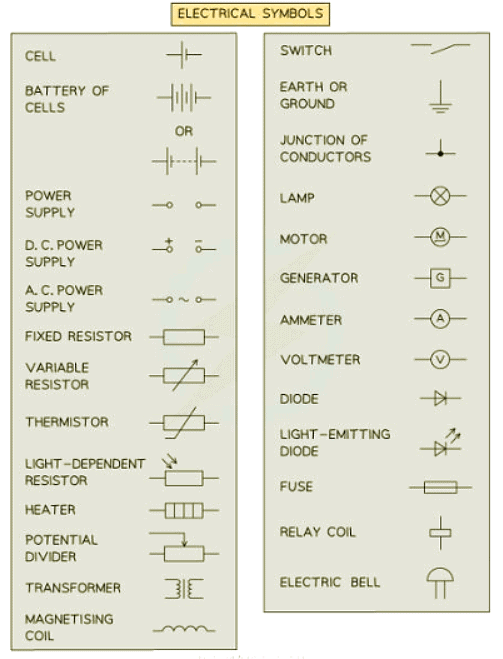
Power supplies
- Power supplies such as cells, batteries, and generators deliver electrical current to a circuit.
- These sources of power are essential for the operation of electronic devices and systems.
Resistors
- Resistors like potential dividers, fixed resistors, and thermistors regulate the flow of current within a circuit.
- They control the amount of current passing through a circuit, affecting the overall performance.
Meters
- Ammeters and voltmeters are instruments used to measure current and voltage in a circuit.
- Ammeters are connected in series to measure current, while voltmeters are connected in parallel to measure voltage.
- Ammeters are connected in series, while voltmeters are connected in parallel.
Electromagnetic Components
- Magnetising coils, relays, and transformers utilize electromagnetic effects.
- Relays use a small current in one circuit to control a larger current in another.
- Transformers can 'step up' or 'step down' current and potential difference.
Fuses
- Fuses safeguard costly components from current surges and serve as a safety precaution against fires.
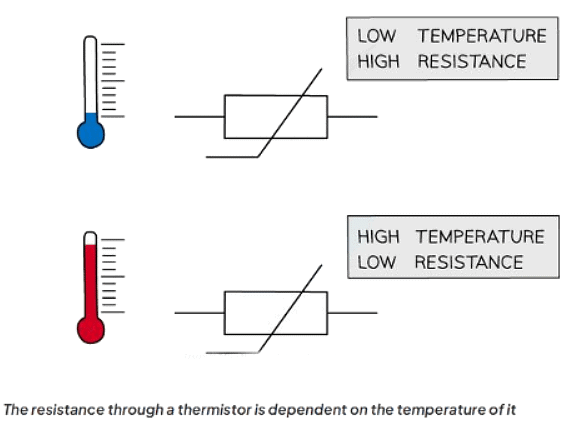
Thermistors
- A thermistor is a type of resistor that is non-ohmic and its resistance varies based on temperature.
- Its resistance decreases as the temperature increases, and vice versa.
- For instance, when the temperature rises, the resistance decreases, and conversely, when the temperature drops, the resistance increases.
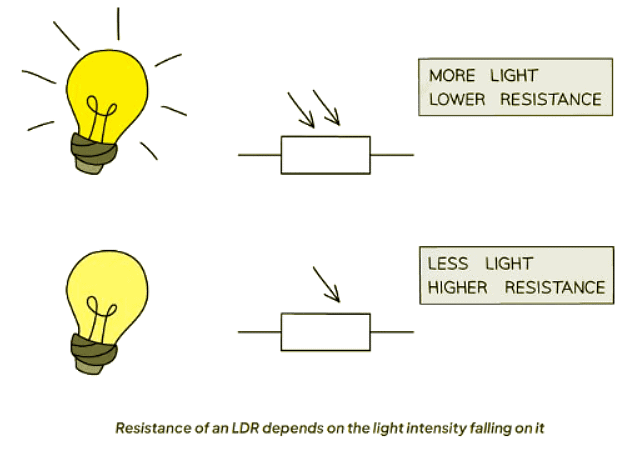
Light-dependent Resistors
- A Light-dependent Resistor (LDR) is a type of resistor whose resistance alters based on the intensity of light it receives.
- As the illumination increases, the resistance of an LDR decreases.
- When exposed to higher light intensities, the resistance of the LDR diminishes correspondingly.
Question for Circuit Diagrams & Circuit ComponentsTry yourself: What is the role of resistors in a circuit?View Solution
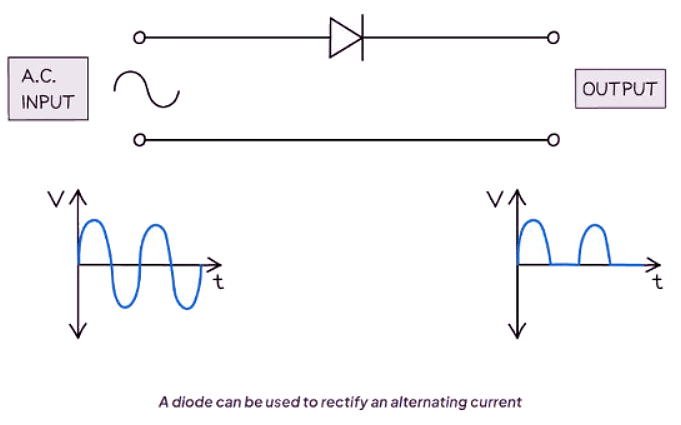
Diodes
- The circuit symbol for a diode can be recognized and drawn in addition to the previously mentioned information.

- Diodes may sometimes be depicted with a horizontal line across their center.
- When connected to an alternating current (a.c.) power supply, a diode allows current flow for half of the time, a process known as rectification.
The document Circuit Diagrams & Circuit Components | Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10 is a part of the Class 10 Course Physics for GCSE/IGCSE.
All you need of Class 10 at this link: Class 10
|
129 videos|188 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Circuit Diagrams & Circuit Components - Physics for GCSE/IGCSE - Class 10
| 1. What is the function of a diode in a circuit? |  |
Ans. A diode is a semiconductor device that allows current to flow in one direction only, effectively acting as a one-way valve for electrical current in a circuit.
| 2. How does a diode protect circuits from damage? |  |
Ans. Diodes protect circuits from damage by preventing the flow of reverse current, which can cause overheating and damage to sensitive components.
| 3. Can diodes be used to convert AC to DC in a circuit? |  |
Ans. Yes, diodes can be used to convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) by allowing only the positive half of the AC waveform to pass through.
| 4. What are the different types of diodes commonly used in circuits? |  |
Ans. Some common types of diodes used in circuits include light-emitting diodes (LEDs), Zener diodes, Schottky diodes, and rectifier diodes.
| 5. How can diodes be tested to ensure they are functioning properly in a circuit? |  |
Ans. Diodes can be tested using a multimeter in diode test mode to check for forward and reverse bias voltage drop, which can indicate whether the diode is functioning correctly.
Related Searches
















